Cells grown as three-dimensional (3D) spheroids are thought to more closely mimic in vivo physiology in terms of morphology, structural complexity, and phenotype. Being more physiologically relevant, 3D cultures can be highly predictive for compound profiling and evaluating cytotoxicity, a critical step in evaluating chemotherapeutic drug candidates. Unfortunately, evaluation of drug cytotoxicity traditionally has relied on the use of two-dimensional (2D) cell culture monolayers. When grown in monolayers, cells are not exposed to soluble gradients, are forced into an apical-basal…
Analytical
Certain Approaches to Understanding Sources of Bioassay Variability
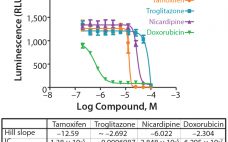
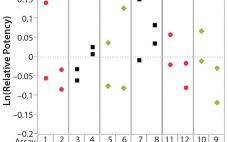
During lifecycle development of a biological assay (bioassay), identifying and reducing sources of variability might be required to improve method performance. Here I recommend some statistical and graphical approaches (consistent with USP <1033>) for practitioners to identify variation from experimental results (1). Sources of Variation in a Bioassay To correctly identify sources of variation in a bioassay, analysts must consider how that bioassay is to be executed. In particular, the experience and technical expertise of each analyst expected to execute…
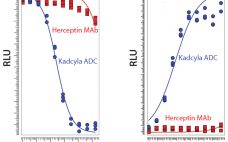
Biological Stealth Bombers: Potency, Regulatory, and Bioprocessing Concerns of Antibody–Drug Conjugates
Seven years ago, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first product in a new class of biologics: antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs). The idea for these products already had been hatched a decade earlier when the promising field of antibody research — touting such molecules as “magic bullets” — had faltered, specifically against oncology-related indications. The early crop of anticancer monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) proved to have only limited efficacy, and interest in developing antibodies as therapeutic agents against cancer…
Process Analytics and Intermediate Purification of Bispecific Antibodies with a Non-Affinity Platform
The therapeutic benefits of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have been demonstrated in recent decades with uncontestable success as treatments for human disease. Despite MAbs’ key features such as specificity, selectivity, and safety, the format has limitations (1, 2). Bispecific antibodies may overcome number of difficulties (3). Multiple formats of bispecific antibodies have been developed, although only the κλ-body is fully human and devoid of linkers or mutations. It requires no genetic modifications of heavy and light chains and results in bispecific antibodies…
Computational Science Changes Biolaboratory Design
Until relatively recently, life-science research was characterized by test tubes, Petri dishes, and centrifuges. Now, as with many industries, the life sciences are undergoing a digital transformation. Computational science is changing laboratory design. The healthcare industries always have generated large amounts of data. What has changed is the available information technology. With the growth of cloud computing, large data sets — and the high-speed tools for analyzing them — are available increasingly to a degree not possible with traditional servers…
Single-Use Sensors and Control and Data Acquisition Tools to Streamline Bioprocess Development
Process development and biomanufacturing in the biopharmaceutical industry have evolved extensively over the past 10 years. More tools are available to study process variables to enable more efficient and productive processes, speed development, and reduce costs. High powered microcontrollers are embedded in laboratory devices to carry out complex tasks. Recently, users have started working with microcontrollers such as Raspberry Pi for personal projects. As personal computer power has accelerated multiplefold,leading to high processing power and compact, high-capacity memory readily available…
Cell Culture Media: An Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient or Ancillary Material?
Cell-based therapies are used to treat diseases that require the replacement of diseased, dysfunctional, and injured cells (1). To produce these therapies, a wide range of reagents and materials such as antibodies, growth factors, and enzymes are used in their manufacturing processes. Such necessary materials are administered through a cell culture medium. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are the main ingredients that make products therapeutic. Ancillary materials (AMs) and raw materials (RMs) are essential components used during production but are not…
Trends in Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls: Next-Generation Technologies and Product Modalities
New technologies bring new regulatory challenges. The biopharmaceutical industry must be cautious in its implementation of new scientific ideas and technology platforms — no matter how promising those might be. Regulators will look skeptically on any claim that isn’t backed up by good data, and with no solid history of successful use to build on, a company must have all the answers itself. How do compliance professionals anticipate what kinds of questions reviewers will ask when the time comes —…
Science Guiding Technology: Cell Line Development and Engineering 2018
Cell line development engineers in the biopharmaceutical industry juggle several, sometimes contradictory priorities. They must present their bioprocessing colleagues with a master cell line that can express a reproducibly high-quality protein product at titers and growth concentrations that will be high enough for manufacturing efficiency — and without those parameters degrading over time. Performing the first step in every bioprocess, these scientists must consider their own budgetary concerns and efficiencies while facing regulatory scrutiny under the 21st-century risk-management paradigm. In…
Myths, Risks, and Best Practices: Production Cell Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cell Cultivation
Health authorities are requesting substantial details from sponsors regarding practices used to generate production cell lines for recombinant DNA–(rDNA) derived biopharmaceuticals. Authorities also are asking for information about the clonality of master cell banks (MCBs) and control strategies to minimize genetic heterogeneity. Such requests are prompted by recent reports indicating “nonclonality” for certain production cell lines. To address these and related issues, the CASSS CMC Strategy Forum on “Production Cell Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cell Cultivation:…