Process development forms the core of BioProcess International’s coverage and interests. From cell-line engineering through seed-train and production cultures, the results of which are harvested and purified to yield a bulk drug substance, every biologic therapy and vaccine begins its life at small scale in a research and development laboratory.Cell lines may be mammalian, insect, microbial, or even plant-sourced (1). They all require different types of culture media and supplements. And purification options are many and diverse. Process intermediates are…
2015
BioProcess Theater: Roundtable
Stretching for the Trifecta Innovative Strategies for Speeding Development, Lowering Costs, and Enhancing Quality On Tuesday 16 June 2015, at noon on the BioProcess Theater stage at BIO 2015, Tom Ransohoff (vice president and principal consultant at BioProcess Technology Consultants, Inc.) will moderate a roundtable discussion with the following panelists: Mark Brower (senior research chemical engineer, Merck & Co.) Parrish Galliher (Xcellerex founder and chief technology officer, GE Healthcare) Joanne Beck (senior vice president of process development, Shire) Lynne Frick…
BioProcess Theater: Formulation, Fill and Finish
Fragile proteins and other biomolecules need protection as stable drug products. The larger a molecule is, the more difficult it will be to make, ship/store, and administer to patients. Biotech drug formulators have many concerns to juggle in their work, beginning with the physicochemical characteristics of an active molecule and including the reliability, cost, and availability of analytical methods; the array of excipients and adjuvants on the market; evolving delivery methods and devices; patient preferences and behavior, as well as…
BioProcess Theater: Clinical and Commercial Manufacturing
When it comes to clinical and commercial manufacturing of therapeutic products, outsourcing is an integral part of the biopharmaceutical industry. In the 21st century, product sponsors are increasingly relying on expert contract assistance in process development and production of clinical and commercial materials. Many companies are reaching beyond their local and national borders to extend networks of partnerships into emerging markets, particularly in Asia (1, 2). Most biologics are proteins, with monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) dominating the scene over a number…
Accelerating Affordable Growth: Careful Planning Can Pave the Way for Commercial-Scale Manufacturing
As this special issue of BioProcess International goes to press, an increasing number of cell-based therapies are advancing through preclinical investigation into clinical development and on toward commercialization. Although clinical efficacy will be the primary metric for product approval, the ability to manufacture these therapeutic products consistently, reliably, and cost-effectively will continue to be a key driver and predictor of commercial success. Several articles presented herein describe major issues and challenges facing developers of cell-based therapies. Although some of the…
Planning for Commercial Scale of Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine Products, Part 1: Achieving Manufacturability and Managing Cost of Goods
Much mystique and mystery surround the emerging industries of cell therapy and regenerative medicine. As companies progress toward commercial manufacture with potential game changers (e.g., cures for cancer and diabetes) the industry could be on the verge of significant breakthroughs. However, with no real successes to date, the question is raised: What core attributes are required to achieve commercial success? The tale of Dendreon’s struggles highlights how difficult it can be to commercialize even an approved cell therapy product. Since…
Foundation Elements for Cell Therapy Smart Scaling
Cell therapy is the injection of cellular material into patients. The injected cell-therapy product (CTP) usually consists of intact living cells. In recent years, cell therapies have evolved and matured, moving from academia to industry. That maturation is reflected in the number of open clinical trials that include the term cell therapy in their descriptions: To date, there are more than 8,700 open trials listed on the US National Institutes of Health’s online database (clinicaltrials.gov), most of which are in…
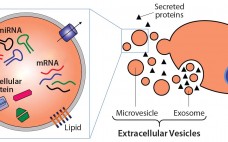
Extracellular Vesicles Commercial Potential As Byproducts of Cell Manufacturing for Research and Therapeutic Use
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as a potential alternative to some stem-cell–derived therapeutics (1, 2). Sometimes called exosomes, they are small, secreted vesicles that can possess similar therapeutic mechanisms to whole cells, possibly representing the active pharmaceutical ingredient. In the past 15 years, academic and industry interest in EVs has exponentially increased as mounting evidence demonstrates their role in physiology and pathology as well as their therapeutic potential. In light of growing efforts in using EVs for research and therapy,…
Maximizing PMBC Recovery and Viability: A Method to Optimize and Streamline Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Isolation, Cryopreservation, and Thawing
The quality of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from whole blood has a significant impact on their subsequent analysis. Maximizing recovery, viability, and functionality of isolated PBMCs is essential to the reliability and consistency of downstream applications, particularly within cell therapy manufacturing. The standard method for purification of PBMCs is density-gradient centrifugation. It requires precise layering of whole blood over a density medium (e.g., Ficoll polysaccharide reagent from GE Healthcare), with careful pipetting of the floating cell layer after…
The Potential Application of Real‑Time Release Testing for the Biomanufacture of Autologous Cell‑Based Immunotherapies
Cell-based immunotherapies (iTx) are emerging as a truly transformative therapeutic modality that is both complementary and convergent with existing regenerative medicine approaches, including gene therapy, cell therapy, and tissue engineering (Figure 1). Critically, iTx offer step-change improvements in efficacy compared with current standards of care (1) for a range of clinical indications and unmet therapeutic needs — particularly oncology. The clear efficacy of iTx is in contrast with some previous regenerative medicine approaches, including early mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapies…