Continuing development in protein and peptide engineering have produced a broad range of new biological products with improved therapeutic and diagnostic potential. In the development pipeline, more than 900 biologic products target more than 100 diseases (1). Increased manufacturing complexities caused by closely related impurities and requirements to improve process efficiencies and reduce operating costs highlight the need for new approaches in protein purification. Platform-based chromatographic approaches have been successfully applied in separating and purifying monoclonal antibody (MAb) products. But…
Chromatography
Preparing for Continuous Bioprocessing: An Interview with Pall Corporation’s Chief Technology Officer Martin Smith
Martin Smith, PhD, has been with Pall for about nine years and assumed the role of chief technology officer at Pall about 18 months ago. He spoke with Cynthia Challener, PhD, about Pall’s biopharmaceutical business unit and how the company is positioning its technology suite for a continuous process paradigm. Smith: There is no doubt in our minds that we see movement toward continuous bioprocessing. When you look across an array of different industries, the move to continuous or parallel…
Continuous Chromatography Is Now Possible for Clinical Manufacturing
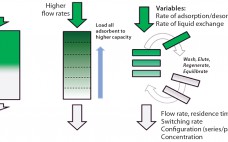
Intensified and integrated bioprocess technologies are creating a paradigm shift toward more efficient, higher flexibility facilities for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Continuous technologies that are designed as single-use systems help to greatly facilitate process intensification, delivering further efficiencies with reduced set-up times and elimination of the need for cleaning and cleaning validation. Chromatography is often considered to be a challenging bioprocess step, which has caused great interest in a simplified, safer solution. Continuous multicolumn chromatography using a single-use flow path is an…
Optimizing Continuous Monoclonal Antibody Polishing By Using Coupled Unit Operations
The biopharmaceutical industry is under a great deal of pressure to modernize manufacturing to meet the challenges of production at vastly different scales for niche drugs as well as for expected massive blockbusters, biosimilars, and regional manufacturing. To address these challenges, the biopharmaceutical industry is embracing process intensification through single-use and continuous processing technologies. Implementing these technologies offers increased productivity and manufacturing flexibility and reduces the footprint, capital outlay, and operating costs. Pall Life Sciences has developed several technologies designed…
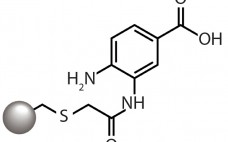
Clearance of Persistent Small-Molecule Impurities: Alternative Strategies
Small-molecule impurities that bind to and copurify with protein biopharmaceuticals traditionally have been removed using bind-and-elute (BE) chromatography. However, that approach may be undesirable for a number of reasons. For instance, it may present a facility-fit challenge or provide a lower process yield than what is acceptable. A common scenario in which BE chromatography may be undesirable is in removal of unreacted conjugation reagents. Bioconjugates represent an important and growing class of pharmaceuticals that include PEGylated proteins, vaccines, and antibody–drug…
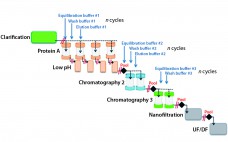
Accelerated, Seamless Antibody Purification: Process Intensification with Continuous Disposable Technology
Process intensification through continuous manufacturing has been practiced in the chemical, petrochemical, and food industries for years and has gained much interest among biopharmaceutical manufacturers (1). Key drivers encouraging biomanufacturers of therapeutic molecules to convert batch processes into continuous operation include flexibility, productivity, cost effectiveness, and product consistency. Continuous upstream processing has been demonstrated for the manufacture of a broad range of molecules, including complex/labile proteins such as enzymes (2) and monoclonal antibodies (3). Recent publications have reported successful application…
Prepacked Chromatography Columns: Evaluation for Use in Pilot and Large-Scale Bioprocessing
Time to market, resource requirements, cost, and flexibility are key considerations in designing purification processes suitable for manufacturing biopharmaceutical products. Over the past decade, many advances have been achieved in disposable processing systems that have allowed for increased processing at a lower cost. That is in part attributable to reductions in necessary resources, changeover costs, and cleaning-validation requirements. Large-scale, prepacked chromatography columns have recently become available for clinical and commercial manufacturing, and they represent a growing trend in the industry.…
Automated Purification of Native and Recombinant Proteins Using Multidimensional Chromatography
In traditional sequential chromatography, columns are run as separate entities. The process requires significant hands-on time and constant manual intervention. By contrast, automated chromatography technology provides the same results more efficiently and reliably and frees researchers to focus on other tasks, thereby shortening protein purification times from days to hours. For drug discovery, purifying protein samples is required to generate enough materials for research experiments. But the process is complex and time consuming. It involves repeated single-column purifications, careful analysis,…
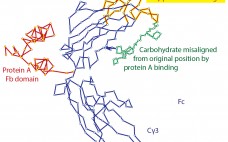
The Secret Life of Protein A
Affinity chromatography with protein A has become the foundation for purification of nearly every therapeutic IgG in commercial production. One of the features most responsible for its success has been its compelling simplicity. IgG binds. Contaminants do not. Load, wash, and elute pure IgG. In the real world, however, protein A does not elute pure IgG. It typically contains several hundred to a few thousand parts per million (ppm) contamination by host-cell proteins (HCPs) and other contaminants. Numerous studies demonstrate…
Optimization and Scale-Up of HCIC-Based MAb Purification Processes, Part 2
In multistep schemes, hydrophobic charge-induction chromatography (HCIC) has been shown to contribute effectively to clearance of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) host-cell proteins (CHOPs), DNA, and viruses. When used for capture chromatography, HCIC can provide better aggregate clearance than protein A sorbents can. Chen et al. enhanced clearance of aggregates, CHOPs, and product- related impurities by controlling HCIC based on both pH and the presence of binding-promoting salt in the wash and elution buffers used (1). Taken together with our findings…