The boundaries of technology can be pushed significantly when insights from different fields reinforce each other. Based on in silico simulations demonstrating the importance of order on the efficiency of chromatographic separations, PharmaFluidics has combined expertise from the analytical chromatography and semiconductor chip manufacturing industries to create a new type of nanoscale liquid chromatography (LC) column. Conventional LC columns contain randomly packed beads as a stationary phase. By contrast, PharmaFluidics uses a lithographic etching process to create a perfectly ordered…
Chromatography
Recent Advances in Endotoxin Removal: An Upgrade to a Traditional Method and a New Adsorption Chemistry
Endotoxin contamination has been the bane of the bioprocessing industry since its inception. Endotoxins are everywhere: They are toxic and/or interfere with every type of therapeutic, diagnostic, and research product; they are indestructible within the limits of product tolerance; and they are difficult to remove (1–4). Beyond that, they interact with various biological species in ways that prevent accurate measurement (5, 6). Managing these issues has been a focus of the industry for at least half a century, yet it…
Moving DSC Downstream: Exploiting Differential Scanning Calorimetry As a Process Development Tool
The primary goal of biopharmaceutical process development is to determine what steps and conditions will maximize and optimize yields of purified product in the most reproducible, robust, and cost-efficient way. Characterized by high batch-to-batch comparability minimizing economic losses associated with batch failures, success relies on a thorough understanding of a given biological drug. Determining how its activity and stability are affected by processing and how to mitigate and control associated risks is advocated by a quality by design (QbD) approach.…
Is Continuous Downstream Processing Becoming a Reality?
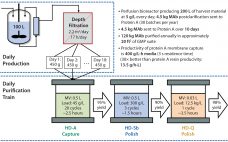
Over the past 30 years, several biopharmaceuticals have been produced by continuous cell culture processes run in a chemostat or perfusion mode. In most cases, no alternative was available to produce certain unstable molecules (1). However, downstream processing is and has remained a step-by-step batch operation. Continuous processing generally requires more process knowledge, equipment, and technological advances than do batch processes. With the maturity of bioprocessing and increasing awareness of manufacturing costs, companies are focusing on developing continuous downstream processing…
Downstream Disposables: The Latest Single-Use Solutions for Downstream Processing
Downstream processing has been considered a “bottleneck” in the manufacture of protein biotherapeutics ever since cell culture engineers began dramatically improving production efficiencies around the turn of the century. And as single-use technologies have grown in importance and acceptance, offering more solutions every year, their biggest challenges too have been in the separation, purification, and processing that follows product expression in cell culture. Many of the technologies familiar to process engineers — e.g., centrifugation and chromatography — present technical and…
Multicolumn Chromatography: Facilitating the Commercialization of Monoclonal Antibodies
Since 2001, global contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) CMC Biologics has completed more than 120 projects with at least 100 pharmaceutical partners. During that time, the company has taken a holistic approach to helping clients balance manufacturing risks and rewards. The team focuses on evaluating key technologies to deploy a constantly evolving set of capabilities in support of biopharmaceutical clients throughout their product lifecycles. Part of that commitment is continually evaluating what would best benefit customers and where key…
Membrane Adsorbers, Columns: Single-Use Alternatives to Resin Chromatography
Filtration membranes are used extensively throughout the biopharmaceutical industry for a range of applications, from coarse filtration to nanofiltration. Advantages of filter technologies include easy scaling, disposability, and (for many membrane filters) rapid and robust performance in a single-pass. The same advantages have been realized with membrane adsorbers. Chromatography resins are inherently disadvantaged by diffusion limits of the pores in chromatography media. Therefore, resin columns must be significantly oversized to match the performance of high productivity bioreactors. By comparison, membrane…
Reducing Clinical-Phase Manufacturing Costs: Collaborating for Savings without Compromising Quality or Performance
In downstream purification of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), the single greatest contributor to manufacturing costs is the expensive capture step typically based on protein A affinity chromatography. Almost since its introduction to bioprocessing, efforts have been made to reduce the cost of this step. Several alternative ligands have been promulgated as potential replacements for protein A, but they have proven difficult to adopt and scale up. Supplier companies have pushed for increases in capacity and economics, but those are always accompanied…
Special Report: A Strategy for Cost-Effective Capture Using Agarose-Based Protein A Resins
It is well recognized that the cost of Protein A resins is substantial. If a developmental monoclonal antibody (MAb) makes it to marketing approval and manufacturing, the high cost of purification using a Protein A resin is amortized over a large number of purification cycles, and the contribution to cost of goods is reduced to acceptable levels. However, a high percentage of clinical projects will fail, and the Protein A resin will be used only for a small number of…
Innovative Downstream Purification Solutions for Viral Vectors: Enabling Platform Approaches to Advance Gene Therapies
Over the past decade, gene therapy applications and their importance in the biopharmaceutical industry have been increasing. Gene therapies promise versatile treatment options that could revolutionize and transform medicine. As treatment modalities, they offer the possibility of long-term and potentially curative benefits to patients with genetic or acquired diseases. Gene therapies are designed to treat disease by delivering genetic material that encodes a protein with a therapeutic effect into a patient’s cells. It can be used to replace a missing…