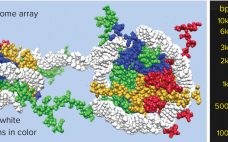
Exosomes are a subject of rapidly growing therapeutic interest in the biopharmaceutical industry for two principal reasons. The first reason is that they are the primary communicators of instructions from source cells to target cells. Exosome surface features define their destination. They recognize complementary features on target cells, dock with them, and deliver their programmed instructions in the form of microRNA. The second reason is that exosomes are immunologically silent. As normal human cell products, and by contrast with gene…
Manufacturing
Building Orthogonality into Biosimilar Testing
Both the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) have developed regulatory guidelines on biosimilars (1, 2). These comprehensive documents provide clear guidance on what the agencies expect from structural characterization studies. Using state-of- the-art instrumentation and techniques is expected, but the use of orthogonal techniques in structural comparability assessments is also required. The application of orthogonal analytical techniques will provide a firm structural foundation to claims of biosimilarity. Characterization methods verifying and supporting conclusions drawn…
A Future-Proof Solution for Bioprocess Applications: The New Eppendorf Flexible Bioreactor Control System Evolves with the Changing Needs of Modern Biotechnology
In the biopharmaceutical industry’s quality-by-design (QbD) era, optimizing tools for process monitoring and control has become a major focus of development and manufacturing. This increased attention brings challenges into upstream and production processes, cell-line development, process optimization, and scale-up. Suppliers of equipment and technologies also focus on helping their customers improve development timelines. With that increased attention to speed, they are offering tools such as the Eppendorf SciVario twin bioreactor control system to streamline development and maximize flexibility. BPI spoke…
Scalable Manufacturing of Lentiviral Gene Therapies
Lysosomal storage diseases are caused by mutated genes that express defective lysosomal proteins, such as essential enzymes. For example, cystinosis is a metabolic disease caused by a defective gene that encodes cystinosin, an exporter protein (Figure 1). Avrobio develops gene therapies to treat lysosomal storage diseases. On 8 October 2019, the company announced that its first patient had been dosed in the AVR-RD-04 investigational gene therapy program, which involves genetic modification of the patient’s own hematopoietic stem cells to treat cystinosis.…
Using Blockchain Technology to Ensure Data Integrity: Applying Hyperledger Fabric to Biomanufacturing
Digitalization of manufacturing operations is a major challenge that many industries face. With the advent of smart equipment, automation of unit operations and complete processes, and digitalization of batch documentation, more data are generated now than ever before. The information must remain manageable, and data integrity needs to be ensured. The challenge for biomanufacturers will be to ensure that their entire large output of data will be attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate (ALCOA) as defined by the US Food…
Ask the Expert: Accelerating Development and Manufacturing Platforms for Viral Vectors
Bai-wei Gu, Juan Lagos, and Matthew Weaver (heads of cell line development, upstream process development, and downstream process development groups, respectively, at WuXi Advanced Therapies, ATU) joined forces on 29 October 2019 to feature their company’s viral-vector manufacturing capabilities for cell and gene therapies. In addition to adherent platforms for lentivirus (LV) and adenoassociated virus (AAV) vectors, ATU soon will offer suspension-cultured viral vector platforms for them as well as analytical measures that support release testing. Transitioning from adherent to…
Better Bioprinting Ahead: Breakthroughs and Remaining Challenges
Bioprinted organs soon could revolutionize clinical trials, transplantation, and regenerative medicine. But as Chris Lo reminds us in a new GlobalData report (1), several technical hurdles must be negotiated before biopharmaceutical companies can harness three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting for such purposes. BPI explores persistent printing problems and promising solutions below by analyzing Lo’s report alongside commentary from founding editorial advisory board member Bill Whitford (bioprocess strategic solutions leader at GE Healthcare Life Sciences), Lev Gerlovin (vice president in the life sciences…
Improving Bioprocess Expression Systems: A Clean Alternative to CRISPR/Cas9
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells have emerged as a robust platform for bioprocessing serving both early and late-stage biotherapeutic drug supply. However, these cells and other hosts (e.g., HEK293), can be optimized for even greater potential through advanced gene editing. For example, when the endogenous glutamine synthetase (GS) gene is knocked out in CHO cells, a sixfold increase in high-producing cell lines is achieved (1). In another study, CHO with annexin A2 (ANXA2) and cathepsin gene (CTSD) knockouts were introduced…
eBook: Peptide Therapies — Small Biomolecules Address Big Health Problems
This crash course in the development of peptide therapies brings together two articles: one on product research and the other on manufacturing and regulatory concerns. In “Fighting Alzheimer’s Disease from Within: A Breakthrough Peptide,” freelance journalist Marc Davis highlights current developments in Alzheimer’s disease treatment, focusing specifically on a peptide approach from Canadian company NervGen. In “Making Peptides Work,” BPI’s senior technical editor adds perspective on developing and manufacturing peptide therapies from the Informa Connect community, with commentary from experts…
eBook: Continuous Bioprocessing — Promises and Challenges
Biotechnological productions are commonly executed as batch processes, especially during downstream processing. Higher titers in fermentations, reductions in operating scale, and the quest for improving product quality all have led to an intensified effort for developing continuous processing. It is forecasted that within the next 10 years, about 50% of all drugs under development will be biopharmaceuticals, making it worthwhile to develop more efficient processes. In this BPI eBook, Babu Halan (project engineer) and Wolfgang Minas (global lead of the…