Gene therapy is the transfer of genetic material to a patient‚Äôs cells to achieve a therapeutic effect. Therapeutic DNA typically is delivered using a viral vector system, and adenoviruses have been used for this purpose for over 20 years (1‚Äď3). Within the past 10 years or so, lentiviruses have shown promise in clinical trials (1‚Äď3), and adenoassociated viruses (AAVs) have been used in the first approved gene therapies in the Western world (4). The number of gene therapy applications based…
Manufacturing
The 2017 World Biological Forum: Successes and Future Trends in Continuous Biomanufacturing
Continuous biomanufacturing was a central topic at the fourth annual World Biological Forum in Oxford, UK, on 26‚Äď28 June 2017. A well-rounded lineup of presenters appeared at this forum held in Oxford University‚Äôs Lady Margaret Hall, an eclectic location that well captured the historic charm of the university. Delegates were well supported throughout the meeting with generous meals, refreshments, and assistance provided by helpful staff. Papers were presented in Talbot Hall in the center of the college. The stately main…
Introduction: Emerging Therapies Come of Age
According to a 2017 industry report, 74% of biopharmaceuticals currently in development (phase 1‚Äď3) are possible first-in-class medicines (those that use a unique mechanism of action), thus representing a potential new pharmacological class of treatment (1). They include regenerative medicines, conjugated monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), and DNA and RNA therapeutics. Some emerging therapies ‚ÄĒ such as antibody‚Äďdrug conjugates (ADCs) and biobetters ‚ÄĒ have been more at the forefront of discussions than others, but all are poised to bring exciting changes to…
Development Approaches to Adenoassociated Virus Production
After many years of development, gene therapy is beginning to deliver on its promises in the clinic, in some cases with spectacular outputs. Those clinical successes also have led to an influx of funding and engagement from large pharmaceutical companies, thereby bringing the required financial support and expertise for late-stage clinical developments and product commercialization. Although many initial studies were confined to small patient groups and focused on a range of rare monogenetic diseases, new approaches to gene editing have…
Process Needs of Antibody Fragments and Bispecifics: A Discussion with Jonathan Royce of GE Healthcare
Although the number of bispecific antibodies approved so far (two) and antibody fragments either approved or with an investigational new drug (IND) filed (‚ąľ20, both antigen-binding and variable) are far below the number of approved and candidate monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), research in both fragments and bispecifics continues to look promising. And as Jonathan Royce, business leader for chromatography resins at GE Healthcare, discusses here, both offer specific therapeutic advantages over MAbs. But manufacturers should be aware that their diverse structures…
Controlling Glycosylation in Fusion Protein Manufacturing to Generate Potent Biobetters
The pipelines of pharmaceutical companies are full of biological drugs. Many of them are innovative therapeutic proteins, but a growing number represent biosimilars and biobetters (Figure 1) (1). Biobetters typically are defined as being ‚Äúbased on innovative biologics but with improved properties‚ÄĚ (2). Their development benefits from known therapeutic approaches and mechanisms of action resulting in low risk, fast paths to the clinic and thus lower costs. Superiority is achieved through extended half-life (t1/2), improved efficacy, and reduced immunogenicity or…
Developments in Antibody‚ÄďDrug Conjugates: A Discussion with Thomas Ryll of ImmunoGen
As a major class of emerging therapies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) already have gained the attention of biopharmaceutical researchers and manufacturers because they combine both the precision of monoclonal antibodies and the potency of highly potent drug compounds. A few ADCs already have entered the market, but many more candidates are progressing through industry pipelines. Platform processes are not yet universal (and it remains to be seen whether they ever will be), but major ADC developers are establishing their own with…
The Unican Concept: Engineering Dual Capability into Single-Use Vessels
Use of disposable bioreactors in the biopharmaceutical industry has increased gradually over the past several years in pilot, clinical, and production scale facilities (1‚Äď4). Reduced time to market in today‚Äôs drug industry has created a need for cost-effective development and production strategies as well as manufacturing flexibility. When compared with traditional stainless steel equipment, disposable bioreactor and mixing systems have smaller space requirements, are portable, and come presterilized to eliminate the need for preuse sterilization procedures such as steam-in-place (SIP).…
Polysorbates, Biotherapeutics, and Anaphylaxis: A Review
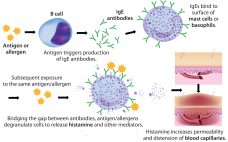
Rapidly increasing use of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in the treatment of neoplastic, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases has led to a dramatic increase in hypersensitivity reactions worldwide, complicating the use of MAbs as first-line therapies and limiting patient survival and quality of life (1). The origins of anaphylaxis are not well understood, though its mechanism is fairly straightforward (Figure 1). It is usually attributed to some undefined intrinsic property or properties of a biotherapeutic ‚ÄĒ despite the fact that biotherapeutic formulations…
Process Development of Microbial Plasmid DNA: Fast-Tracking with Modular Single-Use Minibioreactors
There has been a rapid rise in the number of positive clinical outputs from clinical studies based on gene and cell therapies. This is in addition to the licensing of products such as GlaxoSmithKline‚Äôs Strimvelis ex-vivo stem-cell therapy for treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency caused by adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID) in 2016 (1) ‚ÄĒ has led to an increase in demand for therapeutic vector manufacturing capabilities. Viral vectors are being used for an increasing range of conditions, including monogenetic conditions.…