Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics have been studied over recent decades, and their promise as a new drug modality is now being realized. The growing interest in oligonucleotides is driven by their high potential for treating different medical conditions, the growing number of oligonucleotide drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an increased focus on personalized medicines, the development of therapies for rare diseases, and the wide adoption of nucleotide-based COVID-19 vaccines. Oligonucleotides are short, linear sequences of DNA or…
Author Archives: Romain Dabre
New Antibody Formats on the Block:
More Complex Modalities Demand Innovation in Manufacturing and Purification
Some of the latest, most promising therapeutic developments in the biologics industry use antibody fragments — either separate functional subunits of antibodies or recombinant molecules that are composed of immunoglobulin domains. The most popular fragments are antigen-binding fragments (Fabs), variable single-chain fragments (scFvs), diabodies, and nanobodies. Such molecules raise several advantages over their parent molecules for upstream production but pose several challenges for downstream purification. To facilitate antibody-fragment capture, Tosoh Bioscience has developed Toyopearl AF-rProtein L-650F resin. Its ligand uses…
How to Improve the Capturing of Antibody Fragments
Some of the latest promising biopharmaceutical drug substances are antibody fragments. Antibody fragments are either separate functional subunits of antibodies or recombinant molecules, which, just like antibodies, are composed of immunoglobulin domains. These drugs offer several therapeutic advantages over conventional monoclonal antibodies. Upstream processing for antibody fragments is easier than it is for standard antibodies. Recombinant-based antibody fragments can be modified to meet specific needs of affinity, avidity, valence, and action mode. They also can be produced in prokaryotic cells…
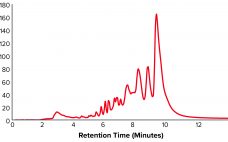
Simple and Effective Method for Purification of DMT-On Oligonucleotides Using HIC Resins
Within the biopharmaceutical industry, oligonucleotide drug pipelines have increased significantly because of the effectiveness of such drug products in treating devastating diseases. Downstream specialists need improved purification techniques for such highly valuable materials. Dimethoxytrityl (DMT) is used to synthesize oligonucleotides and temporarily mask the characteristic chemistry of the 5Í´-hydroxy functional group. DMT can be left on an oligonucleotide following synthesis to provide stability to a molecule during subsequent processing. Herein, we describe a novel, effective, and high-recovery method for purifying…
Reduce Downstream Processing Costs for Monoclonal Antibodies: Switch to Tosoh’s Two-Step Platform
In this study, we showcase the benefits of Tosoh’s two-step process for the purification of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in comparison with the standard industrial process. Combining high-performance protein A capturing and a single polishing step on a salt-tolerant anion-exchange resin, we could reduce the downstream costs by 45% and increase production output by 58%. TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A HC-650F is a high-capacity protein A resin for the purification of MAbs. This resin exhibits dynamic binding capacities (DBC) of 70 g/L at…
Reduce Downstream Processing Costs for MAbs By Switching to a Two-Step Platform
Downstream processing operations make up to 80% of the total costs for processing biotherapeutics. Given the current drive to reduce downstream costs, chromatographers and process engineers will need to streamline processes. Herein, we describe the benefits offered by using Tosoh’s two-step process for purifying monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and compare that method with the standard industrial process. By combining high-performance protein A capture and a single polishing step on salt-tolerant anion-exchange resin, Tosoh’s approach can reduce downstream costs by 45% and…
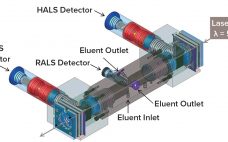
Tosoh LenS3™ MALS Detector: A New Paradigm in Light-Scattering Technology
The multi-angle light scattering (MALS) technique has become the standard for determining molecular weight (MW) and size (radius of gyration, Rg) of proteins, biopolymers, synthetic polymers, and polysaccharides. By combining an extreme low angle (low-angle light scattering (LALS) – 10°) and an extreme high angle (high-angle light scattering (HALS) – 170°) with a right angle (right-angle light scattering (RALS) – 90°) to form a three-angle MALS detector, the new LenS3 detector can determine directly absolute molecular weight and Rg without…
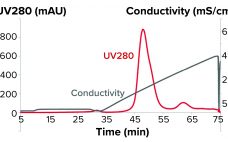
Process Analytics and Intermediate Purification of Bispecific Antibodies with a Non-Affinity Platform
The therapeutic benefits of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have been demonstrated in recent decades with uncontestable success as treatments for human disease. Despite MAbs’ key features such as specificity, selectivity, and safety, the format has limitations (1, 2). Bispecific antibodies may overcome number of difficulties (3). Multiple formats of bispecific antibodies have been developed, although only the κλ-body is fully human and devoid of linkers or mutations. It requires no genetic modifications of heavy and light chains and results in bispecific antibodies…
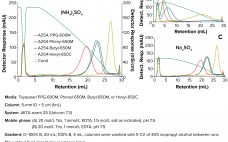
Antibody–Drug Conjugate Surrogate Purification: TOYOPEARL® PPG-600M HIC Resin for DAR-Separation
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) are promising biopharmaceuticals. They combine the high selectivity and affinity to cancer cells with the toxicity of chemotherapeutics in one molecule. ADCs consist of a monoclonal antibody covalently bound by a linker to a highly potent cytotoxic drug. ADC-surrogates contain a nontoxic payload with similar structure and physiochemical properties as the toxic payload of an ADC. Therefore, they can be used as models to develop suitable purification processes or analytical methods. The ADC-surrogate in this work consists…