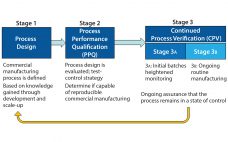
As defined in the ICH Q10 guideline, a control strategy is “a planned set of controls, derived from current product and process understanding, that assures process performance and product quality” (1). Every biopharmaceutical manufacturing process has an associated control strategy. FDA’s 2011 guidance for process validation (2) describes process validation activities in three stages (Figure 1). A primary goal of stage 1 is to establish a strategy for process control that ensures a commercial process consistently produces acceptable quality products.…
Thursday, January 19, 2017 Daily Archives
Response to the Publication of USP ‹1207›
The BioPhorum Operation Group’s (BPOG’s) Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT) workstream would like to congratulate the United States Pharmacopeia’s committee for its latest revision to USP chapter <1207> Package Integrity Evaluation: Sterile Products. Generally, we believe it provides a comprehensive overview of the available methods for container–closure testing and outlines many important elements for consideration in establishing a successful CCIT strategy. We first responded to the USP <1207> draft when it was released for comment in 2014. And from our…
Impact of Post-Grant Proceedings on Biologics and Biosimilars
Biologics, primarily therapeutic antibodies and recombinant proteins, represent a growing share of the current drug market, with projected worldwide sales of about US$278 billion by 2020, partly because of their relatively high costs. Indeed, AbbVie’s therapeutic antibody Humira (adalimumab) is currently the top-selling drug in the world by sales but not even in the top 50 by the number of monthly prescriptions. Although the process for marketing generic versions of small molecules under the Hatch–Waxman Act is well understood, the…
HCP Antigens and Antibodies from Different CHO Cell Lines
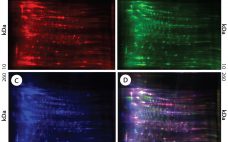
Cell lines derived from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are widely used in therapeutic protein production because they can perform human-compatible posttranslational modifications, they are easy to use for manufacturing, and they do not propagate most human pathogenic viruses (1, 2). Expressed therapeutic proteins are secreted into CHO culture supernatant along with impurities originating from the host cells themselves. Such host cell proteins (HCPs) are important contaminants for monitoring because they directly affect drug quality, safety, and efficacy. HCPs are…
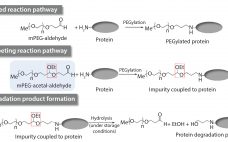
Setting Raw-Material Specifications Using Prediction Models: Determination of a Specification Limit for a Raw-Material Impurity in mPEG-Aldehyde
Impurities related to raw materials used for bioproduction can be inadvertently introduced into a manufacturing process, causing potential failure to meet in-process controls or release specifications. Unexpected impurities also can reduce yield and affect the quality, safety, and effectiveness of a final product (1). Raw-material impurities can originate from starting components or reagents used in manufacture. They can be generated in situ during synthesis or as degradation products. Impurities also can result from improper handling, packaging, and storage. Identification and…
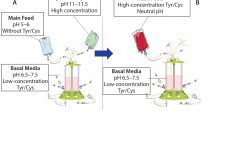
Simplification of Fed-Batch Processes with a Single-Feed Strategy
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells commonly are used to produce recombinant proteins such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes. Culture processes typically rely on a fed-batch approach in which a basal medium enables initial cell growth. Concentrated feeds are used to prevent nutrient depletion, thereby extending culture duration and improving cell growth, viability, and protein titer. A neutral pH feed is desirable because culture pH should remain stable after feedings. The extremely low solubility of l-tyrosine…
Elastomer Stoppers: Working Toward Adopting an Industry-Wide User Requirements Specification for Particulate Levels
Two years ago, the companies involved in the BioPhorum Operations Group (BPOG) fill–finish community agreed that the quality of elastomer stoppers for vials was causing problems for biopharmaceutical manufacturers. So they deemed it to be a priority for the group. The problem is particularly pronounced for vial stoppers used in legacy products, which may have been on the market for several years. Many such medicines remain valuable for large patient populations. The stoppers used on legacy medicines are manufactured using…
MilliporeSigma Launches First Commercial Service to Predict Multiple Sources of DNA Damage
MilliporeSigma has introduced CAN MultiFlow™ screening services to more accurately predict genotoxic and mode of action* properties of substances, ingredients and drug compounds. Offered through its BioReliance® testing facilities, MilliporeSigma will be the first company to provide this service in the United States. The screening process uses flow cytometry to quickly and efficiently screen for clastogens, aneugens and non-genotoxicants (CAN) in pharmaceutical compounds, agricultural chemicals, flavors, fragrances and consumer products. The results from the assay can help manufacturers reject harmful…
Insect Cell Culture and the Baculovirus Expression Vector System: Challenges of Scale-Up and Development
with Sharyn Farnsworth, MSc Scale-up and manufacturing strategy for insect cell culture (ICC) should be assessed at the earliest stages of process development. Your final goals will shape the process and determine at what stage to implement steps that can make the process more reliable and robust at manufacturing scale. Only a few vendors are experienced enough to guide you through them. On 7 December 2016, Sharyn Farnsworth (associate principal scientist at Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies) discussed some upstream challenges BEVS/ICC…