Analytics pervade the entire biopharmaceutical development process — from protein characterization through biomanufacturing process optimization to final-product formulation and clinical testing. Every technical article in BPI requires data to back up the statements made, whether the topic is upstream/production, downstream processing, product development, or otherwise focused. And never mind publishing: Even more detailed documentation is required for regulatory submissions. If a company can’t back up the choices made and results obtained in development, manufacturing, and testing of its biopharmaceutical product,…
Analytical
eBook: Development and Application of a Simple and One-Point Multiparameter Technique — Monitoring Commercial-Scale Chromatography Process Performance
In commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, downstream chromatography steps are still a bottleneck and contribute to significant operational costs (1, 2). Some of those costs are inherent (e.g., resins, large buffer quantities, and cleaning) whereas others are avoidable (e.g., product loss due to rejected lots or deviations that result in production downtime). Maintaining efficient and robust chromatography process performance is therefore critical for minimizing operating costs. To do so, we introduce a simple and one-point multiparameter technique (SOP-MPT) for monitoring chromatographic process…
eBook: Production Cell-Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cultivation — Myths, Risks, and Best Practices
Health authorities are requesting substantial details from sponsors regarding practices used to generate production cell lines for recombinant DNA–(rDNA) derived biopharmaceuticals. Authorities also are asking for information about the clonality of master cell banks (MCBs) and control strategies to minimize genetic heterogeneity. Such requests are prompted by recent reports indicating “nonclonality” for certain production cell lines. To address these and related issues, the CASSS CMC Strategy Forum on “Production Cell Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cell Cultivation:…
The Multi-Mode Mimetic Ligand Library: A New Tool for Rapid Development of Downstream Processes
Recent developments in downstream processing of biomolecules — including continuous processing, bind–elute affinity capture, and flow-through polishing steps — have increased the need for greater selectivity from chromatography adsorbents. This has led to the introduction of a new generation of adsorbents: so-called “mixed-mode” or multimodal ligands. They provide greater selectivity and tolerance to process buffer composition than either ionexchange chromatography (IEC) or hydrophobic-interaction chromatography (HIC) alone can provide. Learn more in this Special Report from Steve Burton, Chief Executive Officer…
Data Science, Modeling, and Advanced PAT Tools Enable Continuous Culture
Bioprocesses traditionally use (fed-)batch cell culture processes for production of recombinant proteins and therapeutics. In batch bioprocessing, material flow is discrete, with a hold step between two unit operations, and product is harvested only once for each unit operation. Batch processes have been studied extensively and optimized through numerous advancements in experimental design (1, 2), monitoring (3–5), measurement techniques (6–9), and control strategies (10–12). However, such processes require large facility footprints for equipment (13) as well as sterilization, load, and…
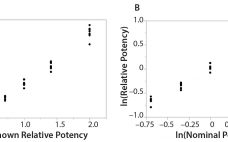
The Relationship Between R2 and Precision in Bioassay Validation
Analytical linearity along with assessments of precision and accuracy determine the range for bioassays (1). Practitioners can include coefficient of determination (R2) criteria from a linearity study in the bioassay validation protocol. Herein I illustrate the relationship of R2 to study design and analytical method variation. Overview of the Simple Linear Regression Model Dilutional linearity assesses the “ability (within a given range) of a bioassay to obtain measured relative potencies that are directly proportional to the true relative potency of the…
Ensuring the Integrity of Single-Use Containers: Providing Robustness, Science, and Helium-Based Technology with a Detection Limit of 2 ÎĽm
Identifying the greatest defect size, both for liquid leaks and microbial ingress, is a fundamental step toward protecting the integrity of single-use systems (SUS) under real process conditions. Integrity testing of such systems may become a prerequisite in the future because they are used in the most critical process steps, with detection limits correlating to liquid leaks and microbial ingress. Such testing guarantees the sterility of drug substances and drug products packaged in single-use systems and, therefore, enhance patient safety.…
Cell Expansion with Dissolvable Microcarriers
In recent years we have seen an exponential increase in the number of companies testing and validating new regenerative medicine products. Many of these products are reaching late-phase trials with the potential to receive final approval and marketing authorization from regulatory agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). In the past several years, we have seen successful launches of regenerative medicine products, including Holoclar (Holostem Advanced Therapies), Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel, Novartis), Yescarta…
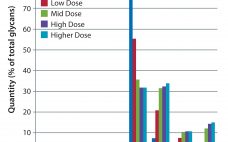
Enhanced Galactosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies: Using Medium Supplements and Precursors of UDP-Galactose, Part 2
In Part 1 of this report, we described our development of a high-throughput assay for analyzing monoclonal antibody (MAb) glycans and how we used it to evaluate the effects of medium supplements on galactosylation of MAbs produced by two different cell lines (1). This month, we examine galactosylation of a MAb produced by a third cell line. A discussion follows on the benefits of this high-throughput assay before we highlight the similarities and differences in galactosylation among the three MAbs…
eBook: Development of a Representative Scale-Down UF/DF Model: Overcoming Equipment Limitations and Associated Process Challenges
Scale-down models (SDM) are physical, small-scale models of commercial-scale unit operations or processes that are used throughout the biopharmaceutical industry for validation studies, commercial deviation investigations, and postapproval process improvements. To support these studies, regulatory guidelines state that SDMs should be representative of the commercial process. For some downstream unit operations such as column chromatography, developing a representative SDM is straightforward because a linear scale-down approach can be used. However, developing a representative SDM for other downstream unit operations such…