Massimo Dominici is scientific founder of Rigenerand srl, a joint venture between RanD (a biomedical company producing bioreactors for liver support and chemohyperthermic technology for cancer) and experts in cell and gene therapy at the University of Modena and Emilia Region in Italy. Rigenerand develops and manufactures medicinal products for cell-therapy applications (primarily for regenerative medicine and oncology) and three-dimensional (3D) bioreactors as an alternative to animal testing for preclinical investigations. The company also produces its own pipeline of cell…
Manufacturing
Raw Materials for Advanced Therapies: When the Process Is the Product, Ingredients Are Key
Scott Burger and Bill Janssen are both established, independent consultants specializing in gene and cell therapies. This past spring, we three discussed several aspects of raw material strategy for advanced therapies as well as the need for trained technicians in the industry. With a bachelor of science degree in biology from Tulane University (New Orleans, LA, 1983) and a medical doctorate from the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, PA, 1988), Scott Burger served his residency training and fellowship at Washington University…
Four Design Factors Shaping Multimodal Cell and Gene Manufacturing
Cell and gene therapy manufacturing is about to hit a breaking point. The tension lies between increasingly diverse research pipelines and a tradition of dedicated facilities built for single-product, large-scale manufacturing. That incompatibility is widening as more cell and gene therapy products progress toward commercial production, forcing manufacturers to make a choice: either invest in major facility modifications and complex technology transfers to keep up or break from tradition and explore the potential of multimodal manufacturing. More than half of…
Toward the Point of Care: Flexibility and Decentralization Are Key to Making Autologous Therapies More Readily Available
Part of the advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) class of therapeutics, cell and gene therapies (CGTs) can be either autologous, using the patient’s own cells, or allogeneic, using master banked donor cells. Global biotechnology company Orgenesis focuses on autologous therapies, with processes and systems developed for closed and automated processing that have been validated for regulatory-compliant production at the point of care for patient treatment. This technology could help overcome the limitations of traditionally cost-prohibitive CGT manufacturing methods that do…
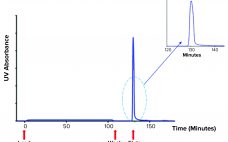
Measuring Viral Titer in AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy Using a PCR Technique for Absolute Quantitation
Gene therapies have reemerged as promising treatments to a number of genetic illnesses. Nearly 400 gene therapy clinical trials are recruiting or ongoing in the United States for diseases such as hemophilia and spinal muscular atrophy (1). The primary vehicles used today to deliver such therapies to patients’ cells are viral vectors such as adenoassociated viruses (AAVs), but producing biologically active vectors for gene therapy can be problematic. One difficulty is generating vectors at the correct concentration to yield a…
Analytical Methods for Cell Therapies: Method Development and Validation Challenges
Advanced-therapy medicinal product (ATMP) characterization and analysis play important roles in providing chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) information for regulatory applications as well as in supporting product-release and stability studies. Each type of advanced therapy presents different analytical development challenges, so each requires specific characterization, potency, purity and identity assays. Variability in cells and among patients, multiple and complex mechanisms of action (MoAs), a general lack of readily available reference materials, and complicated analytical methods and instruments underlie the major…
Ligand-Based Exosome Affinity Purification: A Scalable Solution to Extracellular Vesicle Downstream Bottlenecks
Novel therapeutics based on extracellular vesicles (EVs) recently passed a critical development milestone. During 2020, some of the first experimental EV products developed by biopharmaceutical companies entered human clinical trials (1–3). EVs are nanometer-sized, lipid-wrapped spheres released by almost every cell type in the human body. EVs are loaded with a cargo of proteins, lipids, and RNA, and they are tagged with surface markers that favor uptake by target cells. Thus, EVs are a key mode of cell-to-cell communication (4).…
The Promise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
The term artificial intelligence (AI) has become pervasive in conversations about the future of healthcare. AI has the potential to transform medicine through novel models of scientific discovery and healthcare delivery, ultimately leading to improved individual and public health. Yet misunderstanding and miscommunication abound. Thus, concepts related to AI need to be defined and explained to elevate our general level of understanding and our discourse around the topic. The Promise of AI in Healthcare AI has been studied by computer…
A Complete Solution for MSC Therapy Workflows: Cell Scale-Up, Cryopreservation, and DMSO Removal
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are used frequently for cell therapy applications. As multipotent cells, they can differentiate into other lineages such as adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes. Additionally, they are known to secrete trophic factors that can play important roles in immunoregulation. Although MSCs can be isolated from several different tissue sources, those derived from bone marrow commonly are studied because they are easy to access in quantities large enough for therapeutic dosing (2 × 106 cells/kg of body weight). Still,…
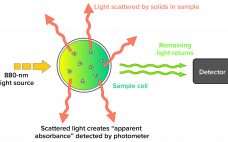
Validation of a Next-Generation Single-Use Turbidity System
Turbidity describes the relative clarity of a liquid as the result of suspended solids. Instruments that measure turbidity typically use a beam of light to detect particles by measuring the difference between the amount of light emitted from the light source and the amount that is received by a detector. Such measurements are affected by the size, shape, and number of particles in a sample of liquid because those solids scatter the incoming light, which provides an apparent absorbance that…