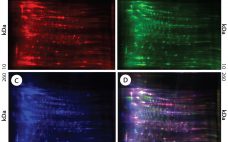
Cell lines derived from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are widely used in therapeutic protein production because they can perform human-compatible posttranslational modifications, they are easy to use for manufacturing, and they do not propagate most human pathogenic viruses (1, 2). Expressed therapeutic proteins are secreted into CHO culture supernatant along with impurities originating from the host cells themselves. Such host cell proteins (HCPs) are important contaminants for monitoring because they directly affect drug quality, safety, and efficacy. HCPs are…
Upstream Processing
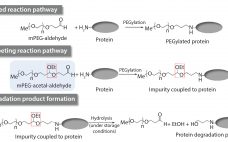
Setting Raw-Material Specifications Using Prediction Models: Determination of a Specification Limit for a Raw-Material Impurity in mPEG-Aldehyde
Impurities related to raw materials used for bioproduction can be inadvertently introduced into a manufacturing process, causing potential failure to meet in-process controls or release specifications. Unexpected impurities also can reduce yield and affect the quality, safety, and effectiveness of a final product (1). Raw-material impurities can originate from starting components or reagents used in manufacture. They can be generated in situ during synthesis or as degradation products. Impurities also can result from improper handling, packaging, and storage. Identification and…
Simplification of Fed-Batch Processes with a Single-Feed Strategy
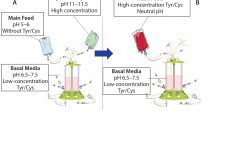
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells commonly are used to produce recombinant proteins such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes. Culture processes typically rely on a fed-batch approach in which a basal medium enables initial cell growth. Concentrated feeds are used to prevent nutrient depletion, thereby extending culture duration and improving cell growth, viability, and protein titer. A neutral pH feed is desirable because culture pH should remain stable after feedings. The extremely low solubility of l-tyrosine…
Design and Performance of Single-Use, Stirred-Tank Bioreactors
Single-use components and systems have been incorporated into many bioprocesses as an alternative to cleanable, reusable systems. A wide range of publications have detailed the reasons for this trend toward a single-use approach. Justification in many cases comes from process-specific benefits such as increased manufacturing flexibility — especially for contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) — enhanced sterility assurance, elimination of cleaning, reduced capital investment, faster processing times with increased productivity, faster start-up, and other benefits (1). One critical factor in the…
Continuous Cell Culture Operation at 2,000-L Scale
In the biopharmaceutical industry, continuous manufacturing is often cited as a method for increasing the productivity of bioprocesses (1). Compared with batch processing, it has the potential to enable production of more product within a smaller facility footprint — while improving product quality, particularly for sensitive and unstable molecules. Investigation into continuous methods is taking place for both upstream and downstream operations. For the full benefit of continuous processing to be realized, an argument has been made that cell culture,…
Providing Lipids Boosts Protein Productivity: Testing a Feed Supplement with Multiple Cell Clones and Media Formulations
As the biologics (and now biosimilar) markets continue to grow, pressure increases on biomanufacturers to reduce cost of goods sold (CoGS). One way they can reduce cost is by increasing protein productivity in terms of protein titer per volume of culture. Media optimization is a key strategy for increasing protein productivity. In the past few decades, average titers across the industry have increased greatly — from <0.5 g/L in the 1980s to >3 g/L today, and it is not uncommon…
Viral Risk Evaluation of Raw Materials Used in Biopharmaceutical Production
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines to patients is a key objective for both health authorities and the pharmaceutical industry. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs). Manufacturers must ensure not only the suitability of RMs for their intended use in a manufacturing process, but also their highest attainable safety with regards to viruses and other adventitious agents. The need to apply a risk-based RM control strategy is in line…
Emerging Technology Trends in Biologics Development: A Contract Development and Manufacturing Perspective
For a contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), process development and manufacturing of recombinant proteins must be linked because of tight timelines driven by client expectations. Those are in turn driven by a need for rapid progression to clinical testing. Early in process development, the choice of raw materials needs to reflect existing supply chain and manufacturing infrastructure, but remain suitable for scaling up to meet future needs. One approach is to establish platform processes for a class of molecules…
Rapid Development of High-Quality, Robust Mammalian Cell Culture Manufacturing Processes
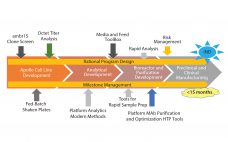
With increasing industry emphasis on providing both rapid and robust processes, companies are reaping the benefits of new tools for risk management and process analytical controls. As a current example of these approaches, Fujifilm Diosynth scientists have accelerated the development process from gene to finish by shortening the timeline, incorporating quality by design (QbD) principles, and designing the process to be as robust as possible. When the Apollo mammalian expression cell line was introduced three years ago, the time from…
Performance Qualification of a Single-Use, Stirred-Tank Bioreactor with CHO-S Cell Culture
The increasing role and importance of cell culture in biophamaceutical manufacturing has led to considerable research and development (R&D) into bioreactor design and performance in recent years. As a result, a greater understanding of bioreactor fluid dynamics and critical physical parameters is now essential to maximize cell growth and productivity. Stirred-tank bioreactors are especially important in this development process because of their favorable properties in areas such as mixing efficiency and homogeneity, energy transfer, and scalability. The design and manufacture…