Bioprocess manufacturers continue to seek technologies for increasing productivity and shortening timelines from discovery to commercialization. Innovations such as high-throughput systems, automated platforms, and the latest clarification systems all have made processes efficient and robust. And with the increasing adoption of quality by design (QbD) principles, including the use of process analytical technologies (PAT), biomanufacturers are mitigating the risks of errors in their operations better than ever before. A critical part of mitigating risk is gathering meaningful process data and…
Analytical
Rapid Implementation of Novel Affinity Purification: Manufacture of Commercial-Scale Next-Generation Antibody Therapies
The rapid and cost-effective production of conventional monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) for clinical trials and commercial supply has contributed toward their wide adoption. Production processes have become more efficient because common purification processes are being used across structurally similar MAbs during key steps of process development and manufacturing. Such successful platform approaches can remove unwanted impurities and are stable across processing conditions, irrespective of the MAb being purified. In addition, they are readily available at the required volume to support large-scale…
CMC Development Platforms and Outsourcing to Reduce Timelines
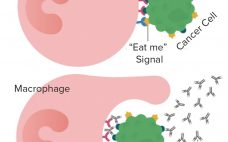
Forty Seven is a company developing novel therapies based on anti-CD47 and other immuno-oncologies. CD47 is called the “don’t eat me” signal that cancer cells give out to escape elimination by the body’s immune system. Qinghai Zhao, vice president of technical development and manufacturing, is one of the scientists working on the company’s magrolimab (5F9) monoclonal antibody that is designed to block the binding of the CD47 signal to the cell receptor SIRP-α while boosting the “eat me” signal that…
Introduction: Reporting from the Frontiers of Cell Line Engineering at BPI Europe and BPI West
Every biomanufacturing process begins with transfection of recombinant genes into pools of cells — followed by a succession of screenings from which will emerge (ideally) a single progenitor cell of the new production cell line. Cast aside will be those cells that do not uptake the correct genetic material, those incapable of thriving in bioprocess conditions, those that fail to produce recombinant protein at relevant levels, and those without demonstrated clonality and relative genetic stability. Over the past several years,…
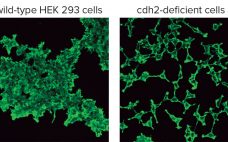
Creating Novel Cell Lines By Genome Editing: Simplifying Cell-Based Assays and Improving Production of Biomolecules
Cultured cell lines have a diverse range of applications. They are used broadly by cell biologists, clinicians, tissue engineers, biotechnology scientists, and bioengineers. The most important uses of cell culture are in the cell-based assays and production of biologically active recombinant proteins. In recent years, genome editing has been used widely to study the structure, function, and localization of endogenous proteins in cultured cells. However, applying the same genome editing techniques to cell lines also could improve the propagation of…
Streamlined Serum-Free Adaptation of CHO-DG44 Cells: Using a Novel Chemically Defined Medium
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have radically transformed the treatment of many chronic diseases, mainly in the fields of oncology and autoimmunity. The overwhelming majority of therapeutic MAbs are manufactured from recombinant Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines. The original CHO cell line was isolated in the 1950s, and since the early 1980s, it has become the workhorse of the biopharmaceutical industry. The CHO-DG44 strain was generated after several rounds of mutagenesis that deleted both copies of dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) genes by…
Control of Protein A Column Loading During Continuous Antibody Production: A Technology Overview of Real-Time Titer Measurement Methods
During production of therapeutic antibodies, harvest titer is measured to monitor product mass loaded onto the protein A capture column. This prevents both column underloading (underusing expensive resin) and overloading (wasting product as flow-through (FT)) while allowing for column yield calculations. Batch production yields a single homogenous harvest pool, thus only one titer measurement (along with volume loaded) is sufficient to determine the mass loaded. During continuous production, however, cell-free harvest (permeate) continuously exits a perfusion reactor and loads a…
Time Is of the Essence: Optimizing Cell Line Development
Cell line development is a critical upstream step for the manufacture of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Cells must be engineered to produce a biologic of interest, and the right clone must be selected to deliver material for preclinical and clinical studies. A high-producing cell line is then needed to support clinical studies and, ultimately, commercialization of the therapeutic. Please fill out the form below to read more. Corresponding authors are Aurore Poles, Global Technical and Compliance Expert, and Guillaume Plane, Global…
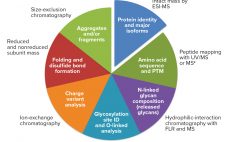
Biosimilarity Assessments: The Totality of Evidence Framework
Biosimilars are evaluated through comparisons with their reference products using abbreviated pathways that have evolved significantly over the past few years. Scientists and regulators now accept that some quality attributes can vary from batch to batch over a product’s lifecycle, even for reference products. Moreover, reference and similar biotechnology products can show differences in noncritical quality attributes but still demonstrate comparable efficacy and safety (1). Here we describe a similarity assessment approach that is also applicable to comparability of lifecycle…
Embedded Particles in Single-Use Bags: Risk to Bag Integrity and Drug Product Purity, or Only a Cosmetic Defect?
When using single-use systems (SUS) to process biopharmaceuticals, preventing drug product contamination from extractables and leachables (E&Ls) and embedded particulate matter (gel particles) in the polymer films used to make bioprocess bags is critical. Using a pressure burst test to assess film integrity, Sartorius Stedim Biotech’s Klaus Wormuth and colleagues compared Flexboy and Flexsafe samples with gel-particle-free materials to assess their potential for contamination. The results showed that only large (2–4 mm2) gel particles affected the burst test results, concluding…