Viral safety is required for biologics manufactured to treat human diseases. Although significant improvements in ensuring viral safety have been made over the past few decades, “zero risk” of viral contamination is a myth. Viral contamination risk can be carefully managed by screening raw materials, testing process intermediates, and evaluating how effectively manufacturing processes remove and inactivate viruses. Viral clearance studies verify virus removal or inactivation by a manufacturing process. Although regulatory agencies have expectations for the designs of those…
2015
Special Report on Product Stability Testing: Developing Methods for New Biologics and Emerging Markets
Stability testing is a vital part of product development and is conducted throughout a product’s life cycle (Figure 1). Stability is part of a biotherapeutic’s quality target product profile, and results help analysts understand how critical quality attributes (CQAs) of both drug substances and products are influenced under specific conditions of temperature, relative humidity (RH), light, storage, pH, and other factors. Manufacturers conduct stability tests to determine degradation pathways and establish shelf lives and storage conditions of their products, for…
Reagent Clearance Capability of Protein A Chromatography: A Platform Strategy for Elimination of Process Reagent Clearance Testing
During the manufacturing of monoclonal antibody (MAb) products, many process reagents are used for cell culture and MAb purification to facilitate and control process performance. Process reagents are considered to be process-related impurities, so demonstration of their clearance is required for the chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) information submission of an investigational new drug (IND) application (1, 2). These reagents may be classified into two categories: generally recognized as safe (GRAS) reagents and potential safety concern (PSC) reagents (3). GRAS…
Optimization and Scale-Up of HCIC-Based MAb Purification Processes, Part 1
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) serve important medical needs in cancer treatment as well as that of autoimmune and infectious diseases (1). Antibodies are also widely used in clinical diagnostic assays. They can be coated on solid surfaces to bind specific analytes, conjugated to reporter molecules (either as whole antibodies or fragments) for analyte detection, used in sensitivity panels for lot-release testing, and supplied as positive controls in diagnostic kits (2). Our study evaluates the use of hydrophobic charge-induction chromatography (HCIC) for…
Bioreactor Design for Adherent Cell Culture — The Bolt-On Bioreactor Project, Part 3: Containment, Sterility
The Bolt-on Bioreactor (BoB) project is an independent initiative aimed at developing and commercializing a bioreactor for the automated and efficient culture of adherent cells, especially for application in the production of therapeutic cells and other biopharmaceuticals (1). After conducting thorough research on available culture systems for adherent cells, the BoB team believes that a successful alternative to existing devices must answer four major challenges. Addressed in the first article of this series (2), the first challenge has to do…
Information Instead of Data: User-Friendly HMI Concept Increases Process Control Efficiency
Today, most plant operators are much more than classic process operators. In addition to operational process control, their range of tasks includes product quality assurance, optimization of resources, and maintenance of high‑throughput rates. Qualified information is necessary to reliably perform those tasks. The human–machine interface (HMI) of a process control system provides visualization. Siemens regards new HMI concepts such as advanced process graphics (APG) as the key to task‑specific or situation‑specific decision‑making (Photo 1). Graphics Monitor: the Process Window Before…
Can English Unite SE Asian Markets?
By 2016, the global pharmaceutical industry is expected to generate an estimated 30% of its total sales in emerging markets (1). After India and China, southeast countries such as Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam, and Thailand are especially attractive markets. The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) Economic Community (AEC) consists of 10 countries united through regional economic cooperation: Thailand, Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines, Cambodia, and Brunei. The ASEAN Community 2015 (AEC 2015) initiative aims to form a…
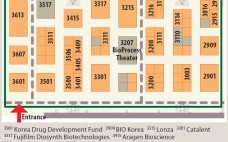
Welcome to the 2015 BioProcess Theater and Zone!
Not too long ago, many bioprocessing professionals perceived the annual BIO International Convention as an event about biotechnology business, financial matters, investing, and partnering — and until not too long ago, for the most part, that was correct. In 2007, the Biotechnology Industry Organization and BioProcess International formed a partnership to create a dedicated destination where bioprocessing professionals could learn about the latest technologies and trends in biopharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Thus was born the BioProcess Theater and Zone. Every…
To Serve and Promote: A Conversation with BIO’s President and CEO
BIO is the world’s largest trade association representing biotechnology companies, academic institutions, state biotechnology centers and related organizations across the United States and in more than 30 other nations. BIO members are involved in the research and development of innovative healthcare, agricultural, industrial, and environmental biotechnology products. BIO plays a leading role in shaping public policy related to the biotechnology industry — at the state, national, and international levels. Jim Greenwood has been BIO’s president and CEO for 10 years,…
BioProcess Theater: Analytical Services
BioProcess International launched about the same time as a major FDA regulatory announcement that has radically altered biopharmaceutical development: The quality by design (QbD) initiative is an important part of the agency’s 21st-century good manufacturing practice (GMP) approach, which is changing how regulators review product applications and thus how companies must approach them (1). It has placed increasing pressure on analytical laboratories, whose work is more important to the success of biotherapeutic products than ever before. Backed by harmonized tripartate…