Serum and other blood-derived products have been used widely in pharmaceutical research for many years. Use of these materials has contributed to many different advances in human and veterinary health, and they continue to have an important role in drug development. Fetal bovine serum (FBS) has had a specific role in the culture of mammalian cells for over 60 years. It is proven to be a useful tool for a broad spectrum of applications because it supports a large range…
Cell Culture Media
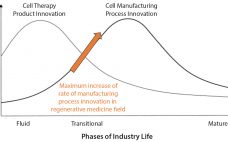
The Need for Adherent Cell Manufacturing: Production Platform and Media Strategies Drive Cell Production Economics
Most commercial biopharmaceuticals originated from academic research laboratories and start-up development laboratories. Despite such products having differences in modalities and targeted disease indications, and whether their target patient populations are relatively small or approaching blockbuster status, at a key point in development, biopharmaceutical production must scale up from laboratory to commercial production. That movement from research to development and then to manufacturing forces attention on economics and speed to market, and it drives innovative approaches to producing biopharmaceutical cell compositions…
Cell Culture Media: An Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient or Ancillary Material?
Cell-based therapies are used to treat diseases that require the replacement of diseased, dysfunctional, and injured cells (1). To produce these therapies, a wide range of reagents and materials such as antibodies, growth factors, and enzymes are used in their manufacturing processes. Such necessary materials are administered through a cell culture medium. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are the main ingredients that make products therapeutic. Ancillary materials (AMs) and raw materials (RMs) are essential components used during production but are not…
Enhanced Galactosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies: Using Medium Supplements and Precursors of UDP-Galactose, Part 2
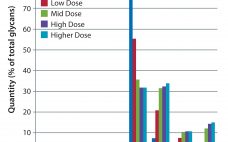
In Part 1 of this report, we described our development of a high-throughput assay for analyzing monoclonal antibody (MAb) glycans and how we used it to evaluate the effects of medium supplements on galactosylation of MAbs produced by two different cell lines (1). This month, we examine galactosylation of a MAb produced by a third cell line. A discussion follows on the benefits of this high-throughput assay before we highlight the similarities and differences in galactosylation among the three MAbs…
Enhanced Galactosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies: Using Medium Supplements and Precursors of UDP-Galactose, Part 1
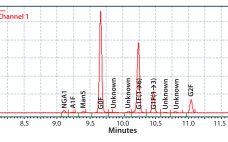
The biopharmaceutical industry needs better understanding of how monoclonal antibody (MAb) glycosylation is influenced by components in cultivation media — and it needs methods to exert some control over the structure of MAb glycans. That structure can affect MAb function. Thus, a high-throughput (HTP) assay is needed for characterizing MAb glycosylation so that developers can observe the effects of cultivation conditions on MAb glycosylation rapidly, with a goal of producing MAbs that have a desired glycan structure. The method also…
Simplification of Fed-Batch Processes with a Single-Feed Strategy
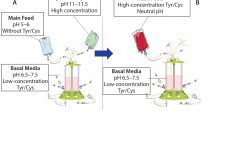
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells commonly are used to produce recombinant proteins such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes. Culture processes typically rely on a fed-batch approach in which a basal medium enables initial cell growth. Concentrated feeds are used to prevent nutrient depletion, thereby extending culture duration and improving cell growth, viability, and protein titer. A neutral pH feed is desirable because culture pH should remain stable after feedings. The extremely low solubility of l-tyrosine…
Providing Lipids Boosts Protein Productivity: Testing a Feed Supplement with Multiple Cell Clones and Media Formulations
As the biologics (and now biosimilar) markets continue to grow, pressure increases on biomanufacturers to reduce cost of goods sold (CoGS). One way they can reduce cost is by increasing protein productivity in terms of protein titer per volume of culture. Media optimization is a key strategy for increasing protein productivity. In the past few decades, average titers across the industry have increased greatly — from <0.5 g/L in the 1980s to >3 g/L today, and it is not uncommon…
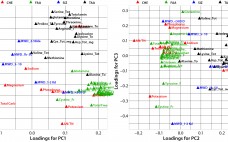
Multivariate Analysis of Biological Additives for Growth Media and Feeds
Biological additives such as yeast extracts and peptones are commonly used in growth-media formulations for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. In spite of drivers encouraging companies to reduce variability in mammalian cell culture processes by using chemically defined media, many microbial and mammalian processes continue to use biological additives in their growth-medium formulations and/or feeds. According to Sheffield Bioscience (Kerry, Inc.), at least six of the top 10 licensed mammalian-cell– derived biotherapeutic products are manufactured using biological additives (1). During process development, it…
Ask the Expert: Cell Culture Media Supplementation
with Dr. James Brooks (BD Biosciences) Improvements in cell culture media and supplementation have enabled significant advancements in bioproduction titers. But optimization to meet the specific needs of individual production cell lines is key to achieving desired production and protein quality, especially for biosimilars. Not only is it desirable to achieve cost-effective levels of production, but quality characteristics also are essential — and for biosimilars must closely resemble those of the originator molecules. Fully chemically defined (CD) media formulations are…
Bioreactor Design for Adherent Cell Culture: The Bolt-On Bioreactor Project, Part 2 — Process Automation
The Bolt-on Bioreactor (BoB) project is an independent initiative to develop and commercialize a bioreactor for automated and efficient culture of adherent cells, especially in production of therapeutic cells and other biopharmaceuticals (1). After conducting thorough research on available culture systems for adherent cells, the BoB team believes that a successful alternative to existing devices must solve four major challenges. Addressed in the first installment of this series (2), the first challenge concerns volumetric productivity. The second challenge is…