Even with increased understanding of host cell proteins (HCPs) and their potential risks, no practical approach has been made available for HCP risk management during bioprocess development. A BioPhorum Development Group (BPDG) team has identified common HCP-related risk factors and built a template for semiquantitative risk assessment during process development based on publicly available information. To this end, the BPDG HCP working team’s assay and knowledge-sharing experts have established a common HCP risk assessment tool and mitigation strategy to guide…
Upstream Development
Host-Cell Protein Risk Management and Control During Bioprocess Development: A Consolidated Biotech Industry Review, Part 1
Host-cell proteins (HCPs) constitute a significant class of process-related impurities during biologics manufacturing. Due to their potential impact on product quality and efficacy as well as patient safety, the total amount of residual HCP in a biological drug substance generally is considered a critical quality attribute (CQA) that usually needs to be tested for during batch release (1, 2). It is both an “industrywide” common understanding and a regulatory requirement to remove HCPs from biologics to acceptably low levels that…
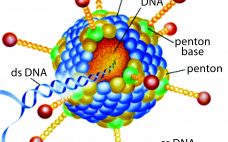
Development of a Freeze-Dried Ebola-Expressing Adenoviral Vector: Unexpected Findings and Problems Solved
In December 2013, a two-year-old child in Guinea became the first person to be killed by Ebola in the most recent outbreak. In March of the following year, that outbreak was declared in West Africa. By mid-2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) had declared it to be a public health emergency of international concern and urged pharmaceutical companies to accelerate their development of candidate vaccines. At the peak of the outbreak in 2014, more than 1,200 new cases of Ebola…
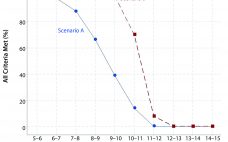
Statistical Assessments of Bioassay Validation Acceptance Criteria
Analytical linearity as well as assessments of precision and accuracy determine the range for a bioassay (1). USP <1033> recommends comparing confidence intervals (CIs) against target validation acceptance criteria in a bioassay validation exercise, but there are no clear guidelines for determining the criteria (2). Here I address several aspects of a bioassay validation, namely • Linearity (coefficient of determination (R2), slope, and intercept parameters) • Accuracy (%relative bias, %RB) • Precision (percent coefficient of variation, %CV) CIs for the…
eBook: Bioprocess and Analytical Laboratories — Proving the Power of Data in Drug Development
Analytics pervade the entire biopharmaceutical development process — from protein characterization through biomanufacturing process optimization to final-product formulation and clinical testing. Every technical article in BPI requires data to back up the statements made, whether the topic is upstream/production, downstream processing, product development, or otherwise focused. And never mind publishing: Even more detailed documentation is required for regulatory submissions. If a company can’t back up the choices made and results obtained in development, manufacturing, and testing of its biopharmaceutical product,…
eBook: Production Cell-Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cultivation — Myths, Risks, and Best Practices
Health authorities are requesting substantial details from sponsors regarding practices used to generate production cell lines for recombinant DNA–(rDNA) derived biopharmaceuticals. Authorities also are asking for information about the clonality of master cell banks (MCBs) and control strategies to minimize genetic heterogeneity. Such requests are prompted by recent reports indicating “nonclonality” for certain production cell lines. To address these and related issues, the CASSS CMC Strategy Forum on “Production Cell Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cell Cultivation:…
Cell Expansion with Dissolvable Microcarriers
In recent years we have seen an exponential increase in the number of companies testing and validating new regenerative medicine products. Many of these products are reaching late-phase trials with the potential to receive final approval and marketing authorization from regulatory agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). In the past several years, we have seen successful launches of regenerative medicine products, including Holoclar (Holostem Advanced Therapies), Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel, Novartis), Yescarta…
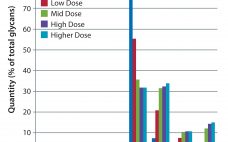
Enhanced Galactosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies: Using Medium Supplements and Precursors of UDP-Galactose, Part 2
In Part 1 of this report, we described our development of a high-throughput assay for analyzing monoclonal antibody (MAb) glycans and how we used it to evaluate the effects of medium supplements on galactosylation of MAbs produced by two different cell lines (1). This month, we examine galactosylation of a MAb produced by a third cell line. A discussion follows on the benefits of this high-throughput assay before we highlight the similarities and differences in galactosylation among the three MAbs…
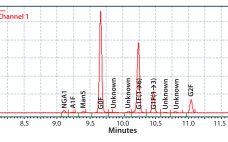
Enhanced Galactosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies: Using Medium Supplements and Precursors of UDP-Galactose, Part 1
The biopharmaceutical industry needs better understanding of how monoclonal antibody (MAb) glycosylation is influenced by components in cultivation media — and it needs methods to exert some control over the structure of MAb glycans. That structure can affect MAb function. Thus, a high-throughput (HTP) assay is needed for characterizing MAb glycosylation so that developers can observe the effects of cultivation conditions on MAb glycosylation rapidly, with a goal of producing MAbs that have a desired glycan structure. The method also…
Therapeutic IgG-Like Bispecific Antibodies: Modular Versatility and Manufacturing Challenges, Part 2
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are bivalent and monospecific, with two antigen-binding arms that both recognize the same epitope. Bispecific and multispecific antibodies, collectively referred to herein as bispecific antibodies (bsAbs), can have two or more antigen-binding sites, which are capable of recognizing and binding two or more unique epitopes. Based on their structure, bsAbs can be divided into two broad subgroups: IgG-like bsAbs and non–IgG-like bsAbs. We have chosen to focus on the former in this review. Part one provides a…