The cell and gene therapy (CGT) segment has grown tremendously over the past decade. And while the industry deals with a steep learning curve inherent to a rapidly developing field, problems must be solved, and solutions must be reduced to practice. One such problem, long understood by the industry but now thrust into the spotlight, is sample handling: proper collection, processing, preservation, storage, and transportation of cellular starting material. Suboptimal techniques for such logistics have been shown not only to…
Manufacturing
Bioprocess Intensification – Fast, Flexible, and Efficient Solutions
Propelled by single-use systems (SUSs), biopharmaceutical companies are approaching the ideal of continuous bioprocessing. In addition to improving process integrity and decreasing production costs, SUSs have enabled exciting ways to configure, operate, and evaluate manufacturing steps. Sensitive process analytical technologies (PATs) and discriminating data analysis platforms are supplementing those developments, helping process engineers and operators to study and modify workflows in unprecedented ways. The goal now is to intensify: to apply increasingly nuanced process knowledge and growing technological capability in…
Single-Use Technologies: Accelerating Bioprocess Design with Key Insights from the Experts
Companies turn more and more to single-use technologies (SUTs) to mitigate production challenges — and with good reason. SUTs clearly decrease conventional costs while increasing process integrity. Yet as the writers in this compilation suggest, SUTs are now making possible new, exciting ways to configure, operate, and evaluate biomanufacturing. In this compilation, BioProcess International gathers key insights from biopharmaceutical industry experts at Sartorius Stedim Biotech to explore how SUTs can realize high-quality yet cost-effective end-to-end bioprocessing. The studies herein identify…
eBook: Automation — The Value of Plug-and-Play Automation in Single-Use Technology
The biopharmaceutical industry’s movement away from large-scale, fixed-tank facilities to flexible facilities featuring single-use technologies (SUTs) has demonstrated the value of modular equipment and agile process design. SUTs have proven to be clear advantages to end users because those technologies enable quick facility build and changeover times. But linking SUT equipment with equally flexible automative technology has been difficult. Herein a group of automation experts from the BioPhorum Operations Group (BPOG) elaborate “plug-and-play” principles and introduce a supervisory control system…
Bioprinting Capabilities and Futures
Bioprinting has advanced rapidly through engineering step changes in the use of three-dimensional (3D) printing. With these developments, living cells can be positioned layer by layer to produce functional tissue structures. Key attributes of this emerging technology are its high scalability and modularity, which enable automated and repeatable manufacture of a wide variety of tissues. These high-throughput biofabrication capabilities equip companies with tools to develop 3D-printed tissues for broad applications, from in vitro drug testing models to therapeutic tissue implants,…
Forward Thinking — Evolving the Cell and Gene Therapy Industry: Modern CAR T-Cell Process Addresses Future Demand
It is an exciting time to be involved in the cell and gene therapy industry. We have come to a tipping point where we have shown that the science works. Now we need to industrialize and standardize it, so we can get these life-saving therapies to more patients. As an industry, we can learn from all the experience in the biologics space. With monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), we have transitioned from a manual process to a more standardized and automated set-up.…
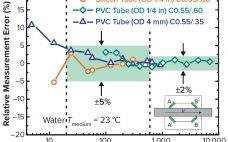
Single-Use Tubing Systems: Confidence Through Validation
Single-use systems (SUSs) are becoming increasingly common in bioprocessing operations because of their low capital requirements and validation costs. As this trend continues to develop, pharmaceutical manufacturers are asking SUS manufacturers to provide assurance that their products comply with current good manufacturing practices (CGMPs) and do not alter drug products by exceeding established operating ranges. Certification of product cleanliness has become common for manufacturers of final packaging components such as vials and stoppers, but rarely are tubing products certified to…
Flow Monitoring in Continuous Processing and Single-Use Systems
Flow sensors placed at critical points in both upstream and downstream processes fulfill the regulatory goals of the process analytical technology (PAT) framework. PAT has been defined as a mechanism for design, analysis, and control of biotechnical and pharmaceutical manufacturing processes through measurement of critical process parameters (CPP). Constant flow monitoring can support its overall targets fundamentally to reduce production cycling time prevent rejection of batches enable real-time release increase automation and control improve energy and material use facilitate continuous…
Technology Highlights from the 2019 BioProcess International Conference
This year’s BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition, held 9–12 September 2019, hosted nearly 200 exhibitors showcasing technical innovations for the biopharmaceutical industry. This year’s conference sessions also included daily technical workshops detailing supplier solutions and technologies. Below are some notable technologies featured that demonstrate the industry’s dedication to finding new ways to help manufacturers shorten time to market. Most systems offer the benefits of single use, integration, process control, economies of scale, automation, and closed-system processing. Upstream Production The exhibit…
eBook: Autologous Cell Therapies: Commercialization Strategies
Autologous cell therapies are derived from a patient’s own stem cells, typically collected from bone marrow. Those cells are then cultured, expanded, and reinfused back into the patient. Unlike allogeneic cell therapies, this process is repeated for each dose and for one patient. The one-to-one process carries several challenges to commercialization, including high development costs, the need to control the risks of manual processing, and compliance with strict timelines. This eBook presents two perspectives on addressing these challenges. The first…