For September’s Ask the Expert, we talked to Bill Whitford (senior manager of the bioprocess market for Thermo Fisher Scientific) about sourcing animal-free raw materials for cell culture media. This has become a requirement for many biopharmaceutical sponsors, but it is not without its issues. But what precisely is meant by animal is not always clear. Regulatory guidance is sparse on this issue. And a designation of animal-derived–component free (ADCF) often involves additional certification, testing, or auditing. Sponsors and material…
Sunday, September 1, 2013 Daily Archives
Reducing Tech-Transfer Risk
Process understanding is the key to mitigating risks associated with technology transfer. In 2007, Justin Neway provided strategies for combining on-demand data access, trending, reporting, and analytics to achieve that understanding throughout process development (pdf). With increasing adaptation of process analytical technology (PAT) and quality-by-design (QbD), process understanding strategies have shifted.
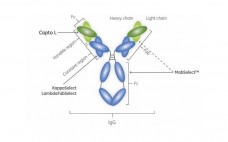
A Platform Approach for the Purification of Domain Antibodies (Dabs)
A three-step purification process for a Dab successfully developed and verified. The step yield ranged between 86% and 99%, giving a total process yield of approximately 81%. The ECP in the start sample was more than 200 000 ppm whereas the final sample contained only 5.5 ppm. The endotoxin content in the feed was approximately 2 million endotoxin units/mg of protein and the final sample was below the limit of quantification. Protein L leakage was undetectable in all samples. This…
MFI for Particle Characterization of Biopharmaceuticals Today
Micro-flow imaging (MFI) is a sensitive, simple and automated method for the analysis of sub-visible particles and translucent protein aggregates that provides particle size, count and morphology. Because it quantifies particle shape, this technology can discriminate groups of particles from each other, and evaluate how these groups change over time. In this article, we provide an overview of how biopharma is using MFI to characterize and monitor their protein formulations in new and emerging applications.
POROS® CaptureSelect™ Affinity Columns for Rapid, Small-Scale Purification and Sample Preparation of Recombinant Proteins
This application note describes a model system in which Enbrel® protein, a fusion protein consisting of TNF receptor and IgG1 Fc, is purified from a dilute sample matrix for further analytical characterization. The resulting purified protein was subjected to N-linked glycan structural analysis by mass spectrometry (MS) and its aggregation state was assessed by analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC). This data set serves as a model to demonstrate the capability of the POROS® CaptureSelect™ product line for the affinity purification of biomolecules…
Enhanced 2-D Electrophoresis and Western Blotting Workflow for Reliable Evaluations of Anti-HCP Antibodies
Biologic drugs are subject to unique regulatory and technical requirements because of their origin and expression in genetically engineered host cells, as well as their underlying physicochemical properties and elaborate purification processes. One such requirement is the accurate monitoring and effective removal of process-derived impurities such as host-cell proteins (HCPs) and DNA/RNA, viruses, cell culture media, chromatographic leachates, and so on (1). Of those impurities, HCPs are perhaps the most challenging to accurately monitor. Each expression system’s proteome consists of…
Moving Forward with a Gene Therapy for Damaged Hearts
A cocktail of three specific genes can reprogram cells in the scars caused by heart attacks into functioning muscle cells. Adding a gene that stimulates the growth of blood vessels enhances that effect, say researchers from Weill Cornell Medical College, Baylor College of Medicine, and Stony Brook University Medical Center in a report that appears online in the Journal of the American Heart Association (1). “The idea of reprogramming scar tissue in the heart into functioning heart muscle was exciting,”…
Automation of Microbioreactors
Current methodologies in genetics and microbiology enable researchers to influence metabolic pathways of microbial cells in many directions. Beside the academic interest in investigating fundamental functions in metabolic pathways, commercial production of valuable compounds by microbial hosts is state of the art. For example, such products include enzymes (lipases, proteases, phytases), therapeutic agents (insulin, antibodies), bulk chemicals (lysine, glutamate, citric acid), or the microbial cells themselves (used in brewing or milk processing), with therapeutic agents probably the fastest growing market.…
Upstream Chemistry Analysis in Cell-Based Process Development
Cell line selection is important to any pharmaceutical company’s development pathway for biological compounds (1). In cell-line selection laboratories, many different, slightly variable cell lines are tested in parallel for desired characteristics. Candidate cell lines are chosen for further development on the basis of their performance in basic tests of critical quality attributes (CQAs). Historically, such cell lines were selected in large-volume containers because it was necessary to have sufficient volume in culture to allow repeated sampling without damaging the…
Poster Presentations
Cell Culture and Upstream Processing Gary Boch (Cevec Pharmaceuticals) Custom Chemically Defined Media for CAP-T Cells Maurizio Cattaneo (BioVolutions) DoE for Continuous BioProcessing of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies Stephanie Dubois (ATMI LifeSciences) Linear Scalability of Virus Production in Integrity®iCELLis®Single-Use, Fixed-Bed Bioreactors from Bench Scale to Industrial Scale Thomas Falkman (GE Healthcare) Assessment of Process Performance and Product Quality in High-Performing Fed-Batch Cultures Kathleen Harrison (Frieslandcampina Domo) Influence of Soy Protein Hydrolysates on Robustness of Cell Culture Experiments Clint Pepper (Bend Research)…