As you receive this issue, Informa’s BPI West conference is taking place at the San Diego Convention Center on 14–17 March 2022, with live digital panel discussions the following week. People appear to be cautious but eager to get back to live-conference attendance. BPI’s senior technical editor, Cheryl Scott, will make the journey down there to represent us this year, so if you plan to be there, please take a moment to visit with her. BPI West was the first…
March 2022
Orphan Drug Designation: Securing the Significant Benefits
When preparing an application for orphan drug designation (ODD) in the European Union (EU), you need to consider key eligibility criteria that are different from those required by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). One factor is justifying the “significant benefit” (defined below) of your drug product over existing therapies for an orphan condition. Significant benefit contributes considerably in securing a successful ODD application if the correct approach is taken — as described in two European Medicines Agency (EMA)…
Maximizing European Market Access: Guidance for Young Biopharmaceutical Companies
Achieving efficient and profitable market access for next-generation pharmaceutical products is extremely challenging. The number of drug launches is rising every year, taking competition levels higher with them. And because these novel products tend to be more tightly targeted to smaller patient populations than the “blockbuster” drugs of old, their pricing/reimbursement terms need to be tailored to match. This is especially the case with highly complex biologic drugs, which typically are expensive to research and develop. Below I offer a…
Smart, Real-Time Quality Insights Boost Life Sciences Manufacturing
The COVID-19 pandemic has shone a light on restrictive business processes, information silos, and poor supply-chain visibility in many sectors. In biopharmaceutical manufacturing, for example, difficulties associated with product-quality management have been exposed and starkly felt. However, public healthcare measures over the past 18 months have put physical distance between team members, thereby hampering the usual form-filling, manual sign-offs and spreadsheet-based recordkeeping associated with monitoring traditional manufacturing processes. In some cases, a lack of formal face-to-face discussions in the workplace…
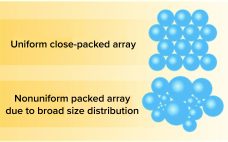
Mycotoxin Risk Determination: Measuring the Potential for Patient Exposure with Antithrombin Alfa Sourced from Transgenic Goat Milk
Antithrombin alfa is a recombinant human antithrombin developed as an anticoagulant treatment for people with hereditary antithrombin deficiency who are undergoing surgical or childbirth procedures (1). Marketed under the ATryn brand name by LFB SA (Les Ulis, France), antithrombin alfa was approved for use in adults by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2009 (2). Antithrombin alfa is expressed in the milk of transgenic goats and purified through a multistep downstream process encompassing both filtration and chromatography.…
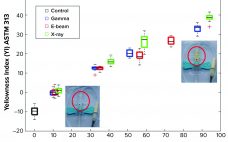
Supplementing Gamma Sterilization with X-Ray and E-Beam Technologies: An International Industry and Academia Collaboration
Ionizing-technology–based industries are growing rapidly around the world. The expansion is driven mostly by the technology’s myriad applications, including polymer crosslinking, medical device sterilization, food pasteurization, and phytosanitary treatment. Ionization also is used in the manufacture of some healthcare products such as medical devices and biopharmaceuticals. Industrial sterilization methods render single-use products and manufacturing components safe and ready for their intended use. ISO11137-1 describes the validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices and mentions the three…
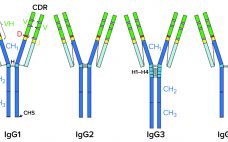
Removing Aggregates and Fragments of Recombinant IgG1: Evaluating a Process Change to Implement Appropriate Chromatographic Media
High–molecular-weight (HMW) and low–molecular-weight (LMW) product variants are critical quality attributes (CQAs) for monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) because they can cause severe immunogenic responses in human recipients. Aggregation is a common problem that can compromise the quality, efficacy, and safety of therapeutic proteins. It can occur at different stages in a biomanufacturing process: during cell-culture–based production, downstream process purification, drug-substance formulation, and storage of bulk drug substances or formulated drug products. Hence, the removal and control of MAb aggregates and fragments…
Improving the Performance of Tried-and-True Chromatography Technology
Efficient and effective downstream processing of biopharmaceuticals reduces manufacturing costs and time. Chromatography is the primary purification method for traditional recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), plasmid DNA, and viral vectors. Although interest in membrane separation technologies is growing, traditional resin-based solutions continue to be preferred when high-resolution purification is required. Ion-exchange chromatography (IEC)(e.g., cation and anion-exchange chemistries) and hydrophobic-interaction chromatography (HIC) are established bioseparation technologies. Cation-exchange resins are used widely for MAb polishing and aggregate clearance steps. Anion-exchange (AEX) resins…
Mind the Gap: Managing Relationships Between Upstream and Downstream Intensification
Process intensification (PI) describes an integrated framework of strategies to maximize the output of a unit operation, a process, or an entire facility. By implementing PI strategies, biomanufacturers can accomplish their productivity goals by increasing production speeds and titers, reducing facility footprints, and cutting costs. Overall, such changes improve production efficiency and flexibility. Collectively, the biotherapeutic industry has made multiple advancements in intensifying upstream processing. PI strategies include using high-density cell banks, implementing seed-train intensification (n – 1 perfusion), and…
A Missing Link to Achieving Higher Vaccination Rates in Developing Countries
Puerto Rico is leading COVID-19 vaccination efforts in the United States, with 89.7% of adults already fully vaccinated (1). However, many other regions are struggling to gain that level of traction, if any. Less than 1% of people in developing countries are fully vaccinated (2). Because Pfizer–BioNTech’s and Moderna’s respective mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines still require ultracold temperatures for long-term storage, vaccine distribution in remote locations is arduous without appropriate cold-chain infrastructure. Puerto Rico’s success in vaccinating its population demonstrates how…