No longer is the biopharmaceutical industry questioning whether it should use single-use technology. The focus has transitioned to how to best implement single-use systems. Rapid adoption of single-use systems has brought added complexity; which is leading to an increasing application of lean manufacturing principles. Standardization projects and establishing appropriate standards are current trends that drive toward reducing the complexity of bioprocessing systems, from design and validation to supply chain and manufacturing integration. Although efforts are underway to develop consensus standards…
Downstream Processing
pDADMAC Flocculant Reagent for Use with Clarisolve® Depth Filters
Advances in cell line engineering and media design have allowed for improvements in monoclonal antibody expression, with cell culture systems exhibiting product titers >10 g/L. These high-density cell cultures pose a great challenge in the use of existing solid liquid separation techniques because of the need to remove larger amounts of biomass and the increase in submicron particles. In addition, the increased level of soluble impurities introduces new bottlenecks for chromatographic processing because of the increased levels of contaminants from…
High-Capacity Protein A Chromatography Medium for MAb Capture from High-Titer Feeds
As product titers continue to increase in upstream cell culture processes, so too the demand for enhanced capacity in downstream purification steps. MabSelect SuRe LX chromatography medium (resin) is specially developed for monoclonal antibody (MAb) capture from high-titer feeds. To help ensure good process economy, the medium can withstand hundreds of rigorous cleaning cycles with NaOH, with retained dynamic binding capacity (DBC) and MAb yield. High Dynamic Binding Capacity (DBC) Large-scale purification of MAbs usually consists of two or three…
Removal of Antibody Aggregates Using Cellufine MAX GS
Purification of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) requires advanced and selective means for separating aggregates from target monomers. Cellufine MAX GS chromatography media are optimized for higher capacity, better separation, and greater selectivity to improve downstream purification of MAbs. JNC Corporation’s new strong cation exchanger, Cellufine MAX GS, has optimized ligand density for improved dynamic binding capacity and selectivity and superior pressure flow characteristics, which are required by MAb purification platforms. MAb Monomer/Aggregates Separation: Cellufine MAX GS exhibits exceptional selectivity between…
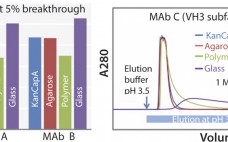
Purification of Monoclonal Antibodies Using Kaneka KanCapA
Industrial-scale production of pure monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) customers require an overall highly efficient affinity resin with a high binding capacity, high alkaline stability, good elution profile, low nonspecific binding, and large-scale column operation. Kaneka has developed a novel protein A ligand and immobilized it to highly cross-linked cellulose beads to totally satisfy all these requirements. Here, we demonstrate the performances of the Kaneka KanCapA using MAbs. Mild pH Elution and High-Binding Capacity: The elution profile of a protein A column…
LEWA EcoPrime®: The Next Plateau in Control, Accuracy, and Reproducibility in Preparative Chromatography Systems
The LEWA EcoPrime® LPLC chromatography platform combines proprietary fluid design and the LEWA Intellidrive® technology to deliver unrivaled batch-to-batch reproducibility and accuracy. The LEWA EcoPrime® features our open architecture automation software and is built on a quality control of the industry’s most vertical supply chain. A single LEWA system has the range of up to three conventional LPLC units while providing a higher level of accuracy. This gives the user great flexibility, more floor space, and plant-friendly integration with simple…
High-Capacity, Single-Use, Strong Anion-Exchange (Q) Chromatography Tools: Speed and Process Flexibility for MAb Purification
Strong anion-exchange (Q) chromatography is an industry standard for polishing purification steps of monoclonal antibody (MAb) production. It is a proven technology that removes DNA, viruses, endotoxins, and acidic host-cell proteins (HCPs) from process feed streams in flow-through mode. Advancements in cell culture technology, the emergence of cost-sensitive biosimilars, and the limitations of conventional purification technologies have led to an industry-wide interest in downstream single-use technologies and more flexible biomanufacturing options. Despite their high binding capacity, traditional resin-based chromatography columns…
TOYOPEARL® NH2-750F: Aggregate Removal from Monoclonal Antibodies
Given the current drive to reduce the cost of manufacturing for biological therapeutics, it is incumbent upon chromatographers and process engineers to streamline the manufacturing process wherever possible. As a result of this need, the demands on downstream unit operations have increased to the point where a single processing step is expected to accomplish a multitude of purification objectives. Introduction Anion exchange chromatography is a widely used technique for protein capture or impurity removal. Typically, anion exchange resins with quaternary…
Purification of Influenza Virus By Ion-Exchange Chromatography on Mustang® QXT Membranes
Membrane chromatography is an effective alternative to conventional beaded sorbents for the purification of large virus molecules or viral-like particles. Membranes have an open pore structure that allows fast kinetics and direct access to ion-exchange binding sites, with flow rates that are orders of magnitude faster than conventional columns. They provide much higher binding capacities than beaded sorbents for large molecules limited by mass transfer. Pall Mustang ion-exchange membranes are scalable membrane chromatography devices used in various therapeutic, vaccine, and…
Successful Filtration Scale-Up for an Automated, Single-Use, Final Bulk-Fill System
This application note describes a case study of the correct sizing for a filter involved in an automated final bulk-fill system for a biopharmaceutical product. It demonstrates how customer batch-processing requirements can be attained with a robust experimental design. Scale-Up Methodology Figure 1 shows a process for successful scale-up. Once the desired process has been defined, filter performance can be determined by either constant flow or constant pressure testing on disc formats. The data can be scaled-up easily to determine…