Hydrophobic Interaction chromatography (HIC) is a powerful polishing tool for the downstream purification and manufacture of biotherapeutics. HIC offers orthogonal selectivity for the clearance of difficult process and product-related impurities such as aggregates, host cell proteins and endogenous and adventitious viruses. In this study, a family of POROS HIC resins with novel ethyl and benzyl chemistries was used to successfully polish two clinical stage monoclonal antibodies harboring very high levels of product aggregation (>10%). In addition to aggregate removal, viral…
Chromatography
Control of Protein A Column Loading During Continuous Antibody Production: A Technology Overview of Real-Time Titer Measurement Methods
During production of therapeutic antibodies, harvest titer is measured to monitor product mass loaded onto the protein A capture column. This prevents both column underloading (underusing expensive resin) and overloading (wasting product as flow-through (FT)) while allowing for column yield calculations. Batch production yields a single homogenous harvest pool, thus only one titer measurement (along with volume loaded) is sufficient to determine the mass loaded. During continuous production, however, cell-free harvest (permeate) continuously exits a perfusion reactor and loads a…
An Integrated Bioprocess for Antibodies: From Harvest to Purified Bulk in Six Hours
Antibody production platform processes have been widely adopted in biomanufacturing, but many unit operations are not suitable for integration and automation. Here we describe the work of integrating unit operations by transforming a column operation to a more robust cassette format. We have selected a biomolecule-friendly buffer (phosphate) to eliminate, or delay, the performance of a circulating tangential flow ultrafiltration/diafiltration (UF/DF) operation, so the harvest-to-purified-bulk process can be integrated, resulting in a single, direct-flow operation, that reduces the batch process…
Making Downstream Processing Continuous and Robust: A Virtual Roundtable
Current biomanufacturing is driven to pursue continuous processing for cost reduction and increased productivity, especially for monoclonal antibody (MAb) production and manufacturing. Although many technologies are now available and have been implemented in biodevelopment, implementation for large-scale production is still in its infancy. In a lively roundtable discussion at the BPI West conference in Santa Clara, CA (11 March 2019), participants touched on a number of important issues still to be resolved and technologies that are still in need of…
On Continuous Chromatography: A Conversation with Sanofi’s George Weeden
George S. Weeden, Jr., is a scientist in global manufacturing science and technology (MSAT) process science at Sanofi. We recently chatted about the topic of continuous chromatography. What are the general reasons for companies to consider continuous chromatography? And what are the caveats? The main driver for considering continuous chromatography is reducing the cost of goods (CoG). Continuous chromatography improves productivity (mass of product per volume of stationary phase over time) and thus increases throughput or decreases volumes of stationary…
Continuous Chromatography: Experts Weigh in on the Possibilities and the Reality
Discussions of continuous processing in the biopharmaceutical industry are an important part of current efforts toward intensifying bioproduction and bioprocessing. Biomanufacturers are looking at all components of their development and manufacturing processes for ways to reduce the size of their facilities, lower costs, and increase speed and flexibility of operations. Increasing options for and availability of single-use technologies have been major enablers of myriad attempts to improve efficiencies. Although the general consensus may still be that single-use components are more…
Development and Application of a Simple and One-Point Multiparameter Technique: Monitoring Commercial-Scale Chromatography Process Performance
In commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, downstream chromatography steps are still a bottleneck and contribute to significant operational costs (1, 2). Some of those costs are inherent (e.g., resins, large buffer quantities, and cleaning) whereas others are avoidable (e.g., product loss due to rejected lots or deviations that result in production downtime). Maintaining efficient and robust chromatography process performance is therefore critical for minimizing operating costs. To do so, we introduce a simple and one-point multiparameter technique (SOP-MPT) for monitoring chromatographic process…
Manufactured by Jetting: The Future in Protein A Affinity Matrix Design
Protein A affinity chromatography continues to be the preferred method for commercial purification of antibodies because of its high selectivity and robust resin performance over repeated purification cycles. Reports estimate that US$125 billion of yearly sales will be generated from monoclonal antibody (MAb) products by 2020 (1). Most of those will be purified by largescale protein A affinity chromatography. With the continued growth and commercial importance of MAb production, availability of high-quality resin material and options for secondary sourcing are…
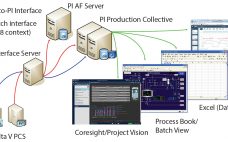
Using Data and Advanced Analytics to Improve Chromatography and Batch Comparisons
With all the hype surrounding the industrial Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and digital transformations, the most important information technology factors still are data and the connections of sensors, systems, and applications that generate, store, find, and use those data to obtain operational intelligence. Data volumes are increasing rapidly, and they will continue to do so. The ability to find and make sense of data to obtain intelligence that improves process outcomes is more important than ever. For clinical-…
Intensification of Influenza Virus Purification: From Clarified Harvest to Formulated Product in a Single Shift
Influenza is a global respiratory disease with an estimated mortality of up to a half million people per year (1). The majority of traditional influenza vaccines are still produced in eggs. Downstream processing typically consists of clarification by centrifugation, concentration by ultrafiltration, and purification by ultracentrifugation (2). Recombinant vaccines are most often purified by chromatography. Chromatographic purification of viruses already has achieved major improvements in recovery and scalability (3), but it also is important because it enables virus purification to…