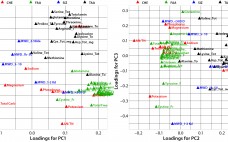
Biological additives such as yeast extracts and peptones are commonly used in growth-media formulations for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. In spite of drivers encouraging companies to reduce variability in mammalian cell culture processes by using chemically defined media, many microbial and mammalian processes continue to use biological additives in their growth-medium formulations and/or feeds. According to Sheffield Bioscience (Kerry, Inc.), at least six of the top 10 licensed mammalian-cell– derived biotherapeutic products are manufactured using biological additives (1). During process development, it…
Upstream Development
Process- and Product-Relate Impurities: Part 1 – Process-Related Impurities An Overview
Introduction by Cheryl Scott The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website (www.casss.org). This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated…
The Case for a Standardized Assay to Test Suitability of Single-Use Systems in Cell Culture Applications
Increased commercial use of single-use systems (SUS) for large-scale biopharmaceutical production creates the need for consensus on industry best practices and standards for materials in SUS components. End users and suppliers are beginning to develop a shared vision of industry needs in such areas (1, 2). For example, highly visible efforts to harmonize extractables testing include contributions from groups such as the BioPhorum Operations Group (BPOG), Bio-Process Systems Alliance (BPSA), Parenteral Drug Association (PDA), ASTM, and ISPE. In addition to…
Development, Qualification, and Application of a Bioreactor Scale-Down Process: Modeling Large-Scale Microcarrier Perfusion Cell Culture
Qualified scale-down models of large-scale cell culture processes are essential to conducting studies for applications such as investigating manufacturing deviations, enhancing process understanding, and improving process robustness. For example, scale-down models can be used for raw material investigations as well as evaluation and qualification of new good manufacturing practice (GMP) cell banks for manufacturing implementation. Process characterization studies are performed also with qualified scale-down models to improve process consistency (1, 2). Often it is impractical to conduct investigational studies at…
Experiences with a Benchtop-Scale Glass Bioreactor: Engineering Data and Cultivation Results
Animal cell lines (the dominant expression systems in biopharmaceutical production processes) are mostly cultivated in stirred bioreactors (1). Although such bioreactors are widely accepted and applicable over a wide range of scales, engineering data for these systems are still lacking. Nevertheless, studies have shown that the correct choice of key parameters (e.g., power input, tip speed, mixing time, and oxygen mass transfer) can influence the growth of animal cell cultures (2). Therefore, detailed characterization is essential. It enables reliable scaling…
Special Report: Turning Discoveries into Products — Developability Assessments and Highly Efficient Process Design
High costs and long timelines for biopharmaceutical development are cause for reflecting on how best to allocate resources from the earliest discovery stage through critical go–no-go junctures. With inputs ranging from science, engineering, and economics, the coined term developability becomes the synthesis of answers to such questions as How well does the target represent a disease state? Does manipulating that state bring about improvement? Does the molecule behave as expected in living systems? What can be done about the emergence of independent safety, toxicology, and/or immunogenicity warning signs? Can the molecule…
Cost-Effective Process Development for Plasmid DNA Manufacture: Evaluation of Single-Use Technologies to Support Escherichia coli Culture
DNA-based gene therapy products have been in clinical development since the 1990s. But over the past 24 months, the overall demand and therapeutic applications for plasmid DNA (pDNA) have rapidly grown and expanded. Currently, pDNA can be used directly as a therapeutic agent (e.g., in gene therapy or generation of vaccine antigens) and indirectly for a range of applications. Those include its use as a critical starting material for transient transfection to produce both viral-vector constructs (e.g., lentivirus or adenoassociated…
Fluid Dynamics of a Single-Use, Stirred-Tank Bioreactor for Mammalian Cell Culture
The benefits of single-use technologies in both upstream and downstream operations are now widely acknowledged by the biopharmaceutical industry, and have led to radical changes in the design and operation of many bioprocesses. Those changes typically provide more robust processes and increased production flexibility. For mammalian cell culture, cleanable multiuse glass or stainless steel stirred-tank reactors (STRs) have been used successfully for growth of suspension-adapted cell lines in both small- and large-scale systems. However, achieving the same or better performance…
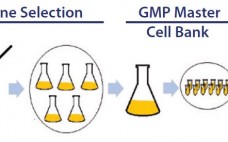
Meeting Lot-Size Challenges of Manufacturing Adherent Cells for Therapy
Adherent cells such as adult primary cell lines and human multipotent (MSCs) and pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) present a manufacturing challenge as lot sizes increase from 109 (billions) to 1012 (trillions) cells (1). Typically, manufacturing platforms are good for one log of expansion. So new methods will be required to achieve commercially relevant lot sizes. Traditional two-dimensional culture methods have been used to grow anchorage-dependent cell types. Although such methods are reliable and well defined, they are very labor intensive…
T-Cell Suspension Culture in a 24-Well Microbioreactor: High-Throughput Screening of Operating Conditions
Cell therapy promises revolutionary new therapeutic treatments for cancer and other serious diseases and injuries. For example, T-cell therapy response rates of >50% and durable complete response rates of 20% have been reported in patients with metastatic melanoma who had failed other therapies (1). In another example, sustained remissions of up to a year were achieved among a small group of advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients upon treatment with autologous T-cells expressing an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (2). Numerous other…