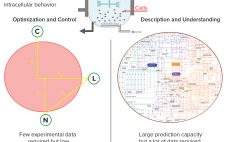
High-throughput technologies have transformed the biotechnology industry. The amount of data they generate is at least a hundred times higher now than it was two decades ago, primarily because of the rise of “-omic” technologies. As in many other industries, the biopharmaceutical sector entered the era of big data the day that high-throughput analytics were routinely implemented in experimental research. Big data refers to “datasets with sizes beyond the ability of commonly used software tools to capture, curate, manage, and…
Information Technology
Trends in Data Analytics As Organizations Undergo a Digital Transformation
The biopharmaceutical industry is in the midst of an exciting transformation as biologics experience massive growth — even outpacing the small-molecule segment (1). Biologics are predicted to comprise over a quarter of the pharmaceutical market in 2020 (2). At the same time, a plethora of new biologically derived therapy concepts — e.g., cell and gene therapies — are in development. Some biologics classes have become mainstream — e.g., monoclonal antibodies — with biosimilars entering the market and contract manufacturing organizations…
The Value of Plug-and-Play Automation in Single-Use Technology
Automation can improve efficiency, track performance, adjust operations, and liberate operators from mundane routines. Automation requires a flexible set of tools that align well with the inherent flexibility of single-use technology (SUT). Although SUT flexibility enhances a biomanufacturer’s ability to modify operations to meet the needs of today’s dynamic industry, it also increases timelines and costs related to customizing and validating automated additions. We present herein the findings of a team of industry automation experts who are sharing their experiences…
eBook: Automation — The Value of Plug-and-Play Automation in Single-Use Technology
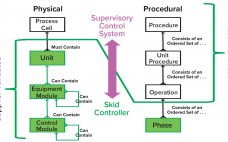
The biopharmaceutical industry’s movement away from large-scale, fixed-tank facilities to flexible facilities featuring single-use technologies (SUTs) has demonstrated the value of modular equipment and agile process design. SUTs have proven to be clear advantages to end users because those technologies enable quick facility build and changeover times. But linking SUT equipment with equally flexible automative technology has been difficult. Herein a group of automation experts from the BioPhorum Operations Group (BPOG) elaborate “plug-and-play” principles and introduce a supervisory control system…
Smart Sensors and Data Management Solutions for Modern Facilities
Bioprocess manufacturers continue to seek technologies for increasing productivity and shortening timelines from discovery to commercialization. Innovations such as high-throughput systems, automated platforms, and the latest clarification systems all have made processes efficient and robust. And with the increasing adoption of quality by design (QbD) principles, including the use of process analytical technologies (PAT), biomanufacturers are mitigating the risks of errors in their operations better than ever before. A critical part of mitigating risk is gathering meaningful process data and…
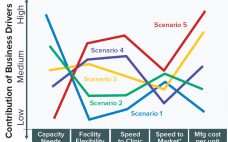
Biomanufacturing Scenarios: From the Biomanufacturing Technology Roadmap
Drug Substance Scenarios Given the complexity of the biopharmaceutical industry and the increasing diversity of products and companies, it is clear that there will be no “one size fits all” solution to biomanufacturing. Instead, we see a range of biomanufacturing scenarios playing out over the next 10 years. Five high-level scenarios were selected for drug substance manufacturing and two for drug product to cover the full spectrum of process and facility types. Each facility type is associated with a representative…
Single-Use Technology in Upstream Processing: A Roundtable Discussion
The Sartorius upstream portfolio addresses key strategic challenges facing the biopharmaceutical industry: Increased speed to clinic/market and lowered capital costs, with improved process control. Fully scalable, proven process solutions for cell line, media, and process development through commercial manufacturing accelerate upstream development and simplify manufacturing. Novel high-throughput development tools for intensified processes incorporate the latest in process analytics, multivariate data analysis (MVDA), and design of experiments (DoE) software tools. These tools are designed to compress development timelines and to scale…
A Harmonized Approach to Data Integrity
Data integrity is achievable when data collection is complete, consistent, and accurate (1). Failure to maintain data integrity compromises a company’s ability to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of its products. Escalation of serious regulatory actions related to data integrity violations has prompted the need to assess data integrity compliance and implement systems designed to guarantee it. Comprehensive measures must be taken to ensure that data are attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate (ALCOA) (2). Preventive measures need to be…
Opportunities for Modern Robotics in Biologics Manufacturing
It should come as no surprise to anyone familiar with biomanufacturing that current designs of bioprocess facilities as well as associated manufacturing spaces and support operations require excessive amounts of manual labor and manual interventions that lead to high labor costs and, consequently, total cost to supply. From receipt of raw materials to process execution and performance review, resolution of quality issues, and product shipping, no industry devotes a greater percentage of operating costs (or cost of goods sold, CoGS)…
Determining Control Chart Limits for Continued Process Verification with Autocorrelated Data
Control charts are used to assist in process monitoring activities. They use an estimate of central tendency (the overall mean) and variation (the standard deviation). Sample standard deviations (S) tend to underestimate process standard deviations (σ) when they are calculated using limited sample sizes of independent results (1). For this reason, the unbiasing constant c4 is used as a divisor when calculating Shewhart control-chart limits. If data used for control charting are positively autocorrelated, that tends to underestimate σ further…