Over the past 10 years, the biopharmaceutical industry has placed increasing pressure on analytical laboratories, whose work is more important to the success of biotherapeutic products than ever before. Nearly concomitant with the appearance of BPI on the scene, the US Food and Drug Administration put forth its final report on the 21st century good manufacturing practice initiative, which in changing how regulators would review product applications, changed how companies must approach them (1). The guiding principles —…
Search Results for: antibody characterization
IBC’s 28th Annual Antibody Development and Prodution
Antibody Development and Production covers the entire spectrum of topics related to development and production of the most promising therapeutics in the biopharmaceutical industry. An estimated 30% of new drug products likely to be licensed in the next decade will be antibodies. With the reality of their biosimilar equivalents getting closer, companies need to develop processes faster to preserve their time on the market free from generic competition and keep costs down. With that in mind, we developed the 2012…
Development of an In-House, Process-Specific ELISA for Detecting HCP in a Therapeutic Antibody, Part 2
During biopharmaceutical manufacturing, final drug products can get contaminated with host-cell proteins (HCPs) derived from a production cell line. HCPs can elicit adverse immune responses, so regulatory authorities require accurate monitoring of their presence and concentration in final drug products. Because they are robust and offer good throughput, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) are the first choice for HCP detection to monitor product quality. Generic ELISA kits are commercially available for HCP detection with a number of commonly used…
Predicting Virus Filtration Performance with Virus Spike Characterization
Evaluating a virus filter should, in theory, be a straightforward exercise. Membrane-based filtration is a robust virus reduction technology that plays an important role in virus safety for most drug production processes. An appropriate virus filter for a given process is generally selected through preliminary testing with relevant drug feed material. Data acquired during such tests are used to determine hydraulic performance targets such as expected flow rates and total throughputs. A virus clearance evaluation study is then performed in…
Development of an In-House, Process-Specific ELISA for Detecting HCP in a Therapeutic Antibody, Part 1
After production and purification of biopharmaceuticals generated by cell culture expression systems, endogenous cell line proteins — commonly referred to as host-cell proteins (HCPs) — sometimes contaminate finished products. HCPs can elicit an immune response following administration of those drugs to patients (1), and cause potentially deleterious side effects. It is therefore imperative to minimize HCP contamination in finished biologics. Regulatory health authorities require monitoring of HCP contamination. They expect validation of each purification process to demonstrate its…
IBC’s 26th International Antibody Development and Production Part of IBC’s Biopharmaceutical Development and Production Week
IBC’s Antibody Development and Production conference offers the latest technical and scientific advances in bioprocessing to help companies of all sizes improve speed, quality, and cost in developing and producing antibodies. Exclusive case studies deliver the latest data together with strategic discussion forums that allow the industry’s leading scientists, engineers, and executives to collaborate and find solutions to their most pressing challenges. Gain from companies sharing “lessons learned” from their own experiences developing and optimizing processes and production of antibody-based…
Biosimilar Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Gaps in Science Limit Development of an Industry Standard for Their Regulatory Approval, Part 2
Last month, Part 1 of this discussion briefly described the regulatory landscape for developing biosimilar therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (TMAbs). We identified certain specific structural components of TMAb drug substances that warrant particular attention because alterations to them are likely to affect therapeutic safety and effectiveness. Now we conclude by considering whether studies of reference materials can further the development of analytical industry standards to ensure comparability of putative biosimilar TMAbs with innovator TMAbs. We suggest that the time is right…
Viral Risk Evaluation of Raw Materials Used in Biopharmaceutical Production
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines to patients is a key objective for both health authorities and the pharmaceutical industry. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs). Manufacturers must ensure not only the suitability of RMs for their intended use in a manufacturing process, but also their highest attainable safety with regards to viruses and other adventitious agents. The need to apply a risk-based RM control strategy is in line…
Rapid Profiling of Reduced and Intact Monoclonal Antibodies By LC/ESI-TOF MS
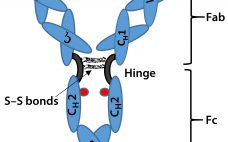
Figure 1. As the pharmaceutical industry focuses on developing biotechnology-derived drugs, bioanalytical groups must produce generic methodologies for antibody characterization with higher throughput and faster sample turnaround times. Although antibody selectivity varies, overall antibody structures are highly conserved. Intact antibody LC/MS analysis is useful for profiling glycovariants and C-terminal Lys processing, and even more information can be gleaned from analysis of a reduced antibody. UltraPerformance LC® (UPLC®) technology permits efficient desalting and rapid LC/MS mass profiling of an intact (4…
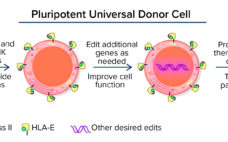
Novel Technologies for Advancing Allogeneic Cell Therapies
In many ways, cells are the ultimate therapeutic product. They can integrate and participate in different biologic processes and replace missing biological functions. Cell therapies are dynamic, versatile, and with the appropriate engineering, capable of influencing and correcting disease processes robustly. Cell therapies essentially are living medicines, and their adaptability contrasts with conventional drug modalities that generally have only a single specific target or effect. Because cell therapies are highly complex modalities, their scientific and R&D challenges are different from…