The Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line was first established by Theodore Puck in the 1950s and was used mainly for cytogenetics studies (1). Since the 1990s, CHO cells have increased in popularity as expression host cells because they can be adapted easily into suspension culture and genetically modified. The CHO cell line also has a human-like glycosylation profile (2–4). Therapeutic proteins undergo different posttranslational modifications (PTMs) during manufacturing. Some modifications can lead to undesired effects such as decreased stability,…
Analytical
Analyzing Single-Use Polymers for Cell Culture Processes: Comparison of Cell Growth and Viability Test Procedures
The acceptance and implementation of single-use systems (SUS) or “disposables” has increased strongly in bioprocess development and biopharmaceutical manufacturing over the past two decades. Typically, suppliers provide SUS presterilized and ready to use. Using SUS eliminates time-consuming and expensive cleaning procedures (which often require corrosive chemicals and a large amounts of water) and removes the need to perform cleaning validation between batches. The application of SUS reduces the risk of product cross-contamination and increases product and patient safety (1–5). Polypropylene…
AAV Downstream Process and Product Characterization: Integrating Advanced Purification and Analytical Tools into the Workflow
The optimization of the downstream process for Adeno-associated virus (AAV) production with consistent quality depends on the ability to characterize critical quality attributes affecting potency, purity and safety of the final product. As the gene therapy field continues to push products through the clinical pipeline, an increasing need for efficient purification and analytical tools has become evident. In addition, the regulatory space has expanded in parallel to the use of AAV, driving the demand for simple and efficient assays to…
eBook: Diagnostics — Developing Rapid and Accessible Testing Solutions
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought myriad economic disruptions, social complications, and public-health calamities to the world. They have understandably overshadowed the silver lining of boosting biomedical science and technology in the realms of infectious disease, oncology, and more. But alongside the much-publicized commercial debut of novel vaccine technologies have come promising advances in medical diagnostics. In this eBook, BPI’s senior technical editor brings together perspectives from industry, academia, and expert organizations to highlight some of the latest diagnostic methods and…
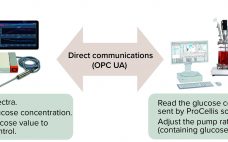
Automated Process Control Based on In Situ Measured Glucose Concentration
A process analytical technology (PAT) strategy involves defining critical process parameters (CPPs) of a biomanufacturing process that influence critical quality attributes (CQAs) and controlling those CPPs within defined limits. Doing that enables consistent product quality and helps companies reduce waste and costs. Glucose is an important CPP in bioprocessing and cell therapy. Glucose often is fed as a bolus addition based on daily off-line measurements, but that can lead to high glucose fluctuations and to excessive glucose feeding, which can…
Finding the Right Partner for Outsourced Cell-Line Development
The successful commercialization of a biopharmaceutical product begins with a robust and productive cell line. Inefficient cell-line development (CLD) can lead to costly delays and roadblocks. For that reason, small, new, and virtual companies — and even established and mid-size companies — often seek the support of outsourcing partners to develop their cell lines. Outsourcing CLD activities can ease many pressures associated with manufacturing new biotherapeutics. The benefits of outsourcing CLD and associated processes include access to specialized expertise and…
Seamless Integration of Glucose Control: Using Raman Spectroscopy in CHO Cell Culture
The process analytical technology (PAT) and quality by design (QbD) guidelines promoted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) support the idea that quality cannot be “tested into” a biologic product but must instead be part of its process design. Seamless integration of analytical data with bioprocess monitoring and control is crucial to understanding a process and overcoming manufacturing challenges that arise in the course of development. Monitoring of product quality attributes (PQAs)…
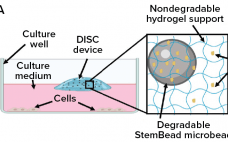
Gain Control of Culture Conditions: Technology for Sustained Delivery of Recombinant Proteins
Growth factors, added at the precise time and concentration to in vitro cultures are essential to control cell proliferation and differentiation. When added to a culture vessel, however, the concentrations of these signaling proteins rapidly decline, altering both levels of individual growth factors and the ratio of factors for cell signaling. When growth factors are replenished by exchanging the medium, concentrations peak, resulting in an ebb and flow of growth factor levels resulting in mixed signaling that can lead the…
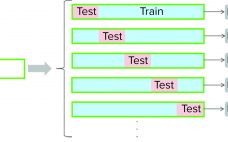
Multivariate Data-Driven Modeling for Continued Process Verification
Continued process verification (CPV) is an integral part of process validation for the manufacture of human and animal drugs and biological products (1). It is designed to meet three primary goals: maintain a validated state of products, their processes, and related systems; enable continuous process improvements; and meet regulatory requirements for life-cycle validation. A CPV program for a biologic product entails regular collection of data related to critical process parameters (CPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs) and the preprocessing, analysis,…
Risk Determination of Potential Mycotoxin Exposure to Patients: Testing Recombinant Human Factor VII from Transgenic Rabbits
Sevenfact eptacog beta is a new recombinant human factor VIIa (rFVIIa) developed by LFB SA in Les Ulis, France, as a bypassing agent (BPA) for treatment and control of bleeding in people with hemophilia A and B and inhibitors (1, 2). The product was approved for use in adults and adolescents by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2020 (3). It is expressed in the milk of transgenic rabbits and purified through a multistep process using both…