Bai-wei Gu, Juan Lagos, and Matthew Weaver (heads of cell line development, upstream process development, and downstream process development groups, respectively, at WuXi Advanced Therapies, ATU) joined forces on 29 October 2019 to feature their company’s viral-vector manufacturing capabilities for cell and gene therapies. In addition to adherent platforms for lentivirus (LV) and adenoassociated virus (AAV) vectors, ATU soon will offer suspension-cultured viral vector platforms for them as well as analytical measures that support release testing. Transitioning from adherent to…
Cell/Gene Therapies
Better Bioprinting Ahead: Breakthroughs and Remaining Challenges
Bioprinted organs soon could revolutionize clinical trials, transplantation, and regenerative medicine. But as Chris Lo reminds us in a new GlobalData report (1), several technical hurdles must be negotiated before biopharmaceutical companies can harness three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting for such purposes. BPI explores persistent printing problems and promising solutions below by analyzing Lo’s report alongside commentary from founding editorial advisory board member Bill Whitford (bioprocess strategic solutions leader at GE Healthcare Life Sciences), Lev Gerlovin (vice president in the life sciences…
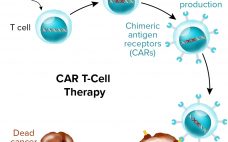
Challenges and Opportunities in CAR T-Cell Development and Manufacturing
Just about anyone in the biopharmaceutical industry will tell you that cost is now the primary concern in cell and gene therapy development. It hasn’t even been a decade since “manufacturability” was the main issue at hand — and cost has risen organically from related discussions. Regenerative medicine evolved from medical research rather than from drug-development companies, and technologies that worked in clinical settings haven’t translated directly to manufacturing facilities. Cost is often the problem. Early product successes (that ultimately…
Cell Banking for Cell and Gene Therapy: Regulatory, Ethical, and Scientific Considerations
Regenerative medicine holds great potential for human disease management, with hundreds of cell and gene therapy (CGT) products for tissue/organ reconstitution or replacement in different stages of development and clinical testing for toxicity, safety, and efficacy. For example, currently more than 60 CGTs have marketing authorization (although many with only conditional approval) from central regulatory agencies worldwide (1). Those products are treating conditions such as hematopoietic malignancies, immunological disorders, and cartilage disorders. Most of those treatments use culture-expanded autologous or…
Do We Need Separate Regulations for Advanced Therapies?
Before we had the 21 CFR 1271 regulation for tissue therapies, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had determined that regenerative medicine was exceptional enough to warrant its own regulations for good manufacturing practice (GMP). Since 2001, the tissue industry has adapted to those new rules while the FDA stepped up enforcement over time. When a cell or tissue product is regulated under 21 CFR 1271, its specific regulations apply before the general regulations for biologics and drugs. But…
CAR-T at the Crossroads: Is Allogeneic the Way to Go?
As cell therapies move through the clinic toward commercialization, respondents to an Informa Connect industry survey are beginning to look to allogeneic — or off-the-shelf — products as “the next big thing.” Almost 200 people contributed to the Cell Therapy Analytics Report, revealing their current positions within the burgeoning cell and gene therapy space and offering their thoughts and predictions for the future. Most survey respondents work within companies developing oncology products. Of those, the largest group (41%) said that…
Measure Twice, Treat Once: Navigating the Regulatory Landscape of Assay Development to Ensure High-Quality CGT Products
Cell and gene therapies (CGTs) are a novel and fast-growing class of transformative therapies designed to address gaps in traditional treatment strategies of some of the most severe diseases. By definition, gene therapy “seeks to modify or manipulate expression of a gene to alter the biological properties of living cells for therapeutic use” (1). That can be either an in vivo delivery of a gene or delivery of a gene to a patient’s cells that are manipulated outside of the…
AAV Vector Manufacturing Platform Selection and Product Development
Adenoassociated virus (AAV) vectors have emerged as the prominent delivery mechanisms of corrective gene therapies. Three such products — Glybera (alipogene tiparvovec, uniQure), Luxturna (voretigene neparvovec-rzyl, Spark Therapeutics), and Zolgensma (onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi, AveXis) — have been licensed, and a growing number of candidates are entering late-stage development. In mapping out an AAV gene therapy product development strategy, biomanufacturers should address fundamental considerations for their manufacturing strategies for both phase 1–2 clinical evaluation and translation for commercial market supply. A manufacturing…
The Cell Therapy Industry Needs High-Quality Healthy-Donor Material
The cell and gene therapy (CGT) segment has grown tremendously over the past decade. And while the industry deals with a steep learning curve inherent to a rapidly developing field, problems must be solved, and solutions must be reduced to practice. One such problem, long understood by the industry but now thrust into the spotlight, is sample handling: proper collection, processing, preservation, storage, and transportation of cellular starting material. Suboptimal techniques for such logistics have been shown not only to…
Bioprinting Capabilities and Futures
Bioprinting has advanced rapidly through engineering step changes in the use of three-dimensional (3D) printing. With these developments, living cells can be positioned layer by layer to produce functional tissue structures. Key attributes of this emerging technology are its high scalability and modularity, which enable automated and repeatable manufacture of a wide variety of tissues. These high-throughput biofabrication capabilities equip companies with tools to develop 3D-printed tissues for broad applications, from in vitro drug testing models to therapeutic tissue implants,…