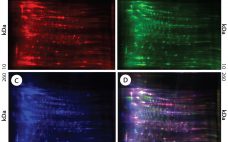
Cell lines derived from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are widely used in therapeutic protein production because they can perform human-compatible posttranslational modifications, they are easy to use for manufacturing, and they do not propagate most human pathogenic viruses (1, 2). Expressed therapeutic proteins are secreted into CHO culture supernatant along with impurities originating from the host cells themselves. Such host cell proteins (HCPs) are important contaminants for monitoring because they directly affect drug quality, safety, and efficacy. HCPs are…
Downstream Validation
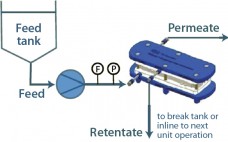
Using Technology to Overcome Bioprocessing Complexity: Advanced Concentration and Analytical Technologies Accelerate Development and Manufacture of mAbs, Vaccines, and Biosimilars
Unlike chemically synthesized drugs, whose structure is known and reproducible, biological drugs are derived from living cells and are sensitive, complex mixtures requiring cutting-edge biological technologies for their production. The growing importance of biosimilars in recent years is reflected in a corresponding rise in market value. The value of the global biologic therapeutic drug market reached approximately US$230 billion in 2014 and, according to BCC Research, will increase to nearly $390 billion by the end of 2019. This corresponds to…
Clearance of Persistent Small-Molecule Impurities: Alternative Strategies
Small-molecule impurities that bind to and copurify with protein biopharmaceuticals traditionally have been removed using bind-and-elute (BE) chromatography. However, that approach may be undesirable for a number of reasons. For instance, it may present a facility-fit challenge or provide a lower process yield than what is acceptable. A common scenario in which BE chromatography may be undesirable is in removal of unreacted conjugation reagents. Bioconjugates represent an important and growing class of pharmaceuticals that include PEGylated proteins, vaccines, and antibody–drug…
Best Practices for Critical Sterile Filter Operation: A Case Study
A number of regulatory guidelines recommend preuse integrity testing of critical sterilizing liquid filters for aseptic processing (1–3). Before sterilization, a preuse test will confirm that a filter is installed properly and was not damaged during shipment or handling. Performing a preuse test after sterilization detects damage that may have occurred during the sterilization cycle. Testing after sterilization limits risk, so it is a practice applied based on risk assessment. Because it is perceived to reduce business loss risk, preuse…
CMC Strategy Forum Special Focus Series: Part 2 Product-Related Impurities, An Overview
Introduction by Cheryl Scott The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website. This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment…
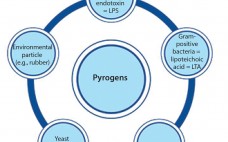
Detecting the Broad Spectrum of Pyrogens with the Human Whole-Blood Monocyte Activation Test
In the early 20th century, some patients injected with the drug Salvarsan experienced febrile reactions due to contamination of the drug’s distilled water. That incident (involving the first effective treatment for syphilis) prompted not only the widespread use of injectable drugs, but also the need for pyrogen control. Pyrogens constitute a heterogeneous group of microbial and nonmicrobial substances that include those derived from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA), respectively, as well as particles…
Defining Your Product Profile and Maintaining Control Over It | A Look Back with Emily Shacter
This is a transcript from a Q&A interview with Emily Shacter, PhD, Consultant, ThinkFDA LLC (former FDA Scientist and Regulator). We will be talking today about the CMC Forum that was published back in 2005. We are revisiting it in the magazine to specifically update our understanding of how to maintain process control; understanding your process. In general, how do you feel the discussions in the four-part paper from 2005 has held up after 10 years? Emily: I think they…
Identification and Quantification of Heat-Shock Protein 70: A Major Host-Cell Protein Contaminant from HEK Host Cells
Recombinant therapeutic proteins are commonly produced by cell lines such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO), human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293, murine myeloma (NS0), and Escherichia coli bacterial cells. Host-cell proteins (HCPs) are indigenous proteins produced by those expression hosts and considered to be process-related impurities generated from the cell culture process (1). HCPs are potentially harmful and immunogenic to patients, and they can compromise the stability of protein drugs (2–4). For those reasons, HCPs must be consistently removed or reduced…
Evaluation of a Variable-Pathlength Spectrophotometer: A Comparable Instrument for Determining Protein Concentration
Protein concentrations in bioprocessing are determined by multiplying the measured absorbance of UV light as it passes through a sample by the protein extinction coefficient. Conventional spectrophotometer measurements are based on a fixed pathlength depending on the cuvette used to hold the sample (typically 10 mm). Only a small portion of the UV curve is linear at that pathlength. As a result, conventional spectrophotometers have a limited linear range and are unable to measure a large range of protein concentrations…
Fundamental Strategies for Viral Clearance Part 2: Technical Approaches
Viral safety is required for biologics manufactured to treat human diseases. Although significant improvements in ensuring viral safety have been made over the past few decades, “zero risk” of viral contamination is a myth. Viral contamination risk can be carefully managed by screening raw materials, testing process intermediates, and evaluating how effectively manufacturing processes remove and inactivate viruses. Viral clearance studies verify virus removal or inactivation by a manufacturing process. Although regulatory agencies have expectations for the designs of those…