Although vaccine platforms based on messenger RNA (mRNA) are enjoying the limelight in the wake of emergency authorizations of products from Pfizer–BioNTech and Moderna, DNA vaccines are poised to make their own commercial debuts soon. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that six of the 48 candidate vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 that remain in clinical trials are DNA-based products, as are 14 others in preclinical study (1). I spoke with Hong Jiang (cofounder and chief operating officer of Aegis Life, Inc.)…
Manufacturing
Cold-Chain Validation: Emerging Vaccines for COVID-19 and Beyond Require More Extensive Evaluation
In the wake of fast-track approvals for Pfizer’s and Moderna’s respective SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, now begins the largest immunization campaign in world history. Its success will depend not only on the products’ safety and efficacy, but also on several mass-distribution programs requiring significant cold-chain infrastructure. The public has become acutely aware of the Pfizer vaccine’s demanding cryostorage specifications, generating considerable anxiety about how mass distribution will happen. Behind the scenes, however, cold-chain engineering companies such as Modality Solutions have worked alongside…
Enhancing Vaccine Platforms: Computational Models Accelerate Development, Manufacturing, and Distribution
Pandemics such as the current COVID-19 outbreak pose tremendous healthcare and economic challenges. Vaccines hold promise for controlling pandemics; however, substantial challenges come with pandemic-response vaccine development, manufacturing, distribution, and administration. To address those now, many companies are using rapid-response vaccine-production platform technologies. Computational modeling tools could help further accelerate development of those technologies, increase production and distribution efficiencies, and reduce costs and risks once vaccine platforms are fully developed and validated. To those ends, a set of modeling methodologies…
Advanced Analytics to Accelerate Development of Genetic Vaccines
Biopharmaceutical companies are racing to develop vaccines that mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic, taking a wide range of vaccine-development approaches that include traditional modalities and cutting-edge technologies based on DNA and RNA. Vaccine developers are leveraging robust manufacturing concepts and integrated processes to shorten timelines. Advanced analytics also are playing a critical role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of those emerging vaccines. A New Wave of Vaccines Vaccines based on attenuated viruses entail development timelines ranging from four years to…
Reacting to a Pandemic: Innovations in Vaccine Development
Traditionally, viruses for vaccines have been grown in embryonated hen eggs. But new challenges introduced by the COVID-19 pandemic have encouraged and catalyzed innovations in the field of vaccine development. The biopharmaceutical industry has recognized an advantage in mammalian cell-culture systems as promising alternatives to egg-based vaccine production. Cell lines can be cultured to large quantities in bioreactors, allowing for much shorter lead times, a more controlled production process, and a higher grade of reproducibility through standardization. In this article,…
The Green Imperative: Part Two — Engineering for Sustainability in Single-Use Technologies
In BPI’s June 2020 issue, the first installment of this series introduces the study and implementation of single-use (SU) technology to provide a more sustainable manufacturing environment (1). We presented evidence showing that the economic and social benefits of SU systems currently outweigh the residual environmental risks. Not only is SU technology often a better environmental choice than traditional biomanufacturing options, it also is sometimes the only choice for rapid process design and facility start-up. In situations such as the…
Removing Oligomers of a Recombinant Human Therapeutic Hormone:
Evaluation of Chromatographic Options for Effectiveness
Aggregation is a common cause of protein instability, which renders a biologic product unfit for therapeutic use. Sometimes it is difficult to purify monomeric proteins from oligomers because of similarities in their isoelectric points (pIs). Proteins such as hormones have pI ranges similar to their oligomers and thus can be difficult to separate out using a conventional polishing chromatographic step such as ion exchange. With those pI similarities, removal of oligomers to a considerable extent by ion exchangers can compromise…
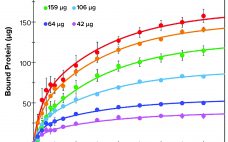
Evaluation of a Novel Peptide-Based Affinity Ligand for Human IgM Purification: Use of an Automated Liquid-Handling System for Rapid Assessment of Binding Kinetics and Capacity
One-step affinity purification of antibodies is a powerful and widely used tool in the biopharmaceutical industry. Although different strategies can be used to purify immunoglobulin isotype G (IgG), the larger antibody isotype IgM has limited options. Human IgM is the largest antibody and primarily exists as a pentamer in the bloodstream (1). IgM molecules exhibit higher avidity than other antibodies do and serve as essential activators for the complement cascade (1–3). Approaches to IgM purification with hydroxyapatite and ion-exchange (IEX)…
Silicone Tubing for Biopharmaceutical Applications: Particulates, Endotoxins, and Bioburden Characterization
Adoption of single-use systems (SUS) has increased steadily over the past few years driven by an increased focus on manufacturing biologics that require smaller scales than blockbuster drugs. Although SUS provide many benefits, some factors need to be considered when implementing them in biopharmaceutical production. With the regulatory landscape intensifying worldwide, drug manufacturers are expecting more data from suppliers to support the purity claims of supplied products, especially related to the purity of their product-contact surfaces. In this article, we…
A Universal Assay Determination Method for Antisense Oligonucleotides: A New Slope Spectroscopy Method
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are short, synthetic, single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides that can alter RNA and reduce, restore, or modify protein expression through several distinct mechanisms. ASO technology has become an important drug discovery platform for most major pharmaceutical companies. To date, six antisense drugs have been approved by regulatory agencies to treat diseases spanning viral infections, hyperlipidemias, and neurological diseases. More than 50 additional ASO drugs are in clinical trials. For an ASO drug product, an assay of its active pharmaceutical ingredient…