Significant growth of the cell and gene therapy (CGT) pipeline in recent years demonstrates the enormous potential of these modalities to treat or even cure otherwise intractable diseases. Several CGT products have been approved for clinical use over the past five years. More than 75 such products have come to the market around the world so far. They include chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies that involve genetic engineering of patient cells ex vivo as well as in vivo gene therapies…
Cell/Gene Therapies
Scalability in Cell and Gene Therapy Facilities: How Today’s Developers Are Preparing for Tomorrow’s Commercial Success
Propelled by year after year of record-setting investments and regulatory approvals, cell and gene therapy (CGT) innovators are on track to revolutionize medicine by providing potential cures for many conditions. Now, CGT manufacturers must plan for a future beyond the production constraints of laboratories. What needs to happen now to prepare for a sustainable, commercially viable scale-up process in years to come? To answer that and other important questions about CGT production, my company, the CRB Group, surveyed more than…
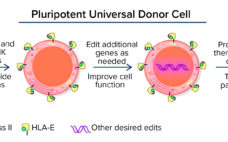
Novel Technologies for Advancing Allogeneic Cell Therapies
In many ways, cells are the ultimate therapeutic product. They can integrate and participate in different biologic processes and replace missing biological functions. Cell therapies are dynamic, versatile, and with the appropriate engineering, capable of influencing and correcting disease processes robustly. Cell therapies essentially are living medicines, and their adaptability contrasts with conventional drug modalities that generally have only a single specific target or effect. Because cell therapies are highly complex modalities, their scientific and R&D challenges are different from…
Process Intelligence: Gene Therapy Case Study Shows That the Journey to Improved Capabilities Starts with One Step
The product development team at a gene therapy contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) was working on a high-priority drug-substance project for a key client. The material was crucial to that client’s early stage clinical trial, with an immediate value over US$500,000 to both the client and the CDMO. Unfortunately, the bioreactor used in the upstream process — a transfection unit operation for an adenoassociated virus (AAV) vector — had developed an intermittent problem that could force it to shut…
Partnerships Are Crucial to Getting Advanced Treatments to Market
New treatments and approaches for tackling serious diseases are being developed using cell and gene therapy (CGT). CGTs are adding a new dimension to the way patients with such conditions can be treated in modern healthcare. But these advanced treatments require complex research, development, and manufacturing processes. CGTs are related and to a degree interchangeable. However, gene therapies typically use some kind of genetic delivery system, (e.g., virus-based vectors) to treat a disease by replacing a malfunctioning gene or introducing…
Advancing Logistics for ATMP Manufacturing
Advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) hold much potential for improving healthcare. They offer hope for treating or even curing patients. The biopharmaceutical industry has recognized the importance of making such therapies accessible to as many people as possible. To provide personalized ATMPs, biomanufacturers are shifting toward flexible, patient-centered production processes. A Paradigm Shift in ATMP Manufacturing Ex vivo cell and gene therapies are particularly promising approaches to personalized regenerative medicine. Thus, it is no surprise that the numbers of US…
Advanced-Therapy Automation Capabilities Can Increase Efficiencies and Reduce Costs
The cell and gene therapy (CGT) industry has grown out of disparate groups of developers, suppliers, and service providers. Players in the sector must collaborate if we expect to commercialize new therapies at scale. Despite concerted efforts in the field, however, the critical question of how to automate CGT production has yet to be answered. Without automated processes in place, the sector risks spiraling costs and operational inefficiencies that could inhibit patient access to much-needed therapies. Understanding such concerns, several…
Navigating New Options for Commercial-Scale Biopharmaceutical Production
Scalability remains a critically important topic for biopharmaceutical companies. For conventional protein products, the strategy once was straightforward: Drug makers would scale up, beginning with cultures in flasks and roller bottles to grow enough cells to inoculate laboratory-scale (often glass) bioreactors, then again to pilot- and commercial-scale, stainless-steel, stirred-tank bioreactors. At their highest volumes, such reactors can handle tens of thousands of liters of cells and growth media. If a drug developer did not have the requisite equipment to scale…
Boosting Yield and Preserving Quality: Increasing Production of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine Applications
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are promising starting materials for several clinical and industrial applications in cell therapy production, drug discovery, and in vitro screening. But as I learned from Maxime Feyeux (cofounder and chief science officer of TreeFrog Therapeutics in Bordeaux, France), such cells are a relatively new option in the toolbox of cell therapy developers. Advanced-therapy products can require controlled proliferation and differentiation of millions or even billions of iPSCs depending on the clinical indication, he pointed out,…
Scaling AAV Production: Easing the Transition from Laboratory Scales to Commercial Manufacturing
Adenoassociated virus (AAV) has emerged as the leading vector for gene therapy delivery. Compared with options such as lentivirus and adenovirus, AAV exhibits a strong safety profile because it has low pathogenicity and requires a helper virus to replicate. AAV is also capable of long-term gene expression, and it can infect both dividing and nondividing cells (1–5). Developers of advanced therapies have found such advantages to be quite attractive. As of January 2021, two gene therapy products have gained US…