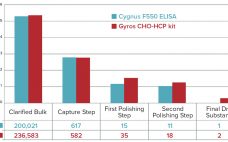
In the past few years, increasing numbers of biotherapeutics have been approved for market (1). Among all the regulatory concerns for commercial biotherapeutics, host-cell proteins (HCPs) are a major class of process-related impurities that remains a critical quality attribute (CQA) for bioprocess development because of associated risks to product quality, safety, and efficacy. HCP identification, clearance, assay setup, and process control are critical points for health authorities, and many guidelines aim for better control of HCP content in final biologic…
Wednesday, December 4, 2019 Daily Archives
Cell Viability in Bioprocesses: Making a Case for Reevaluation
Trypan blue dye exclusion first was proposed as a means of measuring mammalian cell damages over a century ago in 1917 (1). Despite extensive documentation of its limitations (2), it remains the “gold standard” method of measuring cell viability in common use today. But can this method truly measure viability? And how do we define cell viability, for that matter? Those fundamental questions are linked to whether we refer to cells as “alive” or “dead” in the context of bioprocessing…
Making Media a Priority: An Interview with Susan Riley of Advanced Bioprocessing
Susan Riley is vice president and general manager of Advanced Bioprocessing. It’s been a year since Thermo Fisher Scientific’s acquisition of the Advanced Bioprocessing business from Becton Dickinson (BD). Why did Thermo Fisher see the Advanced Bioprocessing (AB) business as a good fit with its life-science offerings? AB has a significant portfolio in premium supplements for cell culture and microbial fermentation. The AB business was seen as a good fit for several reasons: It goes hand-in-glove with Gibco media, for…
Demonstrating Intactness of Biopharmaceutical Products: Intact Molecular-Weight Analysis and Terminal Sequencing of Proteins
Regulations require that biomanufacturers assess the intactness of protein and glycoprotein products as well as confirm the terminal sequences to look for existing variations. ICH Q6B guideline section 6.1.1 c states: Terminal amino acid analysis is performed to identify the nature and homogeneity of the amino- and carboxy-terminal amino acids. If the desired product is found to be heterogeneous with respect to the terminal amino acids, the relative amounts of the variant forms should be determined using an appropriate analytical…
Innovative Strategies for Cell Culture Media Preparation
Although the handling and preparation of cell culture media can seem routine, a number of risks are associated with such operations. Identification and mitigation of associated risks can help ensure consistency of performance, minimize likelihood of contamination, and protect employees while enabling greater efficiencies in upstream processes. Here we describe a number of strategies for reducing risks and streamlining media-related workflows. Simplifying Handling of Cell Culture Powders Media preparation typically is quite labor intensive and poses risks related to containment…
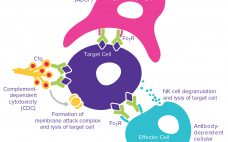
Mitigate Risk with Effector Function Characterization for Antibody Therapeutics
The complexities of biomanufacturing combined with heterogeneity introduced by cellular expression systems present significant challenges to assessing the quality of biologics such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Information related to the critical quality attributes (CQAs) of MAb drug candidates is unknown during early phase drug development. It must be established empirically by physical, structural, and functional analyses as early as possible to accelerate development and mitigate risk through greater understanding of product characteristics. High-resolution analytical techniques are required to answer questions…
Launch of the First Vaccine Bioprocess Training Program: A Standardized but Flexible Course to Boost the Global Vaccine Industry
Based on the many forms that modern vaccines can take, their manufacturing is complicated. Unlike monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), vaccine manufacturers have no “template” platform to follow. Most vaccine producers develop their manufacturing processes from scratch, a prospect that can be challenging for small to mid-sized companies. Bioprocessing is the key challenge in vaccine manufacturing. Without a well-developed and understood process, a manufacturer will face serious challenges in commercial production: e.g., low yields, high costs, and difficulties in meeting quality standards.…
Ask the Expert: Scalable Purification Strategies for Viral Vectors and Vaccines
Viruses and virus-like particles (VLPs) raise unique challenges for downstream recovery and purification. In an Ask the Expert webinar on 19 September 2019, Mark Snyder (R&D applications manager of process chromatography at Bio-Rad Laboratories) discussed purification methods engineered to perform at manufacturing scales. Offering case studies featuring Nuvia resin and CHT Ceramic Hydroxyapatite chromatography support, Snyder emphasized that scalable media can help companies optimize downstream operations and address evolving manufacturing requirements. Snyder’s Presentation Tremendous growth in markets for vaccines and…
Ask the Expert: Risk-Based Approaches to Software Systems Compliance
Software risk management often seems synonymous with extra documentation. But during a 17 October 2019 Ask the Expert webinar, Martin Laferriere (director of information technology services at Avid Bioservices) explained how a thoughtful risk- assessment process at early project management stages can optimize software system validation efforts. Laferriere illustrated the benefits of developing strategic structures for documenting system use, hazards, and testing requirements. Such structures can help biomanufacturers clarify what records and functionalities they need to concentrate on to remain…
Ask the Expert: Rapid Virus Quantification in the Development and Manufacture of Emerging Therapies
The development and manufacture of emerging viral therapies is highly dependent upon accurate infective virus titers as well as total particle counts. But traditional quantification technologies have not kept pace with the needs of the viral vector market. Quantification methods based upon infectious particle counts can easily underestimate total particle counts. Indirect measurements such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) are prone to overestimating the number of virus particles because they measure virus components to…