Amid the continuing frustrations of this time, we are beginning to see what conducting business in a post-COVID-crisis world will be like. A new survey conducted by our Informa Connect Life Sciences group compares responses with those from similar questions in April 2020 — knowing more than we did before about the impact of COVID-19 around the world. The data reveal insights into how the global life-science community has responded to the crisis, the impact the pandemic has had on…
September 2021
Preparing for a Virtual Audit
Audits are a vital quality-management tool of the biopharmaceutical industry. Whether the objective is to verify supplier or partner qualifications, contribute to corrective and preventative actions (CAPA), or fulfill regulatory compliance requirements, conducting proactive auditing is key to successful operations. Over the past year, virtual audits —also known as remote or distance audits — have enabled biopharmaceutical companies to meet compliance and quality assurance demands despite COVID-19–related travel restrictions and social-distancing protocols. Notwithstanding the challenges of virtual audits, the benefits…
No More Sleepwalking: New Mindsets for Manufacturing Cell and Gene Therapies at Commercial Scale
Cell and gene therapies (CGTs) offer potential cures to some of the most challenging illnesses of our time. The number of such therapies approved for market is set to surge in the next 10 years (1). Yet current manufacturing approaches are not fit for purpose. Biomanufacturing must adapt to prevent the industry from unintentionally sleepwalking into causing harm to patients. Some urgently needed changes could come with learning about the mindset of the medical-devices industry. Background and Current State After…
Microbiome-Based Therapeutics: Negotiating Key Development Challenges
Microbiome-based therapeutics have evolved significantly in recent years, with several promising candidates advancing through the clinical pipeline. That progress is the result of growing evidence showing that targeting and manipulating the microbiome could improve human health and treat more than 25 conditions by restoring healthy bacterial populations (1). The human microbiome comprises a diverse community of microorganisms, helpful and harmful. It differs by person based on factors such as genetics, environmental influences, diet, and immune function. Microorganisms play a role…
Integrity of Single-Use Systems: Practical Applications and Deployment
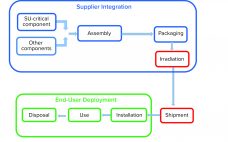
Single-use (SU) technology plays an important role in modern vaccine and biologics manufacturing. System integrity, managed by critical process controls, ensures sterility and is a prerequisite for successful leak-free processing. Nonintegral systems cause loss of product, quality, and time; increase costs through investigations; and lead to potential safety problems. The BioProcess Systems Alliance (BPSA) issued a white paper in 2017, Design, Control, and Monitoring of Single-Use Systems for Integrity Assurance (1), that describes in detail the strategies for design and…
Spontaneous Infection: Did You Leave the Back Door Open to Your Cultivation Suite?
Manufacture of biopharmaceuticals using mammalian cells inherently incurs a risk of viral contamination during cell cultivation. If introduced, viruses can infect and replicate in cells used to produce a therapeutic protein or vaccine. The consequences of such contaminations can be dramatic. Not only can a company lose contaminated batches, but it also faces potentially extensive root-cause investigations, facility cleanup efforts, and introduction of preventive measures. Until contamination issues are resolved adequately, production should not be resumed, and facility downtime brings…
Advanced Data-Driven Modeling for Biopharmaceutical Purification Processes
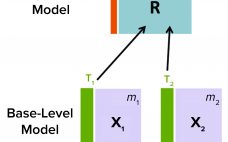
Purification is an essential process in biopharmaceutical manufacturing that separates a therapeutic protein in its active form from impurities. A typical purification process consists of several chromatography unit operations, and each unit operation comprises multiple phases. During the operation of each step, continuous (time-series data per parameter for each batch) and batch data (one data point per parameter for each batch) are generated by in-line sensors installed in chromatography skids on the production floor and with at-line/off-line in-process samples, respectively.…
Simplifying the Bioprocessing 4.0 Journey
Bioprocessing 4.0, the biopharmaceutical version of Industry 4.0, is on course to become a reality in the next decade (1). This is because its “cyber-physical systems” that comprise cloud computing, connected systems, and digital process control offer many benefits. They include better process monitoring and management of a biologic’s critical quality attributes (CQAs) and the chance to control intensified processes for faster, less-expensive production of protein-based biologics and vaccines. Automation also can reduce the number of skilled operators needed while…
Development of a Universal Preparative Anion-Exchange Method to Purify Oligonucleotides
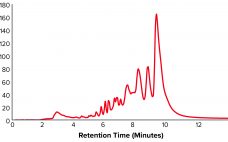
Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics have been studied over recent decades, and their promise as a new drug modality is now being realized. The growing interest in oligonucleotides is driven by their high potential for treating different medical conditions, the growing number of oligonucleotide drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an increased focus on personalized medicines, the development of therapies for rare diseases, and the wide adoption of nucleotide-based COVID-19 vaccines. Oligonucleotides are short, linear sequences of DNA or…
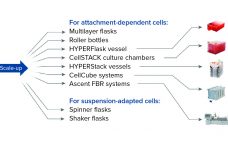
Strategizing Scale-Up and Scale-Out for Cell Therapy Production
When considering strategies for expanding the number of cells being grown to support cell therapy development, companies often focus on decisions regarding scale-up and scale-out: increasing capacity either by using larger vessels to increase production volume or by implementing more units of the same vessel, respectively. Complete workflows often involve both. Figure 1 shows an example of scaling out from one to multiple cell culture flasks of the same dimension before transitioning to a larger format. Scale-out can be straightforward…