A general vaccine purification strategy can be divided into three stages, with one or more steps for each stage. The first stage is to concentrate and isolate the target molecule quickly to remove it from conditions that could lead to its inactivation or loss. Intermediate purification seeks to remove remaining contaminants, typically using an orthogonal approach. That is followed by a polishing step in which trace impurities are removed through high-efficiency steps because those impurities usually are similar to the…
Chromatography
In-Line Turbidity Sensors for Monitoring Process Streams in Continuous Countercurrent Tangential Chromatography (CCTC)
A strong connection between turbidity and total suspended solids (TSS) has been linked in the past to measuring well defined particles in processes. Optical density probes have seen wide adoption in the biotechnology industry for monitoring cell growth within a bioreactor, whereas in-line turbidity sensors have been used to monitor filter performance. Turbidity measurements offer a rapid quantification of suspended solids but have not been used in the biotechnology industry for chromatographic resins. In this study, turbidity measured with equipment developed by PendoTECH was used with novel continuous chromatography technology developed by Chromatan…
Dual Sourcing of Protein A Resin to Mitigate Supply Chain Risk: A Comparative Study to Determine Equivalence
Protein A affinity chromatography is a well-established technology that is used extensively for large-scale purification of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). With this mode of chromatography, very high product purity can be achieved in a single, relatively simple unit operation. A solution containing the target protein of interest is applied to a liquid-chromatography column at near-neutral pH, and one or more wash steps follow to lower product- and process-related impurities (1). Product is eluted through application of a low-pH buffer. Finally, the…
eBook: Development and Application of a Simple and One-Point Multiparameter Technique — Monitoring Commercial-Scale Chromatography Process Performance
In commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, downstream chromatography steps are still a bottleneck and contribute to significant operational costs (1, 2). Some of those costs are inherent (e.g., resins, large buffer quantities, and cleaning) whereas others are avoidable (e.g., product loss due to rejected lots or deviations that result in production downtime). Maintaining efficient and robust chromatography process performance is therefore critical for minimizing operating costs. To do so, we introduce a simple and one-point multiparameter technique (SOP-MPT) for monitoring chromatographic process…
The Multi-Mode Mimetic Ligand Library: A New Tool for Rapid Development of Downstream Processes
Recent developments in downstream processing of biomolecules — including continuous processing, bind–elute affinity capture, and flow-through polishing steps — have increased the need for greater selectivity from chromatography adsorbents. This has led to the introduction of a new generation of adsorbents: so-called “mixed-mode” or multimodal ligands. They provide greater selectivity and tolerance to process buffer composition than either ionexchange chromatography (IEC) or hydrophobic-interaction chromatography (HIC) alone can provide. Learn more in this Special Report from Steve Burton, Chief Executive Officer…
Scale-Up of Twin-Column Periodic Countercurrent Chromatography for MAb Purification
Periodic countercurrent (PCC) processes increasingly are being evaluated as alternatives to single-column batch capture processes. Some of the advantages of PCC processes over single-column processes include shortening of processing time and/or reduction of required resin volume through increased productivity; reduction in resin costs through improved resin capacity use; and reduction in buffer consumption through increased column loading. Those advantages, however, come with increased equipment complexity and hardware costs. PCC processes and systems with two to up 16 columns of the…
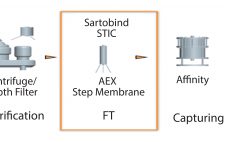
A Two-Step Purification Process: Application of HIC Membrane Chromatography in a Disposable 2,000-L Clinical Facility
Given paradigm shifts in the biopharmaceutical industry over the past decade, product development timelines are squeezed as the number of molecules entering clinical development continues to increase. Manufacturing facilities, especially those supplying clinical trial materials, have had to adapt to this trend. One popular approach is to have fully disposable equipment that allows for quick product changeover and flexible manufacturing capacity to respond to variable clinical demand. Although many facilities-related technologies exist to support that concept (e.g., disposable probes and…
Large-Scale Purification of Factor-IX: Comparing Two Affinity Chromatography Resins
Human clotting factor-IX (F-IX) is a glycoprotein that is essential for normal hemostasis (1). A deficiency of F-IX in human plasma is caused by an absence or functional mutation of the F-IX gene that expresses inactive F-IX in plasma. That leads to hemophilia B (“Christmas disease,” named after its first identified patient), a genetic disorder in which the blood-clotting cascade is disturbed (2, 3). The structure and amino-acid sequence of F-IX are similar to those found in other vitamin-K–dependent glycoproteins.…
Establishing Effective High-Throughput Contaminant Removal with Membrane Chromatography
Bharat Serums and Vaccines Limited (BSV) in India conducted a study based on effective removal of host cell proteins (HCPs) from a recombinant hormone with a wide isoform profile in the acidic range imparting drug-product activity. Because the hormone and HCPs have a similar range of active species, the purification process with conventional chromatography resins had difficultly removing those HCPs from the active isoforms of the hormone. To solve that issue, a membrane chromatography technique was implemented. Our initial choice…
Streamlined Column-Packing Design for a New Commercial Launch Facility
To meet network demand for a commercial launch facility, Genentech (Roche) designed a new downstream train and built it within an existing building shell at the company’s Oceanside, CA, site. This downstream train included new technologies to allow for rapid technology transfer of different new products in the company’s drug pipeline. One technology that was pursued was the Axichrom column platform from GE Healthcare and associated column packing equipment to streamline column packing design. Here we focus on how a…