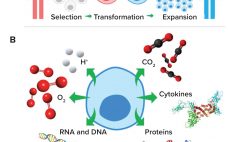
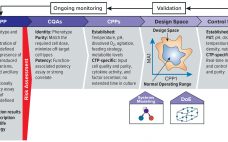
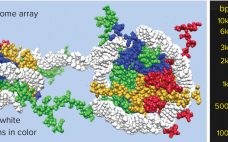
Regenxbio says increasing competition for capacity in the CMO space prompted the adoption of a hybrid gene therapy manufacturing strategy. Industry demand for contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) with the technical skills required to manufacture gene therapies has increased in recent years. According to the Alliance for Regenerative Medicine, as of Q3 last year, 370 trials involving gene therapies were ongoing, which is an increase on the 351 underway in the equivalent period in 2018. Katie Masterson, director of manufacturing operations…
Search Results for: regenerative medicine
Orgenesis acquires cell therapy specialist Koligo for $15m
Orgenesis agrees merger with regenerative medicine company, gaining access to a commercial cell therapy, a COVID-19 candidate, and bioprinting technology. The two companies have entered into a definitive merger agreement, which is expected to close by the year’s end. Orgenesis will pay $15 million (€12.7 million) in shares of its common stock to Koligo Therapeutic’s investors to secure the deal. Koligo possesses one commercially-available treatment, in the form of Kyslecel, which is an autologous pancreatic islet cell therapy used to…
Meeting Regulatory Requirements for Cell and Gene Therapy Manufacturing
Karen Magers, head of regulatory affairs, cell and gene technologies; and Rajesh Thangapazham, head of regulatory strategy, cell and gene technologies, Lonza Pharma and Biotech Magers began with an overview of the complex regulations and guidance applicable to makers of cell and gene therapies. A slide illustrated the development timeline of such therapies and their associated regulations and guidance documents. That framework continues to evolve through revision of documents and guidelines as more information is gained about the technologies and…
Fluorescent Nanosensors: Real-Time Biochemical Measurement for Cell and Gene Therapies
Cell and gene therapies are destined to transform the methods by which global healthcare challenges are approached and overcome (1). The US Food and Drug Administration is reviewing and approving an increasing number of cell and gene therapy products (2), and biopharmaceutical developers are dedicating immense resources to realizing the enormous potential of these therapeutics. Therefore, technologies that facilitate their effective and efficient manufacture will accelerate cell and gene therapies’ transition from medicines of the future to medicines of the…
Gene Therapy Trends and Future Prospects
Gene therapy is defined as the transfer of genetic information to a patient for treatment of a disease. Clinical investigation of such therapies began in 1990 with a treatment for a rare immunodeficiency disorder and since has expanded to almost 1,000 clinical studies in 2019 (1, 2). In its most straightforward incarnation, the goal of gene therapy for genetic diseases is long-term expression of a transferred gene at levels that are high enough to be therapeutic, an approach sometimes called…
Quality By Design for Advanced Therapies: An Informed Route to Enhanced Late-Stage Clinical Success and Empowered Process Flexibility
As advanced therapies, including regenerative medicines, progress toward commercialization and market approval, early warnings from key opinion leaders (1, 2) regarding the importance of better understanding quality target product profiles (QTPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs) of such products have resounded ever louder (see the “Terminology” box for definitions). Costly late-stage delays, redirections, and even abandonment of clinical programs can be linked to quality issues associated with inadequate understanding of process and product. Therefore, a review of the benefits of…
Patient Access Tops the List of Advanced Therapy Milestones at Phacilitate 2020
In a highly anticipated presentation at the 2020 Phacilitate Leaders World event — part of Advanced Therapies Week, along with the World Stem Cell Summit in Miami, FL — Susan Nichols (chief executive officer for Falcon Therapeutics), highlighted 10 events from 2019 that drove conversation, investment, and innovation in regenerative medicine. Although clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR), business consolidations, and production capacity powered the cell and gene therapy (CGT) space in 2019, a new proactive focus on patient…
Discussions at Phacilitate 2020 on Business, Manufacturing, and Future Trends
Presenters in the three main program tracks at the Phacilitate Leaders World conference in Miami, FL, this past January represented sponsor-developers of cell/gene-therapy (CGT) products, contract service providers, and technology suppliers to the industry. Topics include process and product development strategies for advanced therapies, regulatory and inspector expectations, automation and closed-system processing, the choice between in-house and outsourced manufacturing, quality assurance and control, analytical methods, viral vectors, and artificial intelligence and Industry 4.0. At the end of each session, presenters…
The Technology of Tomorrow — Today
Sponsored by BioProcess International and its sister publication BioProcess Insider, the “Tech of Tomorrow Zone” at Phacilitate 2020 played host to a number of companies showcasing platforms and ideas that they believe can revolutionize cell and gene therapy (CGT) manufacturing. Some common themes arose in this diverse zone, highlighting technologies from stem-cell supply solutions to viral-vector filling. Participating companies are aware of the complexities involved in producing regenerative medicines, and each proposed solution was intended to reduce the burden on…
Setting a Cornerstone for Platform Purification of Exosomes
Exosomes are a subject of rapidly growing therapeutic interest in the biopharmaceutical industry for two principal reasons. The first reason is that they are the primary communicators of instructions from source cells to target cells. Exosome surface features define their destination. They recognize complementary features on target cells, dock with them, and deliver their programmed instructions in the form of microRNA. The second reason is that exosomes are immunologically silent. As normal human cell products, and by contrast with gene…