The rapidly developing global cell therapy market poses numerous industry challenges for drug development, process scalability, commercialization, and patient safety. The processes of procuring donated human tissue for clinical applications are fraught with many technical, ethical, and legal issues. Allogeneic cell therapies involving primary cell types such as bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (BM-MSCs), hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), and T and natural killer (NK) cells for immunotherapy applications are especially challenging because of the vigorous process of screening…
Regulatory Affairs
Back to Basics for Biotech: Driving a Culture of Quality and Compliance with Practical Communication Techniques
The robust regulatory environment surrounding biotechnology and bioprocessing demands a comprehensive current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) culture of quality, compliance, and absolute adherence to policy. Employees need to be engaged in their work, with a laser focus on meeting stringent specifications and operating under tight controls. A misstep in quality or compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal concerns, regulatory retaliation, and reputational damage. Communication and stakeholder engagement are critical to aligning organizations and driving the right culture in highly…
Beyond Compliance: Serialization Has More to Offer
As the global pharmaceutical industry implements serialization (track and trace from manufacturing to dispensing) to meet governmental regulatory requirements, other opportunities arise for drug companies. The main driver here is to improve the integrity of the overall drug supply chain, but other meaningful business benefits can come from serialization. Generally accomplished through automated, electronic means, it involves such practices as recording, authenticating, maintaining, and sharing accurate records of products. Outside-the-Box Benefits In addition to tightening up the supply chain and…
Postapproval CMC Changes: Increasingly a Fact of Biopharmaceutical Life
The manufacture of vaccines and therapeutic proteins has suffered from a reputation of being part art and part science, with heavy doses of regulatory uncertainty thrown in. Postapproval changes (PACs) to chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) were initiated reluctantly and carefully in the era of “the process is the product.” Today, CMC PACs are a normal part of the biopharmaceutical industry business. Emma Ramnarine (head of global biologics quality control at Hoffmann-La Roche in South San Francisco, CA) notes that…
eBook: Challenges Facing Biosimilar Entries into US Markets
Since the 2009 enactment of the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA) (1), the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has licensed six biosimilar products under PHS 351(k) and approved one product under FD&C 505 (b)(2). It also provided complete response letters (CRLs) to four biologics license application (BLA) filings (Table 1) (2). By comparison, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved 31 biosimilar products (3) and refused or withdrawn about five. There is no doubt that US market…
Serialization: Background, Justification, Requirements, Timelines, and Readiness Across the Supply Chain
Drug manufacturers are facing unprecedented serialization challenges. Serialization requires weighty consideration and focused strategy for successful commercialization, even for those companies that have yet to bring a product to market. The World Health Organization estimates that 10% of medicines worldwide and up to 50% of drugs consumed in developing nations are counterfeit. In response to increasing drug integrity concerns, more than 40 countries have introduced laws mandating serialization and tracing of pharmaceutical products as they pass through the supply chain.…
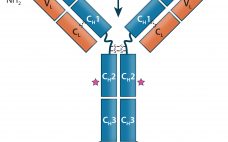
Therapeutic IgG-Like Bispecific Antibodies: Modular Versatility and Manufacturing Challenges, Part 1
Antibody-based immunotherapy has advanced significantly since 1986, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first mouse monoclonal antibody (MAb) for clinical use: Orthoclone OKT-3 (muromonab-CD3). In the intervening years, researchers have applied the tools of genetic engineering to clone immunoglobulin G (IgG) genes into a number of expression vectors. In the 1990s, the bioprocess industry was able to produce fully human antibodies in cultured cells. As of June 2017, the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA)…
Transforming Deviation Management
All biopharmaceutical companies espouse a belief in scientific, risk-based approaches. However, with respect to deviation management systems (DMSs), the industry is falling short of that promise. By and large, companies still use a small-molecule pharmaceutical compliance model that dates back to the 1980s, based on the strategy that all deviations are created equal and require 30-day closure. Most bioprocessors still hold to a default 30-day rule, even though there is no specific regulatory requirement for that time frame. Major or…
Change Happens: Technical and Regulatory Considerations for Pharmaceutical Product Lifecycle Management (CMC Forum)
In the current global regulatory environment, management and implementation of postapproval CMC changes often can be unpredictable and inefficient. Timelines for change approval can vary from months to years, depending on regional regulatory procedures. Therefore, the challenge in postapproval lifecycle management is to maintain a constant supply of high-quality product while supporting innovation and continual improvement. This was the premise of the CASSS Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Strategy Forum held in Gaithersburg, MD, on 20–21 July 2016. The forum…
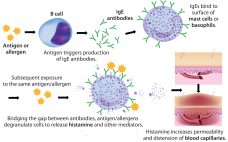
Polysorbates, Biotherapeutics, and Anaphylaxis: A Review
Rapidly increasing use of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in the treatment of neoplastic, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases has led to a dramatic increase in hypersensitivity reactions worldwide, complicating the use of MAbs as first-line therapies and limiting patient survival and quality of life (1). The origins of anaphylaxis are not well understood, though its mechanism is fairly straightforward (Figure 1). It is usually attributed to some undefined intrinsic property or properties of a biotherapeutic — despite the fact that biotherapeutic formulations…