Many physical and chemical factors can affect the quality, safety, and efficacy of biopharmaceutical products, particularly after long-term storage in a container–closure system that can be subject to variations in temperature and light, as well as agitation with shipping and handling. Proteins are inherently complex physiochemically, from their primary amino acid sequences to their higher-order structures, and they require specific conditions to maintain their integrity and functionality. Advanced biological therapies can be even more complicated and particular about their environments.…
Pre-Formulation
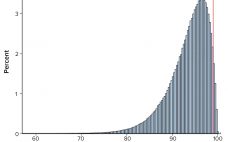
Biopharmaceutical Product Specification Limits and Autocorrelated Data
Calculations, including statistical tolerance intervals, can assist in the development and revision of specification acceptance criteria. Manufacturing results for attributes of a biopharmaceutical product can be positively autocorrelated. The sample standard deviation — calculated from limited, positively autocorrelated data — tends to underestimate the long-term process standard deviation (1). In this article, simulated data are used to assess the relative performance of statistical tolerance intervals, intervals calculated using the minimum process performance index Ppk approach, and the sample range. Prevalence…
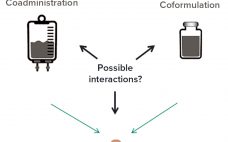
Analytical Strategies for Fixed-Dose Coformulated Protein Therapeutics
Coformulation of two or more proteins in a single formulation is an emerging approach to delivering multiple biotherapeutics that previously have been administered in sequence. This approach brings multiple benefits to all stakeholders. Foremost for patients, the primary benefits are combined therapeutic effects and improved convenience (e.g., fewer administration events). Healthcare providers see logistical benefits and decreased risk of medical errors. Additionally, coformulations also simplify manufacturing logistics, reduce costs of packaging and distribution, and provide new opportunities for product portfolio…
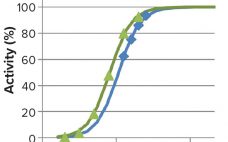
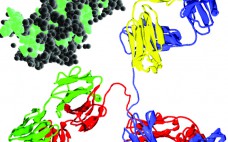
Apparent Matrix Effects in an Iduronate 2-Sulfatase Specific Activity Assay
The recombinant fusion protein SHP631 consists of a chimeric monoclonal antibody binding to human insulin receptor and iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S). This product is being developed as an enzyme replacement therapy to treat cognitive symptoms of Hunter’s syndrome. Because the current therapy (idursulfase, brand name Elaprase from Shire) cannot cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), SHP631 is being developed to do so, enabling the presence of I2S in the brain. The enzymatic activity of this molecule is measured using the substrate 4-methyl umbelliferyl-α-L-idopyranosiduronic…
Development of a Freeze-Dried Ebola-Expressing Adenoviral Vector: Unexpected Findings and Problems Solved
In December 2013, a two-year-old child in Guinea became the first person to be killed by Ebola in the most recent outbreak. In March of the following year, that outbreak was declared in West Africa. By mid-2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) had declared it to be a public health emergency of international concern and urged pharmaceutical companies to accelerate their development of candidate vaccines. At the peak of the outbreak in 2014, more than 1,200 new cases of Ebola…
Aggregation from Shear Stress and Surface Interaction: Molecule-Specific or Universal Phenomenon?
Exposure to solid–liquid and air–water interfaces during production, freezing and thawing, shipment and storage of protein therapeutics may be a contributing factor in their degradation (e.g., aggregation, fragmentation) (1, 2). Surface exposure, particularly during manufacturing processes, often is accompanied by various degrees and durations of shear stresses originating from fluid flow and acting on proteins at interfaces. The magnitude and duration of shear rates depends on velocity gradients within each solution and varies significantly among manufacturing steps. On the low…
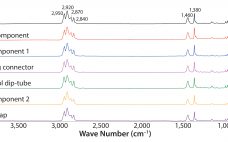
Investigation of Foreign-Particle Contamination: Practical Application of FT-IR, Raman, and SEM-EDS Technologies
The presence of visible foreign particulate matter is considered a critical defect in parenteral products and one of the main reasons they can be recalled (1). Foreign particles present during any stage of manufacturing are considered to be contaminants and can impose a risk to the control of the manufacturing processes (2). For those reasons, particle contamination arising in any manufacturing step initiates a nonconformance or out-of-specification observation. That requires an investigation to identify root cause so as to mitigate…
Osmolality Measurements for High-Concentration Protein–Polymer Solutions: Variation Based on Working Principles of Osmometers
Osmolality is a critical attribute for injectable formulations. It is desirable to have products match physiological osmotic conditions. Furthermore, osmolality provides confirmation of soluble content in solution. Preventing injection of hypo- or hyperosmotic solutions is a key element of parenteral formulation development. Additionally, some investigators have explored correlations between injection pain and formulation osmolality, although no significant correlation has yet been observed (1–4). Osmolality is a valuable in-process test also because it provides a reliable and repeatable value that reflects…
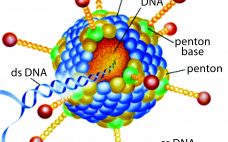
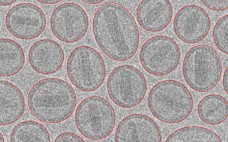
Ask the Expert Liposome and Viral Vector Characterization: Use of Electron Microscopy and Image Analysis
with Dr. Josefina Nilsson For this webcast, Josefina Nilsson (EM Services business unit head) discussed Vironova’s work, including case studies. She focused on characterization of drug and gene delivery platforms with electron microscopy and image analysis, specifically for systems that use viral vectors or liposomes. Along with two colleagues — Gustaf Kylberg (image analysis expert) and Mathieu Colomb-Delsuc (electron microscopist) — she then answered questions from the audience. Nilsson’s Presentation Structural characterization provides important insights into the quality of development and…
Critical Factors for Fill–Finish Manufacturing of Biologics
Over recent decades, protein-based therapeutics have emerged as key drivers of growth in the pharmaceutical industry. Drug development pipelines have filled with biologics, and a handful of monoclonal antibody (MAb) products have become some of the best-selling drugs around the world. Production of biotherapeutics is often challenging because of the inherent instability of these large, complex molecules. Their fragile nature has forced manufacturers to change how bulk drug substances (BDSs) are handled and final drug product is formulated, sterile filtered,…