The Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Strategy Forum held on 22 January 2012 in San Francisco, CA, focused on selected scientific and regulatory aspects in the development of biosimilar products. Such products are an increasingly important area of interest for both the biopharmaceutical industry and its regulatory agencies. Biosimilars are highly complex, so scientists have been unable to demonstrate identity to a level typically possible for small molecules. Consequently, specific scientific and regulatory approaches are required to ensure the high…
Product Characterization
Mapping Success for Commercial Cell Therapy Manufacturing
Commercializing cell therapies can be much more challenging than commercializing traditional pharmaceuticals and biologics. Cell-based drug products are significantly more complex than protein or small-molecule drug products. Their mechanisms of action and product attributes are also more complex. Cell therapy product attributes rely heavily on the associated manufacturing processes. Process changes can influence products in ways that may not be discernible until their effects on efficacy effects become evident. Product characterization is critical, but cell therapy products are living organisms…
Uniting Small-Molecule and Biologic Drug Perspectives: Analytical Characterization and Regulatory Considerations for Antibody–Drug Conjugates
Cosponsored by CASSS (an international separation science society) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the January 2010 CMC Strategy Forum explored antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), which are monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) coupled to cytotoxic agents. The ADC platform of products is being used more and more for clinical evaluation in oncology. More than a dozen companies are developing several types, including products conjugated with calicheamicin, auristatins, and maytansinoids. Such products use the specificity of a MAb to deliver a cytotoxic…
Glycosylation of Therapeutic Proteins: Current Understanding of Structure–Function Relationships
A CMC Strategy Forum held in Washington, DC, on Sunday 28 January 2007 focused on two topics related to protein structure and function (1). First, analytical techniques used in the glycan analysis characterization included recent advances and correlations among the various tools. And second, current understanding of glycosylation’s functional relevance to therapeutic proteins was discussed in the context of its effects on biological activity, pharmacokinetics, and Fc effector functions (for monoclonal antibodies, MAbs). Progress has been made in the field…
Analysis and Structure Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies
On 6 January 2003, 129 attendees participated in the second Well-Characterized Biotechnology Product (WCBP) Chemistry and Manufacturing Controls (CMC) strategy forum, titled “Analysis and Structure Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies (MAbs),” held in San Francisco to discuss lot release and characterization test issues specific to MAbs (1). The objective of the meeting was twofold: to identify a “core” set of assays most useful for lot-release testing of MAbs and to define a mechanism for selecting appropriate potency tests. Two separate workshops…
Lot Release and Characterization Testing of Live-Virus–Based Vaccines and Gene Therapy Products
The January 2005 CMC Strategy Forum was devoted to a discussion of live virus vaccines and viral vectors used for gene therapy. The purpose of the meeting was to determine whether consensus positions could be reached among the delegates regarding lot release, stability, characterization, and comparability testing. Part 1 of this two-part report on that meeting describes factors influencing the choices of lot-release assays for vaccines and gene-therapy products (1). Part 2 presents potency testing, characterization, and comparability studies, including…
Biophysical Analysis: A Paradigm Shift in the Characterization of Protein-Based Biological Products
Generating a stable environment for a biopharmaceutical drug substance is a critical step for ensuring a long drug-product shelf life (1–6). This process begins early in development with preformulation screening. Some of the most critical parameters to maintaining potency and activity are protein conformation (tertiary or three-dimensional (3-D) structure), folding (secondary structure), and proper subunit association (quaternary structure). Collectively, those are known as higher-order structure (HOS) and can be highly influenced by the formulation environment of a protein drug product.…
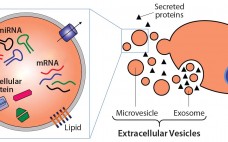
Extracellular Vesicles Commercial Potential As Byproducts of Cell Manufacturing for Research and Therapeutic Use
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as a potential alternative to some stem-cell–derived therapeutics (1, 2). Sometimes called exosomes, they are small, secreted vesicles that can possess similar therapeutic mechanisms to whole cells, possibly representing the active pharmaceutical ingredient. In the past 15 years, academic and industry interest in EVs has exponentially increased as mounting evidence demonstrates their role in physiology and pathology as well as their therapeutic potential. In light of growing efforts in using EVs for research and therapy,…
Hamster Phospholipase B-Like 2 (PLBL2): A Host-Cell Protein Impurity in Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies Derived from Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells
All recombinant protein biotherapeutics must be tested for the presence of residual host-cell protein (HCP) impurities (1–3). The most common analytical method for doing so is a polyclonal sandwich immunoassay. Polyclonal anti-HCP antibodies are selected to recognize the broadest population of HCPs possible. The immunogen and analytical standard are produced from a blank-run fermentation that mimics the production run but lacks the specific biotherapeutic protein. Because of the large number of impurities present in harvested cell-culture fluid (HCCF) that might…
Building a Robust Biological Assay for Potency Measurement
Potency is a critical quality attribute of a biological product and is often determined by a biological assay (also called bioassay or biopotency assay). Specifically, potency is the biological activity or capacity of a product directly linked to its clinical efficacy. Potency tests are performed as part of product release, comparability studies, and stability testing. Nonbiological methods — which measure a product’s molecular or biochemical characteristics (e.g., ligand-binding assay) — have gained interest as replacements for often troublesome bioassays. Even…