Niche Disease: Epidermolysis Bullosa by Cheryl Scott Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of rare diseases that cause skin to blister easily. In severe cases, blisters may even be internal (e.g., in mucosal tissues or organs). More than 300 mutations have been identified in this condition. Most of the many types of EB are inherited, and the condition usually manifests in infants and young children; some patients don’t develop symptoms until adolescence or early adulthood. Exceptionally mild cases may remain…
2015
A Risk-Based Approach to Supplier and Raw Materials Management
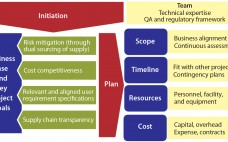
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines is a key objective for the pharmaceutical industry and health authorities alike. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs) used in drug production. However, changes in suppliers, their processes, their providers, and consequently the materials they supply can occur (for a number of reasons) at any time during the life cycle of drug production. A product-supply organization therefore must be prepared to address such…
Outsourcing Stability Testing: Discussions with Contract Laboratories
Stability testing is required for all biopharmaceutical drug products to detect all changes in identity, purity, and potency as a result of a number of environmental and processing factors. Whether testing is conducted in-house or through contact laboratories, it involves the development and performance of comprehensive and specific stability protocols for all stages of a product’s life cycle (1). Testing product stability in-house requires signficant time and resources, and carries challenges associated with commercialization market, time, and capacity. Market: The…
Next-Generation Bioprocessing for Meeting Healthcare Challenges: The Role Single-Use Handling Systems Can Play
The rapid spread of contagious and lethal diseases worldwide has driven bioprocess suppliers to develop technologies for use in producing disease treatments and vaccines. Bioprocessors need to develop new biologics as well as rapid and reliable methods for bringing those treatments to commercialization. Implementing modular process solutions and single‑use handling systems in closed‑manufacturing processing is one approach to addressing those needs. Developing and discovering solutions for meeting global healthcare conditions is an evolving part of bioindustry. As points of reference,…
Special Report on Assays, Test Methods, and Comparability: The CMC Strategy Forum Series, Part 4, Introduction
The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of the forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website (www.casss.org). This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment will continue…
Special Report on Assays, Test Methods, and Comparability The CMC Strategy Forum Series, Part 4, Biosimilar Products: Scientific Principles, Challenges, and Opportunities
The Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Strategy Forum held on 22 January 2012 in San Francisco, CA, focused on selected scientific and regulatory aspects in the development of biosimilar products. Such products are an increasingly important area of interest for both the biopharmaceutical industry and its regulatory agencies. Biosimilars are highly complex, so scientists have been unable to demonstrate identity to a level typically possible for small molecules. Consequently, specific scientific and regulatory approaches are required to ensure the high…
Special Report on Assays, Test Methods, and Comparability The CMC Strategy Forum Series, Part 4, The Role of Higher-Order Structure in Defining Biopharmaceutical Quality
Cosponsored by CASSS (an International Separation Science Society) and the US FDA, the 17th CMC Strategy Forum was designed to explore the relationships between higher-order molecular structure and quality of therapeutic proteins and peptides, vaccines, and blood-derived products. Understanding those relationships is important to defining and controlling the critical quality attributes (CQAs) of biopharmaceutical products. The forum program highlighted the current state of the art for analytical tools used to monitor higher-order structure. Case studies demonstrating the effects of changes…
Special Report on Assays, Test Methods, and Comparability The CMC Strategy Forum Series, Part 4, Demonstrating Comparability for Well-Characterized Biotechnology Products: Early Phase, Late Phase, and Postapproval
Challenges and approaches in demonstrating comparability of a well-characterized biotechnology product after manufacturing changes can be as varied and complex as the products themselves. Participants at the January 2005 CMC Strategy Forum sought to discuss and agree on common implementation strategies for different manufacturing change scenarios (1). Development of flexible, comprehensive approaches in strategy development addressed evaluation of critical product characteristics, appropriate process steps to test, numbers of lots and levels of testing required, and assessment of product comparability. The…
Special Report on Assays, Test Methods, and Comparability The CMC Strategy Forum Series, Part 4, The Roles of Bioactivity Assays in Lot Release and Stability Testing
A January 2007 CMC Strategy Forum on the roles of bioactivity assays in lot release and stability testing was held in Washington, DC (1). Its purpose was to promote an understanding of the design and utility of bioassays throughout product development and to delineate the conditions under which surrogate assays could be used to determine product potency. Topics of discussion included appropriate assay selection at each stage of product development, the potential use of binding assays for potency testing, and…
Quantitative Risk Assessment of Bioaccumulation Attributable to Extractables and Leachables in Cellular Immunotherapy Biomanufacturing
Precious patient samples, contamination concerns, and limited product purification options have compelled manufacturers of cellular immunotherapies (iTx) such as chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T) and T-cell receptor (TCR) technologies toward the disposables industry. Such companies are implementing single-use technologies (SUTs) almost exclusively (1). But despite the dominance of disposable bioprocess platforms and their extraordinary growth in the iTx marketplace, researchers have made limited efforts to understand the perennial and critical bioprocessing risks of leachables and extractables. Here we outline…