by John Otrompke, with Cheryl Scott and S. Anne Montgomery When the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the country’s first ever biosimilar on 6 March 2015, it had been a long time coming. After all, the European Union had approved the first biosimilar in 2006, and a number of others have followed in Europe since then. Still, the approval of biosimilar filgrastim, a recombinant colony-stimulating factor used to offset the complications of chemotherapy, was a welcome step…
2015
Assessing Similarity with Parallel-Line and Parallel-Curve Models: Implementing the USP Development/Validation Approach to a Relative Potency Assay
Potency is a critical quality attribute to support development and release of biopharmaceutical products. Researchers assess most protein-drug potencies using biological assays (such as cell-based assays), which mimic a product’s known mechanism of action or binding assays (if the only known mechanism of action is a drug binding to its target or if a drug is in early phases development). Potency denotes an important feature of complex biologics: their biological activity produced as a direct result of the molecule’s tertiary/quaternary…
Optimization and Scale-Up of HCIC-Based MAb Purification Processes, Part 2
In multistep schemes, hydrophobic charge-induction chromatography (HCIC) has been shown to contribute effectively to clearance of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) host-cell proteins (CHOPs), DNA, and viruses. When used for capture chromatography, HCIC can provide better aggregate clearance than protein A sorbents can. Chen et al. enhanced clearance of aggregates, CHOPs, and product- related impurities by controlling HCIC based on both pH and the presence of binding-promoting salt in the wash and elution buffers used (1). Taken together with our findings…
Evaluation of a Variable-Pathlength Spectrophotometer: A Comparable Instrument for Determining Protein Concentration
Protein concentrations in bioprocessing are determined by multiplying the measured absorbance of UV light as it passes through a sample by the protein extinction coefficient. Conventional spectrophotometer measurements are based on a fixed pathlength depending on the cuvette used to hold the sample (typically 10 mm). Only a small portion of the UV curve is linear at that pathlength. As a result, conventional spectrophotometers have a limited linear range and are unable to measure a large range of protein concentrations…
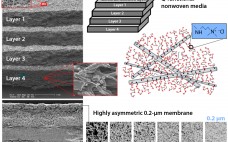
Anion-Exchange Chromatographic Clarification: Bringing Simplification, Robustness, and Savings to MAb Purification
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are the most prominent and successful therapeutic proteins in the pharmaceutical industry. More than 35 MAbs have been approved to treat a range of conditions, and hundreds more are in development (1, 2). Once, the upstream cell culture process was considered the bottleneck to producing high antibody doses required for treatment, but recent advances in cell culture technology have boosted antibody titers to the range of 5–10 g/L (3). That increase in productivity has shifted focus onto…
An Industrial Platform Solution for Antibody Fragment Purification
Compared with traditional approaches such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have become the most successful cancer treatments in the past 20 years (1). With great clinical success in many therapeutic areas, MAbs now account for >40% of the entire biotechnology drug market, and sales are projected to be >US$160 billion over the next few years in the United States alone (2). More than 35 MAbs have been approved for clinical use, and hundreds more are filling industry development…
Paying for Pricey Medications: Debt Financing Options Could Provide a Solution
In an era of US$1,000/dose medications, a new approach may be needed to finance an emerging breed of expensive but highly effective pharmaceuticals and vaccines, according to a new Rand Corporation analysis. In other industries, it is common for suppliers to encourage customer investment — particularly for costly capital purchases such as new automobiles and machinery — through approaches such as equipment leases or supplier-financed credit. The healthcare industry could learn from such approaches. For example, instead of paying up…
ISCT Special Report: Advancing Cell Therapy Manufacturing at the 2015 Annual Meeting
The International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) will host its 21st Annual Meeting at Caesars Palace Hotel and Convention Center, Las Vegas, NV, 27–30 May 2015. More than 1,200 industry and regulatory professionals, clinicians, scientists, and laboratory professionals are expected to attend. The program covers six plenary sessions, six workshops, three technical sessions, and more than 20 total track sessions covering such topics as advances in cell therapy research, commercialization strategies, quality and operations, and regulatory issues. BPI spoke with…
From the Publisher
Today’s competitive financial and market conditions demand that biopharmaceutical companies constantly innovate and create to deliver on promised milestones. In addition to strengthening and improving robust monoclonal antibody (MAb) and other protein pipelines, a number of biopharmaceutical companies are significantly investing, developing, and broadening their research and development efforts and product pipelines with what many are calling the “next generation” of biopharmaceuticals. Those include antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs); biosimilars and biobetters; cell, gene, and tissue therapies; and vaccines and immunotherapies. In…
Spotlight: Niche-Disease — Barth Syndrome
Barth syndrome is a serious X-linked genetic disorder that primarily affects boys. It is caused by a mutation in the tafazzin gene (Taz) that creates an inborn error of lipid metabolism. The condition is named after Dutch pediatric neurologist Peter Barth, who published his discovery of it in 1983. The syndrome often manifests at birth in a number of ways. Patients are born hypotonic, show signs of cardiomyopathy within the first few months of life, and despite adequate nutrition experience…