Recent developments in downstream processing of biomolecules — including continuous processing, bind–elute affinity capture, and flow-through polishing steps — have increased the need for greater selectivity from chromatography adsorbents. This has led to the introduction of a new generation of adsorbents: so-called “mixed-mode” or multimodal ligands. They provide greater selectivity and tolerance to process buffer composition than either ionexchange chromatography (IEC) or hydrophobic-interaction chromatography (HIC) alone can provide. Learn more in this Special Report from Steve Burton, Chief Executive Officer…
Friday, April 20, 2018 Daily Archives
Facilities of the Future: Intelligent Design and Control Enable Quality, Efficiency, and Good Citizenship
Today’s biomanufacturers need to be able to add capacity and capability quickly; provide increased supply service to customers on demand; and streamline the flows of personnel, traffic, utilities, and materials throughout bioprocess facilities. And companies need to be flexible enough to subtract capacity and retool quickly to produce new or different products. Many future facilities will be automated to some extent and use robotics in manufacturing. With personalized medicine on the rise, bioprocessors can benefit from colocation with academic research…
Flexibility, Automation, and Leadership: Drug-Sponsor Perspectives on Modern Biomanufacturing Facility Design
The title of this featured report — Smart(er) Facilities — came about in conversations with our KNect365 colleagues as they worked to plan this year’s BPI West conference, which took place 19–22 March 2018 in San Francisco, CA. For decades, biopharmaceutical facilities have incorporated cutting-edge designs for supporting processes, products, and human development. Each year, design innovations are rewarded for creating workspaces that facilitate both worker comfort and essential movement of promising drug candidates toward commercialization. In that context, biomanufacturing…
Partnerships for Progress: Supplier Perspectives on Facilities of the Future
Biomanufacturers are constantly tasked with making their products ever more efficiently with ever increasing quality. As major advancements come in biomanufacturing technology, companies find themselves in need of “smarter,” more flexible facilities than ever before. Recently, I asked several industry leaders for their thoughts on some criteria for smarter designs, including why there is such a demand: Cristina Amorim (vice president of facilities, EHS, and sustainability in the life sciences group of Thermo Fisher Scientific) Scott Battist (vice president, general…
April From the Editor
A friend of mine was returning home from a vacation in Rome this week, and her flight from Europe to Newark was delayed and diverted because someone’s child had measles on the intended connecting plane. Measles! Someone thought it was okay to spread that around. Often as we put together a themed issue — whether focused on a manufacturing pillar or something new like this month — a subtheme seems to just happen. This month, thanks to authors from Biogen…
April Spotlight
Looking Back, Looking Ahead Check both ways before proceeding — always good advice. Industry analysts at GlobalData and Mergermarket (an Acuris company) have reviewed 2017 and made predictions for the biopharmaceutical industry in 2018. Set against a backdrop of remarkable advances in technology and the growing relevance of biosimilars, last year was marked by both disappointments and noteworthy innovations. GlobalData points to major regulatory approvals in “nearly every major therapeutic area.” These include CAR T-cell oncology treatments, the first biologic…
Cost Analysis of Cell Therapy Manufacture: Autologous Cell Therapies, Part 2
In part 2, we continue to analyze manufacturing costs of an autologous cell therapy. A typical process involves the expansion and activation of cells derived from a single patient, which is currently very labor-intensive. To date, there is little published information on overall production costs (1). In part 1, we used a software modeling platform to identify opportunities for potential cost savings. We developed a baseline model of a cell therapy manufacturing process using the production of autologous dendritic cells…
Data Science, Modeling, and Advanced PAT Tools Enable Continuous Culture
Bioprocesses traditionally use (fed-)batch cell culture processes for production of recombinant proteins and therapeutics. In batch bioprocessing, material flow is discrete, with a hold step between two unit operations, and product is harvested only once for each unit operation. Batch processes have been studied extensively and optimized through numerous advancements in experimental design (1, 2), monitoring (3–5), measurement techniques (6–9), and control strategies (10–12). However, such processes require large facility footprints for equipment (13) as well as sterilization, load, and…
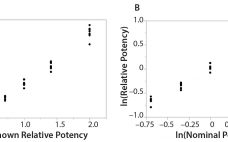
The Relationship Between R2 and Precision in Bioassay Validation
Analytical linearity along with assessments of precision and accuracy determine the range for bioassays (1). Practitioners can include coefficient of determination (R2) criteria from a linearity study in the bioassay validation protocol. Herein I illustrate the relationship of R2 to study design and analytical method variation. Overview of the Simple Linear Regression Model Dilutional linearity assesses the “ability (within a given range) of a bioassay to obtain measured relative potencies that are directly proportional to the true relative potency of the…
Scale-Up of Twin-Column Periodic Countercurrent Chromatography for MAb Purification
Periodic countercurrent (PCC) processes increasingly are being evaluated as alternatives to single-column batch capture processes. Some of the advantages of PCC processes over single-column processes include shortening of processing time and/or reduction of required resin volume through increased productivity; reduction in resin costs through improved resin capacity use; and reduction in buffer consumption through increased column loading. Those advantages, however, come with increased equipment complexity and hardware costs. PCC processes and systems with two to up 16 columns of the…