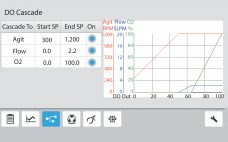
Proper tuning of dissolved oxygen (DO) controller proportional integral (PI) values is essential for optimal cell culture performance in a bioreactor. When DO-PI values are optimized, gas flows are smoothed, and foaming and cell stress are reduced. Traditionally, this tuning has been performed by using nitrogen gas to purge oxygen from a test solution, thus simulating oxygen demand. That method has several drawbacks, however. First, nitrogen gassing cannot simulate the high demands of high-density fermentation. Second, nitrogen competes with other…
Author Archives: Ma Sha
Easy Perfusion for Anchorage-Dependent Cell Culture Using an Eppendorf Vessel with Microcarrier Spin Filter
Anchorage-dependent cells such as Vero cells are used widely as a platform for viral vaccine production. Perfusion bioprocesses enable a constant addition of nutrients and removal of byproducts while cells are in a bioreactor. That results in cell densities that are higher than those for conventional batch or fed-batch processes. In the study herein, Eppendorf researchers tested the suitability of a spin filter as a cell-retention device. They cultivated Vero cells on Cytodex 3 microcarriers (10 g/L) in an Eppendorf…
Eppendorf BioBLU® 10c Single-Use Vessels Simplify Handling of Cell Culture Bioprocesses at Bench Scale
Substituting traditional glass bioreactors with single-use equipment can simplify a bioprocess workflow. Implementing single-use vessels eliminates the need for cleaning and autoclaving, thus reducing the time needed to prepare a bioprocess run and lowering contamination risk. Another advantage is that single-use vessels reduce occupational hazards associated with overweight handling (especially at larger bench scales) because plastic weighs less than glass. Fill out the form below to read the complete white paper now.
Cell Culture Bioprocessing in Perfusion: Assessing Cell Retention Technologies
Upstream bioprocessing in perfusion mode holds great promise for industrial production of cells and biologics. In perfusion, fresh medium is added constantly to the bioreactor, and used medium is harvested while the cells are retained in the bioreactor. As a result, the composition of the cell culture medium stays quite constant during the process. This offers several advantages. In perfusion, higher cell densities can be reached than in batch and fed-batch processes, therefore enhancing volumetric productivity. Because medium composition can…
eBook: Viral Vaccine Production — Cultivation of Vero Cells in Packed-Bed Bioreactors
Vero cells are anchorage-dependent cells that are used widely as a platform for viral vaccine production (1). In stirred-tank bioreactors, they are grown ordinarily on microcarriers. Fibra-Cel disks are an alternative attachment matrix because they provide a three-dimensional environment that protects cells from damaging shear forces. However, such disks have not been tested for the cultivation of Vero cells. We tested whether benchtop single-use and glass bioreactors with a packed bed made of Fibra-Cel disks would be suitable for cultivation…
Push-Button Simplicity: Automatic Fermentation with the BioFlo® 120 Auto-Culture Mode
Learning to use a bioprocess controller is a complex endeavor. Even if someone has previous bioprocess experience, moving to a new software platform can entail much learning and reduce process efficiency. With the auto-culture modes of the Eppendorf BioFlo 120 bioprocess control station, a user can select with a push of a button either a predefined Escherichia coli batch fermentation protocol or a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) batch cell culture process. Proof of Concept: E. coli Auto-Culture Fermentation The auto-culture…
Comparing Culture Methods in Monoclonal Antibody Production: Batch, Fed-Batch, and Perfusion
Recombinant protein manufacturing with Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells represents over 70% of the entire biopharmaceutical industry (1). In fact, human monoclonal antibodies (hMAbs) produced by CHO cells have played a major role in both the diagnostic and therapeutic markets for decades. One of the first human–mouse chimeric MAbs to obtain FDA approval was Roche’s rituximab treatment for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and rheumatoid arthritis. Since that approval in 1997, scores of chimeric, humanized, and human MAbs have gained…