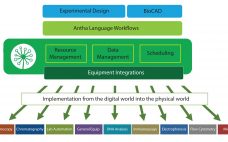
To meet network demand for a commercial launch facility, Genentech (Roche) designed a new downstream train and built it within an existing building shell at the company’s Oceanside, CA, site. This downstream train included new technologies to allow for rapid technology transfer of different new products in the company’s drug pipeline. One technology that was pursued was the Axichrom column platform from GE Healthcare and associated column packing equipment to streamline column packing design. Here we focus on how a…
Manufacturing
Addressing the Challenge of Complex Buffer Management: An In-Line Conditioning Collaboration
Read this article from scientists at Cytiva (GE Healthcare at the time of publication) to learn more about buffer preparation strategies now. Preparation and storage of buffers is a challenge for biopharmaceutical companies developing protein-based pharmaceuticals. The need for volumes of buffer to purify increasing upstream titers have become a major bottleneck in biopharmaceutical downstream processing. Italian biopharmaceutical company Kedrion Biopharma collects and fractionates blood plasma to produce plasma-derived therapeutic products for treating and preventing serious diseases, disorders, and conditions…
Advanced Control Strategies at Biotech Week Boston
Attendees at this year’s Biotech Week Boston (24–28 September) had the opportunity to participate in several preconference symposia on the first day, including one on advanced control strategies for bioprocessing and biomanufacturing. Chaired by William Whitford (GE Healthcare), the session included presentations from Dan Kopec (Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics), Markus Gershater (Synthace), Jonathan Bones (National Institute for Bioprocessing), Robert Thomas (Loughborough University), Chris McCready (Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics), and Victor Konakovsky (Newcastle University). BPI has collaborated with conference organizer KNect365…
Integrated PAT Automated Feedback Control of Critical Process Parameters Using Modern In Situ Analytics
Simply put, the best way to control a critical process parameter (CPP) is to measure that specific parameter, integrate the live signal into your control system, and apply a smart feedback algorithm for an automated control loop. The challenge in doing this for bioprocesses has been due, in part, to the complex, highly dynamic, and variable nature of the process along with the lack of robust, scalable, and multiformat (single-use or multiuse) technologies that can monitor (in real time) such…
Accelerating Process Development Through Flexible Automated Workflows
Synthace began as a bioprocess optimization company in 2011, spun out of University College, London. The company worked on multifactorial approaches with 15–30 factors simultaneously instead of seven or eight. The work investigated genetic strain engineering factors alongside process parameters, defining deep interactions between the way strains were designed and the way they were treated in bioprocesses. Those complex experiments gave unique insight into the complexities of biological processes, but they were exceptionally taxing to plan and carryout manually. Automation…
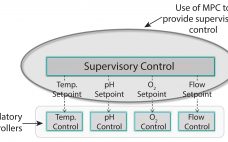
Model Predictive Control for Bioprocess Forecasting and Optimization
Automation hierarchy in bioprocess manufacturing consists of a regulatory layer, process analytics technology (PAT), and (potentially) a top-level model-predictive or supervisory layer. The regulatory layer is responsible for keeping typical process measurements such as temperature, pressure, flows, and pH on target. In some cases, spectral instrumentation in combination with multivariate analysis (MVA) can be configured to measure parameters such as glucose concentration. A cascade control structure can be set up when the nutrient flow setpoint is adjusted to maintain the…
CO2, O2, and Biomass Monitoring in Escherichia coli Shake Flask Culture: Following Glucose–Glycerin Diauxie Online
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important parameter in microbial cultures because it can inhibit or stimulate growth under certain conditions. In our experiment, we monitored Escherichia coli diauxie growth phases online and focused on dissolved CO2 (dCO2) and oxygen readings. We assessed diauxic growth in medium containing glycerin and glucose online with the SFR vario system (from PreSens), which optically measures oxygen, pH, and biomass in an Erlenmeyer flask. The shake flask contained an oxygen sensor spot and an optical…
Data Analysis and Visualization to Improve Biopharmaceutical Operations Part 1: What Are You Trying To Measure?
This begins a five-article series of “how-to” guides for tackling the most common obstacles in assessing, measuring, analyzing, and improving the performance of global biopharmaceutical manufacturing operations. Each installment covers a component of proper collection, analysis, and use of data for the best possible performance outcomes. When taken as a whole, the series should provide imperative best practices for handling business-performance data. First, consider what you want to know about your bioprocesses. How can you more appropriately measure those data…
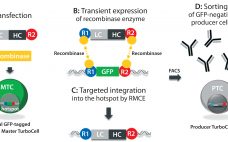
Antibody–Drug Conjugates: Fast-Track Development from Gene to Product
In the fight against cancer, antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) represent an increasingly important therapeutic approach. These biopharmaceuticals are designed to maximize the therapeutic index of cytotoxic small-molecule drugs through their selective delivery to tumor cells while leaving normal, healthy cells untouched. Structurally, an ADC is a monoclonal antibody (MAb) conjugated by a chemical linker to a potent cytotoxic drug. Conceptually, the MAb serves as the delivery component, targeting a specific tumor antigen that ideally is not expressed (or is expressed at…
Particulate Contamination in Single-Use Systems: Challenges of Detection, Measurement, and Continuous Improvement
Patients receiving particulate contamination through parenteral delivery of biopharmaceuticals presents a significant potential health risk. However, the severity of that risk often is unclear. It depends on the route of administration, dosage volume administered, particle properties and amount received, and the ultimate fate of particles within a patient’s body (1). The appearance of particulate contamination also can be a visible indicator of product quality. Consequently, when such contamination is discovered within biopharmaceutical manufacturing operations, often it triggers costly investigations and…