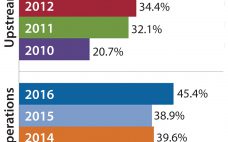
India’s position as a global participant in small-molecule generic drugs, vaccines, and enzymes has been proven over decades. The country is one of the most populous and fastest-growing regions in the world, both economically and technically. But India’s potential as a biologics participant has not been realized. Its competence as a global biologics producer has not yet caught up. Global industry concerns regarding the country’s position in the (bio) pharmaceutical industry haven’t changed much over the past eight years since…
Business
Funding for Life-Science Ventures: Accelerating Innovation in Tools and Services
As a cofounder of Wave Biotech (now a division of GE Healthcare), my partners and I often struggled with critical choices regarding partnering and funding opportunities. Every new, attractive, and potentially disruptive technology will court attention once it experiences some modest adoption and acceptance, even while attempting to “fly under the radar” of major players. The challenge for life-science entrepreneurs is how best to navigate those decisions and select the right path as company founders. Weighing and evaluating potential partners…
Postapproval Changes for Biopharmaceutical Drug-Substance and Drug-Product Manufacture: Regulatory Complexity and Impact
Pharmaceutical products save or improve the lives of millions of people each year. Thorough regulatory review of chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) information is critical to ensure drug product safety, quality, and efficacy as well as to secure patients’ continuous access to such products. But achieving all of that at an effective cost is difficult. Companies race to launch products to patients as soon as possible after clinical efficacy is demonstrated. Biomanufacturers often need to make changes such as increasing…
Reducing Clinical-Phase Manufacturing Costs: Collaborating for Savings without Compromising Quality or Performance
In downstream purification of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), the single greatest contributor to manufacturing costs is the expensive capture step typically based on protein A affinity chromatography. Almost since its introduction to bioprocessing, efforts have been made to reduce the cost of this step. Several alternative ligands have been promulgated as potential replacements for protein A, but they have proven difficult to adopt and scale up. Supplier companies have pushed for increases in capacity and economics, but those are always accompanied…
Special Report on Process- and Product-Related Impurities (A CMC Strategy Forum Special Focus Series): Extractables, Leachables, Particles, and Aggregates
The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website (www.casss.org). This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment will continue to…
Outsourcing of Buffer Preparation Activity Is Increasing
The major fluid products used in bioprocessing — culture media and buffers — are classically prepared in-house by rehydrating (dissolving and mixing) powders purchased from suppliers. Most bioprocessing facilities consider in-house preparation of these fluids to be a core bioprocessing task. However, some companies are outsourcing the work either by purchasing preprepared materials from vendors or hiring contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) to prepare them. Buffer fluid preparation is one area of downstream production operations that are seeing an increase in…
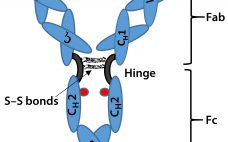
Biosimilar Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Gaps in Science Limit Development of an Industry Standard for Their Regulatory Approval, Part 2
Last month, Part 1 of this discussion briefly described the regulatory landscape for developing biosimilar therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (TMAbs). We identified certain specific structural components of TMAb drug substances that warrant particular attention because alterations to them are likely to affect therapeutic safety and effectiveness. Now we conclude by considering whether studies of reference materials can further the development of analytical industry standards to ensure comparability of putative biosimilar TMAbs with innovator TMAbs. We suggest that the time is right…
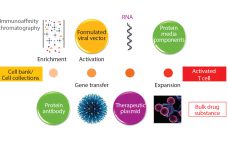
Progress Toward Commercial Scale and Efficiency in Cell Therapy Bioprocessing
Regenerative medicine includes both cell and gene therapies. Currently 672 regenerative medicine companies operate around the world, and 20 products have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Of 631 ongoing clinical trials by the end of 2015 (1), over 40% are in oncology, followed in prominence by cardiovascular and infectious diseases. Here I focus on gene and cell therapy bioprocessing in which the final products delivered to patients are cells. Cell therapies are either autologous (derived…
Manufacturing Plasmid DNA: Ensuring Adequate Supplies for Gene and Cell Therapies
The concept of gene therapy is far from new, with initial studies performed over 20 years ago (1). However, in the past few years an explosion of interest in this area has gone beyond initial regenerative approaches using viral vectors. Interest is now moving increasingly into potential use of T cells modified using recombinant viral vectors for immunotherapy applications. Such therapies are based on using either adenoassociated virus (AAV) or lentivirus (1), both vectors being frequently generated through transient expression…
Designing the Optimal Manufacturing Strategy for an Adherent Allogeneic Cell Therapy
Cell therapies (CTs) offer potential treatments for a wide range of medical conditions (1–6) by replacing cells, repairing tissues affected by either disease or damage (7), or delivering genetic or molecular agents that promote self-healing (8). CT research and development is continuously growing (9), with increasing numbers of CT candidates reaching phase 3 clinical trials (9–11). Developers aim to make products that can survive in a competitive landscape while complying with stringent regulatory requirements to control the quality and safety…