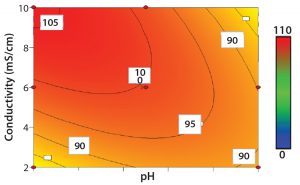
![]() Cellulose is well known as a natural raw material that has mechanical strength, lower nonspecific adsorption, and good biocompatibility. In addition, cellulose particles have unique pore-size characteristics appropriate for chromatography of biopharmaceuticals. Ion-exchange chromatography (IEX) is an important step for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Specifically, cation-exchange chromatography (CEX) can be used as a capture step in monoclonal antibody (MAb) purification. Recently, advanced IEX resins have been developed using polymer modification techniques. Initial screening of conditions such as pH and ionic strength is important for IEX resin. The objective of this study is to reveal the differences of adsorption properties in polymer-modified, cellulose-based CEX resins.
Cellulose is well known as a natural raw material that has mechanical strength, lower nonspecific adsorption, and good biocompatibility. In addition, cellulose particles have unique pore-size characteristics appropriate for chromatography of biopharmaceuticals. Ion-exchange chromatography (IEX) is an important step for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Specifically, cation-exchange chromatography (CEX) can be used as a capture step in monoclonal antibody (MAb) purification. Recently, advanced IEX resins have been developed using polymer modification techniques. Initial screening of conditions such as pH and ionic strength is important for IEX resin. The objective of this study is to reveal the differences of adsorption properties in polymer-modified, cellulose-based CEX resins.
Screening for Optimal Adsorption Conditions with Cellufine CEX Resins