Every biomanufacturing process begins with transfection of recombinant genes into pools of cells — followed by a succession of screenings from which will emerge (ideally) a single progenitor cell of the new production cell line. Cast aside will be those cells that do not uptake the correct genetic material, those incapable of thriving in bioprocess conditions, those that fail to produce recombinant protein at relevant levels, and those without demonstrated clonality and relative genetic stability. Over the past several years,…
Search Results for: antibody characterization
Streamlined Serum-Free Adaptation of CHO-DG44 Cells: Using a Novel Chemically Defined Medium
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have radically transformed the treatment of many chronic diseases, mainly in the fields of oncology and autoimmunity. The overwhelming majority of therapeutic MAbs are manufactured from recombinant Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines. The original CHO cell line was isolated in the 1950s, and since the early 1980s, it has become the workhorse of the biopharmaceutical industry. The CHO-DG44 strain was generated after several rounds of mutagenesis that deleted both copies of dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) genes by…
CMC Considerations for Commercial-Ready ADC Manufacturing Processes to Enable Accelerated Timelines
Courtney Morgret, senior scientist, AbbVie Morgret’s presentation focused on antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) manufacturing and ways to accelerate it. She pointed out that ADCs have the potential to be filed for market approval based on phase 2 data. A few such products have been approved and are on the market today, with many more in the pipeline. ADCs provide an opportunity to address unmet medical needs. The task of a CMC (chemistry manufacturing and controls) group is to move a product…
Making Downstream Processing Continuous and Robust: A Virtual Roundtable
Current biomanufacturing is driven to pursue continuous processing for cost reduction and increased productivity, especially for monoclonal antibody (MAb) production and manufacturing. Although many technologies are now available and have been implemented in biodevelopment, implementation for large-scale production is still in its infancy. In a lively roundtable discussion at the BPI West conference in Santa Clara, CA (11 March 2019), participants touched on a number of important issues still to be resolved and technologies that are still in need of…
Analytical Tools to Improve Decision-Making During Product Development
Speed to clinic testing — and then speed to market — are highly significant metrics for companies developing biopharmaceuticals. By increasing the pace of drug development, these companies can reduce costs, obtain revenues early, and establish commanding positions in the market relative to their competitors. High-throughput development tools have contributed much to the acceleration of drug development in recent years. Such technologies enable the testing of many process parameters in parallel. Combining them with multifactorial “design of experiment” (DoE) analysis…
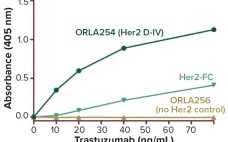
Modeling Virus Clearance: Use of a Noninfectious Surrogate of Mouse Minute Virus As a Tool for Evaluating an Anion-Exchange Chromatography Method
Viral safety is a critical focus during biopharmaceutical manufacturing (1–5). Although well-characterized mammalian cells such as the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) line have been used for decades, both endogenous expression of retroviral-like particles and exogenous contamination events from viruses warrant continued vigilance (6, 7). International regulatory agencies require biomanufacturers to validate the “viral clearance” efficacy of their downstream manufacturing process steps before resulting products can be awarded clinical trial or commercial approval (8–10). Currently, viral clearance testing is based on…
Clearing the Way for Viral Clearance
This webcast features: David Cetlin, CEO, MockV Solutions and John Li, Staff Scientist, Thermo Fisher Scientific To determine the viral clearance efficacy of biomanufacturing steps, mammalian viruses are “spiked” into in-process solutions, processed and analysed for reduction. Due to the infectious nature of these live viruses, “spiking studies” are typically conducted in specialized BSL-2 facilities. The costs and logistics associated limit viral clearance analysis during process development and characterization. To overcome this challenge, a non-infectious Minute Virus of Mice –…
2019 Archive
Cost of Goods Is Crucial for the Future of Regenerative Medicine: CAR-T Cell Therapy Provides a Case Study in Perspective
In the history of regenerative medicine, 2017 was a critical year. With approvals for Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) from Novartis AG, Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel) from Kite Pharma (a Gilead company), and Luxturna (voretigene neparvovec-rzyl) from Spark Therapeutics, cell and gene therapies finally made their mark on the regulatory landscape. Then in 2018, those products began both treating patients and bringing in revenues for their sponsor companies. “Patients are being treated, and biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies are being paid for treating them,” said…
The Role of Single-Use Polymeric Solutions in Enabling Cell and Gene Therapy Production: Part 1: Introduction and Manufacturing Process
by Bio-Process Systems Alliance Cell and Gene Therapy Committee The Bio-Process Systems Alliance (BPSA) was formed in 2005 as an industry-led international industry association dedicated to encouraging and accelerating the adoption of single-use manufacturing technologies used in the production of biopharmaceuticals and vaccines. Corporate members include plastic-equipment suppliers, service providers, and users in the biopharmaceutical industry who share this mission. A key focus of BPSA’s core activities is to educate its members and others through sharing of information and development…