Regenerative medicine includes both cell and gene therapies. Currently 672 regenerative medicine companies operate around the world, and 20 products have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Of 631 ongoing clinical trials by the end of 2015 (1), over 40% are in oncology, followed in prominence by cardiovascular and infectious diseases. Here I focus on gene and cell therapy bioprocessing in which the final products delivered to patients are cells. Cell therapies are either autologous (derived…
Analytical
Viral Risk Evaluation of Raw Materials Used in Biopharmaceutical Production
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines to patients is a key objective for both health authorities and the pharmaceutical industry. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs). Manufacturers must ensure not only the suitability of RMs for their intended use in a manufacturing process, but also their highest attainable safety with regards to viruses and other adventitious agents. The need to apply a risk-based RM control strategy is in line…
Emerging Technology Trends in Biologics Development: A Contract Development and Manufacturing Perspective
For a contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), process development and manufacturing of recombinant proteins must be linked because of tight timelines driven by client expectations. Those are in turn driven by a need for rapid progression to clinical testing. Early in process development, the choice of raw materials needs to reflect existing supply chain and manufacturing infrastructure, but remain suitable for scaling up to meet future needs. One approach is to establish platform processes for a class of molecules…
Selective and Flexible Chromatography Media: Improving Biopharmaceutical Operational Efficiencies
Continuing development in protein and peptide engineering have produced a broad range of new biological products with improved therapeutic and diagnostic potential. In the development pipeline, more than 900 biologic products target more than 100 diseases (1). Increased manufacturing complexities caused by closely related impurities and requirements to improve process efficiencies and reduce operating costs highlight the need for new approaches in protein purification. Platform-based chromatographic approaches have been successfully applied in separating and purifying monoclonal antibody (MAb) products. But…
Viral Clearance in Antibody Purification Using Tentacle Ion Exchangers
Manufacturers strive toward cost-effective purification of target molecules and a high level of confidence that their biologics are safe and not compromised by the presence of endogenous retrovirus-like particles or adventitious viruses (1). Reliable reduction of viral particles throughout downstream purification processes must be ensured through different techniques such as chemical treatment, filtration, and chromatography. Common monoclonal antibody (MAb) purification schemes use both cation- and anion-exchange chromatography steps (CEX, AEX). Although CEX (to remove product- and process-related impurities) is not…
Quality By Design for Monoclonal Antibodies, Part 2: Process Design Space and Control Strategies
Process design space and control strategy are two fundamental elements of quality by design (QbD) that must be established as part of biopharmaceutical development and regulatory filings. Like all of QbD, they are interconnected and iterative. Both are based on knowledge gained during product and process development — but both need to be in place (in a potentially very limited form) when a company begins to manufacture drug substance for clinical trials. Part 1 of this discussion appears on pages…
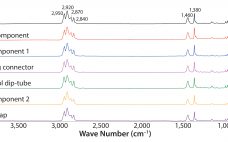
Investigation of Foreign-Particle Contamination: Practical Application of FT-IR, Raman, and SEM-EDS Technologies
The presence of visible foreign particulate matter is considered a critical defect in parenteral products and one of the main reasons they can be recalled (1). Foreign particles present during any stage of manufacturing are considered to be contaminants and can impose a risk to the control of the manufacturing processes (2). For those reasons, particle contamination arising in any manufacturing step initiates a nonconformance or out-of-specification observation. That requires an investigation to identify root cause so as to mitigate…
Science, Risks, and Regulations: Current Perspectives on Host Cell Protein Analysis and Control
State-of-the-art analytics guide process development by providing companies with thorough understanding, effective removal, suitable control, and comparability assessment after process changes of host cell proteins (HCPs) in recombinant biotechnology products. An array of analytical techniques and approaches can be used to establish control strategies for host cell proteins. Techniques used for HCP characterization and comparability include two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis with a range of stains, 2D immunoblotting, 2D high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), 2D difference gel electrophoresis (DIGE), and increasingly mass…
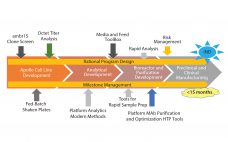
Rapid Development of High-Quality, Robust Mammalian Cell Culture Manufacturing Processes
With increasing industry emphasis on providing both rapid and robust processes, companies are reaping the benefits of new tools for risk management and process analytical controls. As a current example of these approaches, Fujifilm Diosynth scientists have accelerated the development process from gene to finish by shortening the timeline, incorporating quality by design (QbD) principles, and designing the process to be as robust as possible. When the Apollo mammalian expression cell line was introduced three years ago, the time from…
Regulating Quality in Continuous Processing
Regardless of the industry and product being manufactured, continuous processing has demonstrated numerous benefits. In addition to smaller manufacturing footprints, reduced material consumption and waste generation, increased efficiencies, and lower capital and operating costs continuous manufacturing typically leads to more consistent processes and product quality. In the pharmaceutical industry, the latter two attributes align perfectly with FDA’s Quality by Design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) initiatives. The challenge is determining how to apply these concepts in practice. Applying the…