In the past decade, single-use bioreactors have gained wide acceptance for biomanufacturing. The biopharmaceutical industry is increasingly interested in performing modern production processes in single-use facilities. That trend is driven by the time and cost benefits of single-use technologies, as well as the enhanced manufacturing flexibility they offer (1). With single-use bioreactors increasingly used in late-phase clinical trials and commercial production, their quality, reliability, and assurance of supply becomes more critical. Many industry experts consider process control of film and…
Upstream Development
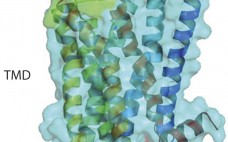
Targeting G Protein–Coupled Receptors with Biologics for Therapeutic Use, Part 2
In part 1, we summarized the advances made in new approaches developed to address the challenges of antigen generation for targeting G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs). We reviewed the antibody and biologics pipeline with progress highlighted by some interesting case studies on new targets (1). Here, we conclude by reviewing progress attained with other biologics. Peptides Targeting G Protein–Coupled Receptors More than 50 peptide-based therapeutic products are commercially available, but very few of them have been derived from recombinant display technology.…
Expansion of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Using Microcarriers and Human Platelet Lysate
Cell therapy holds the promise of delivering the next generation of future medical breakthroughs. In this respect, multipotent progenitor cells such as human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) have attracted high clinical interest because of their ability to differentiate into various cell types and their immunoregulatory properties. Furthermore, hMSCs express only low levels of class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC I) molecules on their surfaces and are therefore invisible to a host’s immune system. Finally, hMSCs can actively suppress the innate…
A Novel Solid-Media E. coli Platform: Comparison with Standard Fermentation Processes
MicroProtein Technologies Inc. has developed the MPTxpress high-yield, low‑cost, recombinant Escherichia coli manufacturing platform. Rather than using liquid culture media within stirred bioreactors, the system uses trays filled with semisolid (gelled) culture media overlaid with or without a permeable membrane on which the E. coli is cultured. Compared with conventional liquid fermentation platforms, the MPTxpress system reduces the number of steps in up- and downstream processing and required infrastructure, significantly improves yields, and lowers costs. It provides simplicity for mixing…
Due Diligence of Early Stage Technologies: Achieving Rapid Product Development with Low R&D Costs
Increased understanding of human diseases at molecular and cellular levels is leading to development of novel life-science technologies. Such advancements typically pertain to discovery and manufacturing of novel human therapeutics, new modes of drug delivery, and novel diagnostic technologies. The majority of those technologies are developed by early stage biopharmaceutical companies that have a greater appetite for risk than do larger companies. Early stage biopharmaceutical companies, however, have limited capital raised through personal sources, angel investors, venture capital, or government…
Targeting G Protein–Coupled Receptors with Biologics for Therapeutic Use, Part 1
G -protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent a target superfamily linked to many disorders across all therapeutic areas. Although this target class has been historically treated by small molecules and peptides, antibodies can offer a number of advantages over such molecules by virtue of their specificity, dosing frequency, and restricted penetration. They also can provide other functional effects specifically mediated by the Fc region (ADCC and CDC) as well as different modalities such as those offered by bispecific and antibody drug…
Process Challenges of Antibody–Drug Conjugates
With two products now on the market, and a host of others in clinical trials, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are slowly becoming a big business. Designed to deliver extremely active cytotoxic drugs that are otherwise undosable, they take advantage of the targeting ability of a specifically designed monoclonal antibody (MAb) to “shield” a highly potent API (HPAPI) as it travels through a patient’s bloodstream after administration. Once the antibody reaches its target on the cancer cell, it will release the payload,…
Qualification of Scale-Down Bioreactors: Validation of Process Changes in Commercial Production of Animal-Cell-Derived Products, Part 2 — Application
Here we apply our approach to validation of animal cell culture process changes using qualified, scale-down bioreactors. As described in Part 1 (including Table 1, Figures 1 and 2, and References 1–23), the goal is to facilitate implementation for the benefit of both the patients and industry. “Qualification of Scale-Down Bioreactors: Validation of Process Changes in Commercial Production of Animal-Cell–Derived Products, Part 1 — Concept” appears on pages 38–45 of BioProcess International’s May 2014 issue. Process changes often entail validation,…
Qualification of Scale-Down Bioreactors: Validation of Process Changes in Commercial Production of Animal-Cell-Derived Products, Part 1 — Concept
Implementing continuous process improvements is increasing in priority for the biopharmaceutical industry. Such implementation can be driven by product safety, purity, and stability enhancement opportunities as well as by cost-reduction pressures. Companies invest in projects to improve product quality assurance, safety, and yield as well as production efficiency (1). Such changes may come at any process stage, from early cell-growth methods through final-product packaging improvements. Examples include growth medium optimization, purification column operation optimization, and enhanced recovery during final filling…
Activatable Immunoconjugates for Target Cancer-Cell–Specific Diagnosis and Therapy
In cancer treatment, early diagnosis and targeted therapies are assumed to yield the highest cure rates. However, most current methods are limited by their low sensitivity to early disease and a lack of specificity for targeted cell killing. Newly developed, activatable immunoconjugates assist in the accurate detection of cancer through in vivo imaging with high target-to-background contrast (1,2). They also provide for the possibility of highly specific, light-mediated treatment with minimal effects on healthy cells surrounding tumors (3). In fact,…