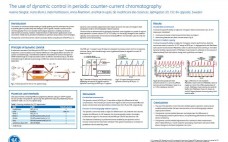
The interest in continuous bioprocessing to introduce productivity gains and cost savings is rapidly growing. Periodic counter-current chromatography (PCC) is one suitable technological approach, enabling continuous downstream processing. However, implementation in downstream applications is still uncommon mainly due to perceived complexity in operation and process control strategies. This work demonstrates the dynamic control function of ÃKTA⢠pcc 75 chromatography system when applied to a protein A capture step operated in a three-column PCC (3C PCC) setup. Dynamic control enables sample…
Downstream Processing
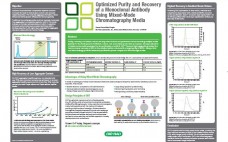
Optimized Purity and Recovery of a Monoclonal Antibody Using Mixed-Mode Chromatography Media
Purity, recovery, and elution volume are important factors and parameters when screening multiple media (resins) for the development of efficient, robust, and economical production processes. Among a selection of mixed-mode media evaluated for the purification of MAb S, CHT⢠Ceramic Hydroxyapatite provided the best monomer recovery at 83% in the smallest elution volume with a target purity of 99.5%. Using a bind and elute strategy provided enhanced purification power compared to flow-through modes.
Application of QbD Concepts to a Final Sterile Filtration Step
The International Committee for Harmonization (ICH) defines quality by design (QbD) as âa systematic approach to development that begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product and process understanding and process control, based on sound science and quality risk management.â When implementing a QbD approach, biomanufacturers need to identify a productâs critical quality attributes (CQAs) from which a reliable manufacturing process capable of delivering the CQAs can then be developed. This is achieved by performing a risk assessment on each attribute…
NatriFlo® HD-Q Membrane Adsorber: A New Single-Use High-Capacity Polishing Tool with Excellent Salt Tolerance and Process Robustness for MAb Purification
Strong anion exchange (Q) chromatography has become an industry standard in MAb production. It is a proven technology to remove DNA, viruses, endotoxins and acidic host cell proteins from process feed streams in flowthrough mode. Recent trends show an increasing interest in downstream single-use technologies and flexible biomanufacturing due to advancement in cell culture technology and emergence of biosimilars. Traditional chromatography columns are slow, often oversized and not suitable for flexible biomanufacturing. Conventional membrane adsorbers cannot provide sufficient process robustness…
Gyrolab⢠CHO-HCP Kit Panel Simplifies HCP Assay Selection in Bioprocess Development
Host cell protein (HCP) levels in drug products are critical to product quality since HCPs may pose a serious risk to patient safety. The challenge is to accurately quantify the complex mixture of HCP impurities, which vary in properties and abundance depending on the cell line, media, and process parameters. Generic immunoassays commonly used to measure HCP impurities are based on polyclonal antibodies raised against HCPs from non-transfected cell lines. How well a particular HCP assay recognizes all proteins depends…
Enhanced Endotoxin Removal By Synergistic Effect of Positively Charged Depth Filtration and Polyethylene Glycol
Recombinant therapeutic proteins derived from E. coli require robust endotoxin removal, ideally performed using multiple process steps providing orthogonal and robust clearance. Typical recovery processes for E. coli expressed proteins consist of cell harvest by centrifugation, homogenization, collection of inclusion bodies by centrifugation, solubilization, refold, and clarification by depth filtration. Endotoxin clearance across the recovery operations is usually on the order of one log. Here, we demonstrate that endotoxin clearance can be enhanced to five logs by using 16% polyethylene…
Cell Debris Removal By Single-Use Diatomaceous Earth (DE) Filtration
Many biotechnological products are obtained by the help of native or recombinant microbial cells in fermentation processes. In order to get intracellular target molecules, like proteins or enzymes, the cells have to be destructed. This is done with cell rupture techniques (e.g. high-pressure homogenization) which generate a suspension containing cell debris and cell contents (proteins, DNA, mRNA, etc.). The first step in the following purification sequence is the removal of the cell debris. One possibility to do this is the…
Design of a New Range of High Capacity and High Flow Agarose Resins
With the continuing development of high titer cell lines, resins with very high capacity at relevant residence times are becoming increasingly important. This paper will present application and characterization data from a set of novel, agarose-based resins, with ion exchange functionality as well as with immobilized alkaline stable Protein A. The cation exchanger has a dynamic binding capacity of more than 120 mg monoclonal antibody/mL resin without the introduction of surface extenders. Performance data from an alkaline stable Protein A…
Purification of Clinical Grade MAb using Hydrophobic Cation Exchange Chromatography Resin
A three-step non-rProtein A capture process shows how the selectivity afforded by Nuvia cPrime resin can be used to clear a light chain contaminant that has a homologous sequence and similar pI to the target MAb monomer. The unique balance between the hydrophobic and charged character of Nuvia cPrime allows for a compact process with reduced buffer consumption and feed conditioning.
PureFlex⢠Plus Single-Use Process Container Film Extractables and Leachables Study
Biopharmaceutical companies are using single-use disposable sterile containers and assemblies for upstream and downstream processes at an ever increasing rate, as these specialized technologies and products enable efficient and scalable processes. The newly developed PureFlex⢠Plus film contains many of the same ultra low density polyethylene, poly(vinyl acetate) and poly(vinyl alcohol co-ethylene) layers that are in current PureFlex⢠film.  The only modification is the outer layer, to provide enhanced mechanical strength, creep resistance and limited permeability to air and gases.…