This eBook introduces new analytical approaches that enable in-line chromatographic detection of exosomes. One approach can discriminate extracellular vesicles from nonvesicle contaminants, and one potentially can discriminate exosomes from other vesicles. Examples illustrate how they enable development of more effective and better documented purification methods. The special qualifications of monolithic chromatography media for exosome purification are discussed. New process tools designed to accommodate some of the special challenges of exosome purification are introduced. Exosomes represent one of several species of…
Analytical
Analytical Strategies for Fixed-Dose Coformulated Protein Therapeutics
Coformulation of two or more proteins in a single formulation is an emerging approach to delivering multiple biotherapeutics that previously have been administered in sequence. This approach brings multiple benefits to all stakeholders. Foremost for patients, the primary benefits are combined therapeutic effects and improved convenience (e.g., fewer administration events). Healthcare providers see logistical benefits and decreased risk of medical errors. Additionally, coformulations also simplify manufacturing logistics, reduce costs of packaging and distribution, and provide new opportunities for product portfolio…
Recommended Practices for Assuring Integrity of Single-Use Systems
The increasing uptake of single-use technologies (SUTs) in critical current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) processes and applications has made their integrity a critical quality attribute (CQA) for both suppliers and end users of such systems. Current regulations focus on final packaging, however, without taking into account the unique aspects of assemblies used in bioproduction. Ongoing initiatives include revision of PDA TR 27 (1) and creation of A STM workstreams (2, 3) to propose good practices for the integrity of single-use…
Points to Consider in Quality Control Method Validation and Transfer
The concept of an analytical lifecycle has been well received in the biopharmaceutical industry. In 2016, the US Pharmacopeia (USP) advocated for lifecycle management of analytical procedures (1) and defined its three stages: method design development and understanding, qualification of the method procedure, and procedure performance verification. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has published guidance on process validation with a similar division into three stages: process design, process performance qualification, and process performance verification (2). For a manufacturing…
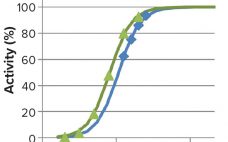
Apparent Matrix Effects in an Iduronate 2-Sulfatase Specific Activity Assay
The recombinant fusion protein SHP631 consists of a chimeric monoclonal antibody binding to human insulin receptor and iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S). This product is being developed as an enzyme replacement therapy to treat cognitive symptoms of Hunter’s syndrome. Because the current therapy (idursulfase, brand name Elaprase from Shire) cannot cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), SHP631 is being developed to do so, enabling the presence of I2S in the brain. The enzymatic activity of this molecule is measured using the substrate 4-methyl umbelliferyl-α-L-idopyranosiduronic…
Developing an End-to-End Scale-Down Model for a Commercial-Scale Downstream Process: Enhancing Technology Transfer Efficiency
Large and complex protein molecules used as therapeutic agents are manufactured in a series of process steps that start with thawing of cell-bank vials and finish with filling and packaging (Figure 1). The cost and complexity of commercial-scale biomanufacturing processes make them prohibitive to troubleshoot or experiment at full commercial scale. Biopharmaceutical companies routinely use scale-down models (SDMs) of licensed commercial-scale processes to evaluate raw material changes, process improvements, and deviations (1) (Figure 2). Here, we outline some considerations in…
Continuous Chromatography: Experts Weigh in on the Possibilities and the Reality
Discussions of continuous processing in the biopharmaceutical industry are an important part of current efforts toward intensifying bioproduction and bioprocessing. Biomanufacturers are looking at all components of their development and manufacturing processes for ways to reduce the size of their facilities, lower costs, and increase speed and flexibility of operations. Increasing options for and availability of single-use technologies have been major enablers of myriad attempts to improve efficiencies. Although the general consensus may still be that single-use components are more…
Aspects of Acceleration: Biomanufacturers Need Smart Strategies to Speed Products to Market
No matter what the industry, it’s widely accepted that slow-moving companies give their nimbler competitors an advantage, allowing them room to dominate the market even if their products are not superior. “Me-too” products and their sponsors often are seen as followers rather than leaders — even if they offer improvements over what is already available. Fast movers are flexible and adaptive to a dynamic business environment. They capitalize on opportunities and navigate risks and challenges by responding quickly to changes…
Qualitative and Quantitative Host Cell Protein Analysis Using Mass Spectrometry
Host cell proteins (HCPs) originate from host organisms that are used to produce biopharmaceutical products. They are in-process contaminants that must be minimized during downstream process operations. According to regulatory agencies, the maximum permitted level of total HCP in a biopharmaceutical product is 100 ng per mg (100 ppm) (1). HCPs can decrease drug efficacy and pose a risk to patient safety because they can bring on undesirable immune responses. Thus, HCPs are a critical quality attribute that should be…
Using Slope Spectroscopy Methods: Risk Assessment and Cost Savings
The biopharmaceutical industry’s need for rapid, accurate concentration measurements of protein-containing products is critical. The protein-concentration assay measures ultraviolet absorption at 280 nm (A280) and usually is performed both as an in-process test and for product-release testing. The SoloVPE system can analyze samples across a wide range of target concentrations without the need for labor-intensive and error-prone dilutions. Slope Spectroscopy methods provide companies with a universal platform for determining protein concentration for all in-process, clinical, and commercial methods. During in-process UV…