The BioPhorum Operation Group’s (BPOG’s) Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT) workstream would like to congratulate the United States Pharmacopeia’s committee for its latest revision to USP chapter <1207> Package Integrity Evaluation: Sterile Products. Generally, we believe it provides a comprehensive overview of the available methods for container–closure testing and outlines many important elements for consideration in establishing a successful CCIT strategy. We first responded to the USP <1207> draft when it was released for comment in 2014. And from our…
Regulatory Affairs
Postapproval Changes for Biopharmaceutical Drug-Substance and Drug-Product Manufacture: Regulatory Complexity and Impact
Pharmaceutical products save or improve the lives of millions of people each year. Thorough regulatory review of chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) information is critical to ensure drug product safety, quality, and efficacy as well as to secure patients’ continuous access to such products. But achieving all of that at an effective cost is difficult. Companies race to launch products to patients as soon as possible after clinical efficacy is demonstrated. Biomanufacturers often need to make changes such as increasing…
Special Report on Process- and Product-Related Impurities (A CMC Strategy Forum Special Focus Series): Extractables, Leachables, Particles, and Aggregates
The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website (www.casss.org). This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment will continue to…
Biosimilar Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Gaps in Science Limit Development of an Industry Standard for Their Regulatory Approval, Part 2
Last month, Part 1 of this discussion briefly described the regulatory landscape for developing biosimilar therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (TMAbs). We identified certain specific structural components of TMAb drug substances that warrant particular attention because alterations to them are likely to affect therapeutic safety and effectiveness. Now we conclude by considering whether studies of reference materials can further the development of analytical industry standards to ensure comparability of putative biosimilar TMAbs with innovator TMAbs. We suggest that the time is right…
Progress Toward Commercial Scale and Efficiency in Cell Therapy Bioprocessing
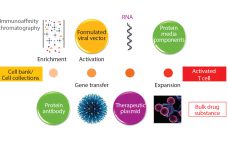
Regenerative medicine includes both cell and gene therapies. Currently 672 regenerative medicine companies operate around the world, and 20 products have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Of 631 ongoing clinical trials by the end of 2015 (1), over 40% are in oncology, followed in prominence by cardiovascular and infectious diseases. Here I focus on gene and cell therapy bioprocessing in which the final products delivered to patients are cells. Cell therapies are either autologous (derived…
Manufacturing Plasmid DNA: Ensuring Adequate Supplies for Gene and Cell Therapies
The concept of gene therapy is far from new, with initial studies performed over 20 years ago (1). However, in the past few years an explosion of interest in this area has gone beyond initial regenerative approaches using viral vectors. Interest is now moving increasingly into potential use of T cells modified using recombinant viral vectors for immunotherapy applications. Such therapies are based on using either adenoassociated virus (AAV) or lentivirus (1), both vectors being frequently generated through transient expression…
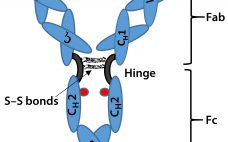
Biosimilar Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Gaps in Science Limit Development of an Industry Standard for Their Regulatory Approval, Part 1
Biosimilars are biologically derived pharmaceuticals intended to have clinical similarity to a legally marketed innovator product when that product’s patent or market exclusivity has expired. By contrast with generic small-molecule drugs, clinical performance of a biologic pharmaceutical is a function of its structural complexity and higher-order structure (HOS). Biomanufacturing controls of such complex products cannot fully ensure chemical similarity between an innovator product and putative biosimilar because minor differences in chemical modifications and HOS can significantly alter a product’s safety…
Collaboration Is Key to Innovation in Biotechnology
A new report from Thomson Reuters shows that innovation in biotechnology declined slightly in 2015, and biotech is the only one of a dozen worldwide industries examined to show that kind of decline (1). To measure innovation, compilers used metrics such as patents filed and scientific literature cited. Looking at the details, however, the dip was just a 2% drop from 42,584 events in 2014 to 41,624 in 2015. The same dynamics had revealed a 7% increase in innovation from…
Managing Customer and Regulatory Expectations
Partnering with a contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) allows drug-product sponsors to turn fixed costs into variable costs. Market forecasting by pharmaceutical companies drives numerous decisions in development programs: sales-force resources, geographic resource distribution, and (of course) manufacturing planning. It is a widely accepted fact in the pharmaceutical industry that accurate forecasting is a challenge, especially for new drug launches. A number of models can be used to develop drug forecasts, but none of these models is perfect. No…
Quality By Design for Monoclonal Antibodies, Part 2: Process Design Space and Control Strategies
Process design space and control strategy are two fundamental elements of quality by design (QbD) that must be established as part of biopharmaceutical development and regulatory filings. Like all of QbD, they are interconnected and iterative. Both are based on knowledge gained during product and process development — but both need to be in place (in a potentially very limited form) when a company begins to manufacture drug substance for clinical trials. Part 1 of this discussion appears on pages…