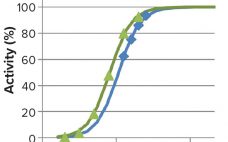
The recombinant fusion protein SHP631 consists of a chimeric monoclonal antibody binding to human insulin receptor and iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S). This product is being developed as an enzyme replacement therapy to treat cognitive symptoms of Hunter’s syndrome. Because the current therapy (idursulfase, brand name Elaprase from Shire) cannot cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), SHP631 is being developed to do so, enabling the presence of I2S in the brain. The enzymatic activity of this molecule is measured using the substrate 4-methyl umbelliferyl-α-L-idopyranosiduronic…
Formulation
Rational Selection of Sugars for Biotherapeutic Stabilization: A Practitioner’s Perspective
Biotherapeutics from recombinant DNA technology include diverse modalities such as peptides; enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins; nucleic acids; and cellular therapies. Such products present physical, chemical, and biophysical challenges. Excipients used in stabilization of these biotherapeutics can be broadly classified into the following classes (subgroups) that have been reviewed carefully elsewhere (1–4) : Buffers (e.g., phosphate, acetate, and histidine) Tonicity agents/stabilizers (sugars such as sucrose, polyols such as sorbitol) Bulking agents (lyoprotectants such as mannitol) Surfactants (e.g., polysorbates) Antioxidants (e.g.,…
Development of a Freeze-Dried Ebola-Expressing Adenoviral Vector: Unexpected Findings and Problems Solved
In December 2013, a two-year-old child in Guinea became the first person to be killed by Ebola in the most recent outbreak. In March of the following year, that outbreak was declared in West Africa. By mid-2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) had declared it to be a public health emergency of international concern and urged pharmaceutical companies to accelerate their development of candidate vaccines. At the peak of the outbreak in 2014, more than 1,200 new cases of Ebola…
Rational Design of Liquid Protein Formulations: Application of Biophysical Stability Predictors and Descriptors to Reformulate Biotherapeutics
Successful development of liquid biopharmaceutical formulations requires careful assessment of the biophysical properties of the protein in solution, primarily focused on achieving optimal conformational and colloidal stability of the drug-substance molecule (1–11). It also involves extensive stability studies under stressed conditions. Using state-of-the-art biophysical tools for characterization of developed products, those studies are based on key biophysical descriptors and extended particulate characterization methods (subvisible particles in micro- and nano-size range) to deliver a stable product for market with a shelf…
eBook: Alternative Delivery of Biologics — Underdogs Pursue Roads Less Traveled
A number of failures in development of noninjectable delivery methods for therapeutic proteins have caused numerous development programs to crash and burn along with investors’ hopes, dreams, and cash. Most everyone reading BioProcess International is familiar with the issues and challenges: Needles hurt and involve risks to both caregivers and patients. Injections often require administration by trained personnel in specialized settings. But alternative delivery methods are fraught with greater challenges related to dosing, bioavailability (particularly for oral dosing), and inherent…
Conference Report: The Drug Product Track at 2017’s BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition in Boston, MA
At the Hynes Convention Center in Boston, MA, during Knect365’s “Biotech Week Boston” in late September of 2017, one track of the BioProcess International Conference focused on drug products, fill–finish, and formulations. Presenters represented a number of major biopharmaceutical companies — AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Genentech (Roche), GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, Lonza, Pfizer, and Sanofi — as well as suppliers Bosch, Merck (MilliporeSigma), ReForm, and Single-Use Support. They focused on predictive modeling, quality by design (QbD) and process analytics,…
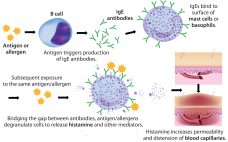
Polysorbates, Biotherapeutics, and Anaphylaxis: A Review
Rapidly increasing use of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in the treatment of neoplastic, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases has led to a dramatic increase in hypersensitivity reactions worldwide, complicating the use of MAbs as first-line therapies and limiting patient survival and quality of life (1). The origins of anaphylaxis are not well understood, though its mechanism is fairly straightforward (Figure 1). It is usually attributed to some undefined intrinsic property or properties of a biotherapeutic — despite the fact that biotherapeutic formulations…
Validation of Controlled Freezing and Thawing: A 9-L Bottle Study
Freeze–thaw processes affect the quality of biopharmaceutical proteins (1–13) and human cells (14). It has been reported that no method consistently controls freezing and thawing rates for biological formulations (1). My recent study refutes that claim with validated rate-controlled freezing and thawing of such formulations in 16-L single-use bags (15). The study reported herein presents a consistent method for controlled-rate freezing and thawing of bottled formulations. It also highlights the effect of load and container position on freeze rates. The…
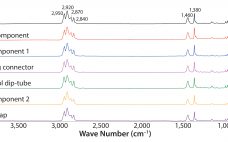
Investigation of Foreign-Particle Contamination: Practical Application of FT-IR, Raman, and SEM-EDS Technologies
The presence of visible foreign particulate matter is considered a critical defect in parenteral products and one of the main reasons they can be recalled (1). Foreign particles present during any stage of manufacturing are considered to be contaminants and can impose a risk to the control of the manufacturing processes (2). For those reasons, particle contamination arising in any manufacturing step initiates a nonconformance or out-of-specification observation. That requires an investigation to identify root cause so as to mitigate…
Osmolality Measurements for High-Concentration Protein–Polymer Solutions: Variation Based on Working Principles of Osmometers
Osmolality is a critical attribute for injectable formulations. It is desirable to have products match physiological osmotic conditions. Furthermore, osmolality provides confirmation of soluble content in solution. Preventing injection of hypo- or hyperosmotic solutions is a key element of parenteral formulation development. Additionally, some investigators have explored correlations between injection pain and formulation osmolality, although no significant correlation has yet been observed (1–4). Osmolality is a valuable in-process test also because it provides a reliable and repeatable value that reflects…