Every now and then in the biopharmaceutical industry, a technology or concept seems to take hold and suddenly appears everywhere — in print, at conferences, in workshops and online media offerings, and as part of new product launches. This happened in the 1990s when process validation was (seemingly suddenly) the theme of the day, and it happened briefly later that decade when transgenics appeared to be a potential game changer. Single-use technologies of course precipitated arguably the most widespread set…
May 2016
Spotlight
Niche Disease: Autoimmune/Noninfectious Uveitis Uveitis is the inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer that lies between the eye’s inner retina and its outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The most frequent etiologies are autoimmune diseases such as Behçet disease. Noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis (NIU) represents 10–15% of uveitis cases, making it the fourth leading cause of blindness in the developed world. About one in 4,500 patients suffer with this condition. Uveitis typically has been treated…
Bioreactor Manufacturing Platforms for Cell Therapies
As an increasing number of cell therapies move into late-phase trials, developers are considering innovative solutions to address scale-up and commercialization challenges. Many of their questions focus on the technologies and engineering strategies that will be needed to optimize their processes, especially bioreactors. At the January 2016 Phacilitate Cell and Gene Therapy World conference, Siddharth Gupta, a scientist at Lonza (Walkersville, MD), talked about the effects of upstream process decisions on product quality in his presentation “Bioreactor Manufacturing Platforms: So…
Special Report on Continuous Bioprocessing: Upstream, Downstream, Ready for Prime Time?
Once an engineering curiosity and smallscale laboratory technique, continuous bioprocessing has evolved in just a few short years to a topic of intense and increasing interest to most bioprocessors. Critics point to a steep learning/adoption curve, but that is nothing new in biomanufacturing.Andrew Zydney is a distinguished professor of chemical engineering at Pennsylvania State University. He has noted these challenges facing continuous processing: commercially unproven unit operations (especially downstream), a lack of equipment robustness, sterility concerns, and uncertain development timelines…
Clearance of Persistent Small-Molecule Impurities: Alternative Strategies
Small-molecule impurities that bind to and copurify with protein biopharmaceuticals traditionally have been removed using bind-and-elute (BE) chromatography. However, that approach may be undesirable for a number of reasons. For instance, it may present a facility-fit challenge or provide a lower process yield than what is acceptable. A common scenario in which BE chromatography may be undesirable is in removal of unreacted conjugation reagents. Bioconjugates represent an important and growing class of pharmaceuticals that include PEGylated proteins, vaccines, and antibody–drug…
Best Practices for Critical Sterile Filter Operation: A Case Study
A number of regulatory guidelines recommend preuse integrity testing of critical sterilizing liquid filters for aseptic processing (1–3). Before sterilization, a preuse test will confirm that a filter is installed properly and was not damaged during shipment or handling. Performing a preuse test after sterilization detects damage that may have occurred during the sterilization cycle. Testing after sterilization limits risk, so it is a practice applied based on risk assessment. Because it is perceived to reduce business loss risk, preuse…
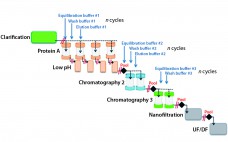
Accelerated, Seamless Antibody Purification: Process Intensification with Continuous Disposable Technology
Process intensification through continuous manufacturing has been practiced in the chemical, petrochemical, and food industries for years and has gained much interest among biopharmaceutical manufacturers (1). Key drivers encouraging biomanufacturers of therapeutic molecules to convert batch processes into continuous operation include flexibility, productivity, cost effectiveness, and product consistency. Continuous upstream processing has been demonstrated for the manufacture of a broad range of molecules, including complex/labile proteins such as enzymes (2) and monoclonal antibodies (3). Recent publications have reported successful application…
Validation of Controlled Freezing and Thawing Rates: A 16-L–Bag Study
It is well understood that freeze– thaw processes affect the product quality of biopharmaceuticals (1–3). It has been reported that there is no consistent method of controlled freezing and thawing rates for biological formulations (4). Traditionally, ultralow temperature storage chambers that were not designed for freezing have been used to provide an energy state for the environment surrounding the product with very little excess capacity to change the state of the product. This study details a consistent method for controlled-rate…
Orbital Shaking and Acoustic-Resonance Mixing: Comparing Culture Characteristics
Production of recombinant proteins usually happens in suspension cultures, with oxygen limitation playing a major role. Oxygen and nutrition feeds are of great significance to aerobic suspension cultures. Oxygen is often the controlling factor in orbital shaken systems because oxygen transfer occurs only through diffusion, which is limited by gas-exchange surface and mixing characteristics. Here, we compare growth characteristics of microbial cultures in a standard shaken incubator with those of cultures in a RAMbio fermentation system, paying particular attention to…
A Turning Point for US Biosimilars
The next 12–18 months could be a critical time for biosimilars in the United States (1). This product class has grown rapidly since passage of the Biosimilars Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA) of 2010. That landmark legislation allowed for biosimilar market approvals based on previously approved “reference products,” creating an expedited pathway that reduces biosimilar development costs and speeds regulatory review so patients get faster access to essential medicines. Increased competition from biosimilars could save the US healthcare system…